Abstract
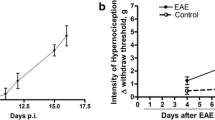
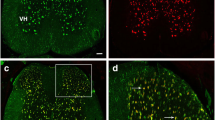
Neuropathic pain (NPP) is a frequently reported symptom described by 50–80% of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Although Th1 cell activation is known to drive the pathology of MS, this critical step has also been suggested to be involved in the neuroimmune induction of NPP. The release of pain inducing inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) from activated Th1 cells may have key implications in the development of MS-induced pain. We hypothesize that immune mediated antigenic induction of inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα within dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and spinal cord (SC) facilitate the cellular events underlying induction of pain. A rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS was utilized to identify the cellular source and expression changes of TNFα protein and mRNA in the DRG and SC. The TNFα levels in the DRG and SC were correlated with the behavioral testing indicative of NPP. We show significant increases in TNFα protein and mRNA expression in DRG and SC of EAE animals at 12 days post induction (EAE12) relative to naïve control (NC) and active control (AC) groups. Further, we show increased TNFα protein and mRNA expression at the dorsal root entry point, which suggests the anterograde transport of both protein and mRNA. Further, the onset of NPP coincides with increased TNFα expression in the SC. These results demonstrate that the elevated expression of TNFα in the DRG and SC may be associated with the pathological induction of NPP in an animal model of MS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicher SA, Silverman MB, Winkler CW, Bebo BF Jr (2004) Hyperalgesia in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Pain 110(3):560–570
Balkowiec-Iskra E, Vermehren-Schmaedick A, Balkowiec A (2011) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in trigeminal ganglion neurons in an activity-dependent manner. Neuroscience 180:322–333
Begum F, Zhu W, Namaka MP, Frost EE (2010) A novel decalcification method for adult rodent bone for histological analysis of peripheral-central nervous system connections. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 187(1):59–66
Blumenthal DT (2009) Assessment of neuropathic pain in cancer patients. Curr Pain Headache Rep 13(4):282–287
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Caminero A, Comabella M, Montalban X (2011) Role of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and TNFRSF1A R92Q mutation in the pathogenesis of TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome and multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 166(3):338–345
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63
Chatel M, Lanteri-Minet M, Lebrun-Frenay C (2001) Pain in multiple sclerosis. Rev Neurol (Paris) 157(8–9 Pt 2):1072–1078
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32
Figiel I, Dzwonek K (2007) TNFalpha and TNF receptor 1 expression in the mixed neuronal-glial cultures of hippocampal dentate gyrus exposed to glutamate or trimethyltin. Brain Res 1131(1):17–28
Frost EE, Nielsen JA, Le TQ, Armstrong RC (2003) PDGF and FGF2 regulate oligodendrocyte progenitor responses to demyelination. J Neurobiol 54(3):457–472
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32(1):77–88
Hattori A, Hayashi K, Kohno M (1996) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) stimulates the production of nerve growth factor in fibroblasts via the 55-kDa type 1 TNF receptor. FEBS Lett 379(2):157–160
Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR (2006) The neurobiology of multiple sclerosis: genes, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. Neuron 52(1):61–76
Hermann GE, Rogers RC, Bresnahan JC, Beattie MS (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces cFOS and strongly potentiates glutamate-mediated cell death in the rat spinal cord. Neurobiol Dis 8(4):590–599
Jancalek R, Dubovy P, Svizenska I, Klusakova I (2010) Bilateral changes of TNF-alpha and IL-10 protein in the lumbar and cervical dorsal root ganglia following a unilateral chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. J Neuroinflammation 7:11
