Summary
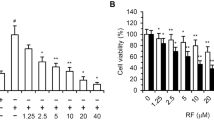
P-450-dependent epoxygenase pathway of arachidonic acid and the products of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) have been demonstrated to be involved in angiogenesis and tumor progression. This study examined the expression of EETs and the role of the pathway in the angiogenesis of multiple myeloma (MM). MM cell lines of U266 and RPMI8226 were cultured, and the EETs levels (11, 12-EET and 14, 15-EET) in the supernatant were determined by ELISA. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured and used for analysis of the angiogenesis activity of the two MM cell lines, which was examined both in vitro and in vivo by employing MTT, chemotaxis, tube formation and matrigel plug assays. 11, 12-EET and 14, 15-EET were found in the supernatant of the cultured MM cells. The levels of the two EETs in the supernatant of U266 cells were significantly higher than those in the RPMI8226 cell supernatant (P<0.05), and the levels paralleled the respective angiogenesis activity of the two different MM cell lines. 17-octadecynoic acid (17-ODYA), as a specific inhibitor of P450 enzyme, suppressed HUVECs proliferation and tube formation induced by MM cells. Furthermore, 17-ODYA decreased the EET levels in the supernatant of MM cells. These results suggest that EETs may play an important role in the angiogenesis of MM, and the inhibitor 17-ODYA suppresses this effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vacca A, Ribatti D, Roncali L, et al. Bone marrow angiogenesis and progression in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol, 1994,87(3):503–508
Rajkumar SV, Leong T, Roche PC, et al. Prognostic value of bone marrow angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res, 2000,6(8):3111–3116
Pruneri G, Ponzoni M, Ferreri AJ, et al. Microvessel density, a surrogate marker of angiogenesis, is signific antly related to survival in multiple myeloma patients. Br J Haematol, 2002,118(3):817–820
Gupta D, Treon SP, Shima Y, et al. Adherence of multiple myeloma cells to bone marrow stromal cells upregulates vascular endothelial growth facter secretion: therapeutic applications. Leukemia, 2001,15(12):1950–1961
Dankbar B, Padró T, Leo R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 in paracrine tumor-stromal cell interactions in multiple myeloma. Blood, 2000,95(8): 2630–2636
Podar K, Anderson KC. The pathophysiologic role of VEGF in hematologic malignancies: therapeutic implications. Blood, 2005,105(4):1383–1395
Xu JL, Lai R, Kinoshita T, et al. Proliferation, apoptosis, and intratumoral vascularity in multiple myeloma: correlation with the clinical stage and cytological grade. J Clin Pathol, 2002,55(7):530–534
Rajkumar SV, Mesa RA, Fonseca R, et al. Bone marrow angiogenesis in 400 patients with monoclonal gammop athy of undetermined significance, multiple myeloma, and primary amyloidosis. Clin Cancer Res, 2002,8(7):2210–2216
Michaelis UR, Fisslthaler B, Barbosa-Sicard E, et al. Cytochrome P450 epoxygenases 2C8 and 2C9 are implicated in hypoxia-induced endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. J Cell Sci, 2005,118(Pt23):5489–5498
Michealis UR, Fleming I. From endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) to angiogenesis: epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and cell signaling. Pharmacol Ther, 2006,111(3):584–595
Potente M, Fisslthaler B, Busse R, et al. 11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-induced inhibition of FOXO factors promotes endothelial proliferation by downregulating p27Kip1. J Biol Chem, 2003,278(32):29619–29625
Yan G, Chen S, You B, et al. Activation of sphingosine kinase-1 mediates induction of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Cardiovasc Res, 2008,78(2):308–314
Michaelis UR, Falck JR, Schmidt R, et al. Cytochrome P4502C9-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2005,25(2):321–326
Chen JK, Capdevila J, Harris RC. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor mediates the biological effects of P450 arachidonate epoxygenase metabolites in epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002,99(9):6029–6034
Michaelis UR, Fisslthaler B, Medhora M, et al. Cytochrome P450 2C9-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids induce angiogenesis via cross-talk with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). FASEB J, 2003,17(6): 770–772
