Abstract
Purpose
The A1AR antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-3-(3-fluoropropyl)-1-propylxanthine ([18F]CPFPX) has recently been shown to be a suitable radiotracer for quantitative in vivo imaging of the A1 adenosine receptor (A1AR) in rats. The present study evaluates the reproducibility of non-invasive longitudinal A1AR studies with [18F]CPFPX and a dedicated small animal positron emission tomography (PET) scanner.
Procedures
Twelve male Sprague Dawley rats underwent four repeated dynamic PET scans with a bolus injection of [18F]CPFPX. A1AR availability was determined by different non-invasive approaches including simplified and multilinear reference tissue (olfactory bulb)-based models and graphical methods. The outcome parameter binding potential (BP) was evaluated in terms of variability and reproducibility.
Results
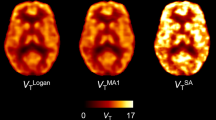
Repeated estimations of [18F]CPFPX BP ND gave reliable results with acceptable variability (mean 12 %) and reproducibility (intraclass correlation coefficients raging from 0.57 to 0.68) in cortical and subcortical regions of the rat brain. With regard to kinetic models, test-retest stability of the simplified reference-tissue model (SRTM) was superior to multilinear and graphical approaches.
Conclusions
Non-invasive quantification of A1AR density in the rat brain is reproducible and reliable with [18F]CPFPX PET and allows longitudinal designs of in vivo imaging studies in rodents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paul S, Elsinga HP, Ishiwata K, Dierckx RAJO, van Waarde A (2011) Adenosine A1 receptors in the central nervous system: their functions in health and disease, and possible elucidation by PET imaging. Curr Med Chem 18:4820–4835
Elmenhorst D, Meyer PT, Matusch A et al (2007) Test-retest stability of cerebral A1 adenosine receptor quantification using [18F]CPFPX and PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34:1061–1070
Meyer PT, Bier D, Hoschbach MH et al (2004) Quantification of cerebral A1 adenosine receptors in humans using [18F]CPFPX and PET. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:323–333
Elmenhorst D, Kroll T, Wedekind F et al (2013) In vivo kinetic and steady-state quantification of 18F-CPFPX binding to rat cerebral A1 adenosine receptors: validation by displacement and autoradiographic experiments. J Nucl Med 54:1–9
Christie MA, McKenna JT, Connolly NP, McCarley RW, Strecker RE (2008) 24 hours of sleep deprivation in the rat increases sleepiness and decreases vigilance: introduction of the rat-psychomotor vigilance task. J Sleep Res 17:376–384
Holschbach MH, Olsson RA, Bier D et al (2002) Synthesis and evaluation of no-carrier-added 8-cyclopentyl-3-(3-[18F]fluoropropyl)-1-propylxanthine ([18F]CPFPX): a potent and selective A1-adenosine receptor antagonist for in vivo imaging. J Med Chem 45:5150–5156
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J et al (2007) Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1533–1539
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP (1996) Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 4:153–158
Ichise M, Loiw JS, Lu JQ et al (2003) Linearized reference tissue parametric imaging methods: application to [11C]DASB positron emission tomography studies of the serotonin transporter in human brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1096–1112
Wu Y, Carson RE (2002) Noise reduction in the simplified reference tissue model for neuroreceptor functional imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1440–1452
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND et al (1996) Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:834–840
Elmenhorst D, Aliaga A, Bauer A, Rosa-Neto P (2012) Test-retest stability of cerebral mGluR5 quantification using [11C]ABP688 and positron emission tomography in rats. Synapse 66:552–560
Weir JP (2005) Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J Strength Cond Res 19:231–240
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39:175–191
Xie X, Ramkumar V, Toth LA (2007) Adenosine and dopamine receptor interactions in striatum and caffeine-induced behavioral activation. Comp Med 57:538–545
Collins LE, Galtieri DJ, Collins P et al (2010) Interactions between adenosine and dopamine receptor antagonists with different selectivity profiles: effects on locomotor activity. Behav Brain Res 211:148–155
Karcz-Kubicha M, Antoniou K, Terasmaa A et al (2003) Involvement of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in the motor effects of caffeine after its acute and chronic administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1281–1291
Costa MS, Ardais AP, Fioreze GT et al (2012) Treadmill running frequency on anxiety and hippocampal adenosine receptors density in adult and middle-aged rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 36:198–204
Casteels C, Vermaelen P, Nuyts J et al (2006) Construction and evaluation of multitracer small-animal PET probabilistic atlases for voxel-based functional mapping of the rat brain. J Nucl Med 47:1858–1866
Alexoff DL, Vaska P, Marsteller D et al (2003) Reproducibility of 11C-raclopride binding in the rat brain measured with the microPET R4: effects of scatter correction and tracer specific activity. J Nucl Med 44:815–822
Aznavour N, Benkelfat C, Gravel P et al (2009) MicroPET imaging of 5-HT1A receptors in rat brain: a test–retest [18F]MPPF study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:53–62
Casteels C, Bormans G, van Laere K (2010) The effect of anaesthesia on [18F]MK-9470 binding to the type 1 cannabinoid receptor in the rat brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:1164–1173
Elfving B, Bjornholm B, Knudsen GM (2003) Interference of anaesthetics with radioligand binding in neuroreceptor studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:912–915
Kilbourn MR, Ma B, Butch ER, Quesada C, Sherman PS (2007) Anesthesia increases in vivo N-([18F]fluoroethyl)piperidinyl benzilate binding to the muscarinic cholinergic receptor. Nucl Med Biol 34:479–482
Crema LM, Pettenuzzo LF, Schlabitz M et al (2013) The effect of unpredictable chronic mild stress on depressive-like behavior and on hippocampal A1 and striatal A2A adenosine receptors. Physiol Behav 109:1–7
Svenningsson P, Fredholm BB (1997) Glucocorticoids regulate the expression of adenosine A1 but not A2A receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:1094–1101
Acknowledgments
Magdalene Vögeling, Dina Alghzawi, Tanja Juraschek, Larissa Damm, and Michaela Bohlen are gratefully acknowledged for excellent technical assistance, and Andreas Matusch for proofreading the manuscript. We thank Nikola Kornadt-Beck for the fruitful discussions and valuable support. Johannes Ermert and Heinz H. Coenen are gratefully acknowledged for the supply of the radioligand.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kroll, T., Elmenhorst, D., Weisshaupt, A. et al. Reproducibility of Non-Invasive A1 Adenosine Receptor Quantification in the Rat Brain Using [18F]CPFPX and Positron Emission Tomography. Mol Imaging Biol 16, 699–709 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0729-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0729-0