Kiguchi N, Maeda T, Kobayashi Y, Saika F, Kishioka S (2009) Involvement of inflammatory mediators in neuropathic pain caused by vincristine. Int Rev Neurobiol 85:179–190
Lassmann H, Ransohoff RM (2004) The CD4-Th1 model for multiple sclerosis: a critical [correction of crucial] re-appraisal. Trends Immunol 25(3):132–137
Lee HL, Lee KM, Son SJ, Hwang SH, Cho HJ (2004) Temporal expression of cytokines and their receptors mRNAs in a neuropathic pain model. Neuroreport 15(18):2807–2811
Lekan HA, Carlton SM, Coggeshall RE (1996) Sprouting of A beta fibers into lamina II of the rat dorsal horn in peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci Lett 208(3):147–150
Leung L, Cahill CM (2010) TNF-alpha and neuropathic pain–a review. J Neuroinflammation 7:27
Liou JT, Yuan HB, Mao CC, Lai YS, Day YJ (2012) Absence of C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 in mice leads to decreased local macrophage recruitment and behavioral hypersensitivity in a murine neuropathic pain model. Pain 153(6):1283–1291
Lublin FD (2005) Clinical features and diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Clin 23(1):1–15, v
Lynch JL, Gallus NJ, Ericson ME, Beitz AJ (2008) Analysis of nociception, sex and peripheral nerve innervation in the TMEV animal model of multiple sclerosis. Pain 136(3):293–304
Mannie M, Swanborg RH, Stepaniak JA (2009) “Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the rat.” Curr Protoc Immunol Chapter 15: Unit 15 12
Marchand F, Perretti M, McMahon SB (2005) Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(7):521–532
McCoy MK, Tansey MG (2008) TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflammation 5:45
Melanson M, Miao P, Eisenstat D, Gong Y, Gu X, Au K, Zhu W, Begum F, Frost E, Namaka M (2009) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-induced upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the dorsal root ganglia. Mult Scler 15(10):1135–1145
Mendell LM, Albers KM, Davis BM (1999) Neurotrophins, nociceptors, and pain. Microsc Res Tech 45(4–5):252–261
Miao P, Madec K, Gong Y, Shen H, Eisenstat D, Melanson M, Gu X, Leong C, Klowak M, Namaka M (2008) Axotomy-induced up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the dorsal root ganglia. Neurol Res 30(6):623–631
Millan MJ (1999) The induction of pain: an integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 57(1):1–164
Moller KA, Johansson B, Berge OG (1998) Assessing mechanical allodynia in the rat paw with a new electronic algometer. J Neurosci Methods 84(1–2):41–47
Nakamura S, Myers RR (1999) Myelinated afferents sprout into lamina II of L3-5 dorsal horn following chronic constriction nerve injury in rats. Brain Res 818(2):285–290
Namaka M, Gramlich CR, Ruhlen D, Melanson M, Sutton I, Major J (2004) A treatment algorithm for neuropathic pain. Clin Ther 26(7):951–979
Namaka M, Leong C, Grossberndt A, Klowak M, Turcotte D, Esfahani F, Gomori A, Intrater H (2009) A treatment algorithm for neuropathic pain: an update. Consult Pharm 24(12):885–902
Namaka M, Turcotte D, Leong C, Grossberndt A, Klassen D (2008) Multiple sclerosis: etiology and treatment strategies. Consult Pharm 23(11):886–896
Namaka MP, Ethans K, Jensen B, Esfahani F, Frost EE (2011) Multiple sclerosis. Therapeutic Choices/e-Therapeutic. Canadian Pharmacists Association Publishers, Ottawa, pp 309–319
Nurmikko TJ, Gupta S, Maclver K (2010) Multiple sclerosis-related central pain disorders. Curr Pain Headache Rep 14(3):189–195
Obata K, Noguchi K (2006) BDNF in sensory neurons and chronic pain. Neurosci Res 55(1):1–10
Olechowski CJ, Truong JJ, Kerr BJ (2009) Neuropathic pain behaviours in a chronic-relapsing model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Pain 141(1–2):156–164
Osterberg A, Boivie J (2009) “Central pain in multiple sclerosis—Sensory abnormalities.” Eur J Pain
Pezet S, McMahon SB (2006) Neurotrophins: mediators and modulators of pain. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:507–538