Jiang JG, Ning YG, Chen C, et al. Cytochrome p450 epoxygenase promotes human cancer metastasis. Cancer Res, 2007,67(14):6665–6674
Zagorac D, Jakovcevic D, Gebremedhin D, et al. Antiangiogenic effect of inhibitors of cytochrome P450 on rats with glioblastoma multiforme. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2008,28(8):1431–1439
Kim YM, Kim YM, Lee YM, et al. TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE) induces angiogenesis through the activation of Src and phospholipase C (PLC) in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem, 2002,277(9):6799–6805
Yahata Y, Shirakata Y, Tokumaru S, et al. Nuclear translocation of phosphorylates STAT3 is essential for vascular endothelial growth factor-induced human dermal microvascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation. J Biol Chem, 2003,278(41):40026–40031
Zhang C, Harder DR. Cerebral capillary endothelial cell mitogenesis and morphogenesis induced by astrocytic epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. Stroke, 2002,33(12):2957–2964
Wang Y, Wei X, Xiao X, et al. Arachidonic acid epoxygenase metabolites stimulate endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis via mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosohatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2005,314(2):522–532
Capdevila JH, Falck JR, Harris RC. Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid bioactivation. Molecular and functional properties of the arachidonate monooxygenase. J Lipid Res, 2000,41(2):163–181
Karara A, Dishman E, Jacobson H, et al. Arachidonic acid epoxygenase. Steraochemical analysis of the endogenous epoxyeicosatrienoic acids of human kidney cortex. FEBS Lett, 1990,268(1):227–230
Karara A, Dishman E, Falck JR, et al. Endogenous epoxyeicossatrienoyl-phospholipids. A novel class of cellular glycerolipids containing epoxidized arachidonate moieties. J Biol Chem, 1991, 266(12):7561–7569
Spector AA, Norris AW. Action of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cellular function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2007,292(3):C996–C1012
Spector AA, Fang X, Snyder GD, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): metabolism and biochemical function. Prog Lipid Res, 2004,43(1):55–90
Fleming I, Busse R. Endothelium-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and vascular function. Hypertension, 2006,47(4):629–633
Wong PY, Lai PS, Falck JR. Mechanism and signal transduction of 14(R), 15(S)-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (14, 15-EET) binding in guinea pig monocytes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 2000,62(4):321–333
Wong PY, Lai PS, Shen SY, et al. Post-receptor signal transduction and regulation of 14(R), 15(S)-epoxyeicos atrienoic acid (14, 15-EET) binding in U-937 cells. J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal, 1997,16(3):155–169
Wong PY, Lin KT, Yan YT, et al. 14(R), 15(S)-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (14(R), 15(S)-EET) receptor in guinea pig mononuclear cell membranes. J Lipid Mediat, 1993,6(1–3): 199–208
Cheranov SY, Karpurapu M, Wang D, et al. An essential role for SRC-activated STAT-3 in 14, 15-EET-induced VEGF expression and angiogenesis. Blood, 2008,111(12): 5581–5591
Webler AC, Michaelis UR, Popp R, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids are part of the VEGF-activated signaling cascade leading to angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2008,295(5):C1292–C1301
Zheng M, Sun H, Zhou J, et al. Proliferation and apoptosis of bone marrow CD4(+) T cells in patients with aplastic anemia and impacts of the secreted cytokines on hematopoietic stem cells from umbilical cord blood. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog [Med Sci], 2010,30(1): 37–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81071943) and the Foundation of Natural Sciences of Hubei Province of China (No. 2007ABA072).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, J., Li, Q., Wang, H. et al. P-450-dependent epoxygenase pathway of arachidonic acid is involved in myeloma-induced angiogenesis of endothelial cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 596–601 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0567-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0567-0