Schafers M, Geis C, Brors D, Yaksh TL, Sommer C (2002) Anterograde transport of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the intact and injured rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci 22(2):536–545
Schafers M, Svensson CI, Sommer C, Sorkin LS (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation by activation of p38 MAPK in primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 23(7):2517–2521
Shubayev VI, Myers RR (2002) Anterograde TNF[alpha] transport from rat dorsal root ganglion to spinal cord and injured sciatic nerve. Neurosci Lett 320(1–2):99–101
Sommer C, Schafers M (1998) Painful mononeuropathy in C57BL/Wld mice with delayed wallerian degeneration: differential effects of cytokine production and nerve regeneration on thermal and mechanical hypersensitivity. Brain Res 784(1–2):154–162
Sommer C, Schmidt C, George A (1998) Hyperalgesia in experimental neuropathy is dependent on the TNF receptor 1. Exp Neurol 151(1):138–142
Spengler RN, Sud R, Knight PR, Ignatowski TA (2007) Antinociception mediated by alpha(2)-adrenergic activation involves increasing tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) expression and restoring TNFalpha and alpha(2)-adrenergic inhibition of norepinephrine release. Neuropharmacology 52(2):576–589
Thibault K, Calvino B, Pezet S (2011) “Characterisation of sensory abnormalities observed in an animal model of multiple sclerosis: a behavioural and pharmacological study.” Eur J Pain 15(3):231 e231–216.
Tsai EC, Dalton PD, Shoichet MS, Tator CH (2004) Synthetic hydrogel guidance channels facilitate regeneration of adult rat brainstem motor axons after complete spinal cord transection. J Neurotrauma 21(6):789–804
Vallejo R, Tilley DM, Vogel L, Benyamin R (2010) The role of glia and the immune system in the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain Pract 10(3):167–184
Vora P, Mina R, Namaka M, Frost EE (2010) A novel transcriptional regulator of myelin gene expression: implications for neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuroreport 21(14):917–921
Wagner R, Myers RR (1996) Endoneurial injection of TNF-alpha produces neuropathic pain behaviors. Neuroreport 7(18):2897–2901
Wasan AD, Ossanna MJ, Raskin J, Wernicke JF, Robinson MJ, Hall JA, Edwards SE, Lipsius S, Meyers AL, McCarberg BH (2009) Safety and efficacy of duloxetine in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain in older patients. Curr Drug Saf 4(1):22–29
Woolf CJ, Allchorne A, Safieh-Garabedian B, Poole S (1997) Cytokines, nerve growth factor and inflammatory hyperalgesia: the contribution of tumour necrosis factor alpha. Br J Pharmacol 121(3):417–424
Yuan S, Shi Y, Tang SJ (2012) “Wnt Signaling in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis-associated chronic pain.” J Neuroimmune Pharmacol
Zhu W, Frost EE, Begum F, Vora P, Au K, Gong Y, Macneil B, Pillai P, Namaka M (2012) The role of dorsal root ganglia activation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in multiple sclerosis. J Cell Mol Med 16(8):1856–1865
Zimmermann M (2001) Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429(1–3):23–37
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of our funding agencies for their support. Biogen Idec (MN), Pfizer UK Global (MN), Pfizer Canada (MN,CC), University of Manitoba Research Grant Program (MN), Manitoba Institute for Child Health (MN), WZ was recipient of a Millennium Fund Scholarship, FB was recipient of Manitoba Health Research Council Studentships. We would also like to acknowledge the technical assistance of Kim Madec and Jeremy Paterson, and the staff of the University of Manitoba Central Animal Care Services.
Disclosure statement
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests, and have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Begum, F., Zhu, W., Cortes, C. et al. Elevation of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Dorsal Root Ganglia and Spinal Cord is Associated with Neuroimmune Modulation of Pain in an Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8, 677–690 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-013-9449-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-013-9449-5