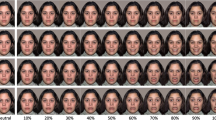
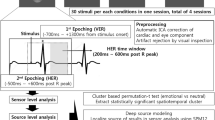
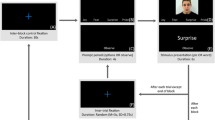
Abstract
Yawning is contagious. However, little research has been done to elucidate the neuronal representation of this phenomenon. Our study objective was to test the hypothesis that the human mirror neuron system (MNS) is activated by visually perceived yawning. We used functional magnetic resonance imaging to assess brain activity during contagious yawning (CY). Signal-dependent changes in blood oxygen levels were compared when subjects viewed videotapes of yawning faces as opposed to faces with a neutral expression. In response to yawning, subjects showed unilateral activation of their Brodmann’s area 9 (BA 9) portion of the right inferior frontal gyrus, a region of the MNS. In this way, two individuals could share physiological and associated emotional states based on perceived motor patterns. This is one component of empathy (motor empathy) that underlies the development of cognitive empathy. The BA 9 is reportedly active in tasks requiring mentalizing abilities. Our results emphasize the connection between the MNS and higher cognitive empathic functions, including mentalizing. We conclude that CY is based on a functional substrate of empathy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
Brodmann’s Area
- BOLD:
-
Blood oxygenation level-dependent
- CY:
-
Contagious yawning
- fMRI:
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
- IFG:
-
Inferior frontal gyrus
- IPL:
-
Inferior parietal lobule
- MNS:
-
Mirror neuron system
- STS:
-
Sulcus temporalis superior
References
Anderson, J. R., & Meno, P. (2003). Psychological influences on yawning in children. Current Psychology Letters, http://cpl.revues.org/document390.html. Accessed 01–12 2012.
Anderson, J. R., Myowa-Yamakoshi, M., & Matsuzawa, T. (2004). Contagious yawning in chimpanzees. Proceedings of the Biological Sciences/The Royal Society, 271(Suppl 6), S468–S470.
Arnott, S. R., Singhal, A., & Goodale, M. A. (2009). An investigation of auditory contagious yawning. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 9(3), 335–342.
Barkley, R. (2001). The executive functions and self-regulation: an evolutionary neuropsychological perspective. Neuropsychology Review, 11(1), 1–29.
Beauregard, M., Levesque, J., & Bourgouin, P. (2001). Neural correlates of conscious self-regulation of emotion. Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 21(18), RC165.
Bien, N., Roebroeck, A., Goebel, R., & Sack, A. T. (2009). The brain’s intention to imitate: the neurobiology of intentional versus automatic imitation. Cerebral Cortex, 19(10), 2338–2351.
Blair, R. J. R. (2005). Responding to the emotions of others: dissociating forms of empathy through the study of typical and psychiatric populations. Consciousness and Cognition, 14(4), 698–718.
Brass, M., Ruby, P., & Spengler, S. (2009). Inhibition of imitative behaviour and social cognition. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 364(1528), 2359–2367.
Carr, L., Iacoboni, M., Dubeau, M. C., Mazziotta, J. C., & Lenzi, G. L. (2003). Neural mechanisms of empathy in humans: a relay from neural systems for imitation to limbic areas. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(9), 5497–5502.
Cooper, N. R., Puzzo, I., & Pawley, A. D. (2008). Contagious yawning: the mirror neuron system may be a candidate physiological mechanism. Medical Hypotheses, 71(6), 975–976.
Decety, J., & Lamm, C. (2006). Human empathy through the lens of social neuroscience. The Scientific World Journal, 6, 1146–1163.
Gallese, V. (2003). The roots of empathy: the shared manifold hypothesis and the neural basis of intersubjectivity. Psychopathology, 36(4), 171–180.
Gallese, V. (2007). Before and below ‘theory of mind’: embodied simulation and the neural correlates of social cognition. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 362(1480), 659–669.
Hagenmuller, F., Rössler, W., Endrass, J., Rossegger, A., & Haker, H. (2012). Impaired resonance in offenders with psychopathic traits (Empathische Resonanzfähigkeit bei Straftätern mit psychopathischen Persönlichkeitszügen). Neuropsychiatrie, 26(2). doi:10.1007/s40211-012-0015-9.
Haker, H., & Rössler, W. (2009). Empathy in schizophrenia: impaired resonance. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 259(6), 352–361.
Haker, H., Schimansky, J., & Rössler, W. (2010). Sociophysiology: basic processes of empathy (Soziophysiologie: Grundlegende Prozesse der Empathiefahigkeit). Neuropsychiatrie, 24(3), 151–160.
Iacoboni, M. (2005). Neural mechanisms of imitation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15(6), 632–637.
Joly-Mascheroni, R. M., Senju, A., & Shepherd, A. J. (2008). Dogs catch human yawns. Biology Letters, 4(5), 446–448.
Keysers, C., & Gazzola, V. (2007). Integrating simulation and theory of mind: from self to social cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(5), 194–196.
Lehmann, H. E. (1979). Yawning: a homeostatic reflex and its psychological significance. Bulletin of the Menninger Clinic, 43, 123–136.
Leslie, K. R., Johnson-Frey, S. H., & Grafton, S. T. (2004). Functional imaging of face and hand imitation: towards a motor theory of empathy. NeuroImage, 21(2), 601–607.
Lieberman, M. D. (2006). Social cognitive neuroscience: a review of core processes. Annual Review of Psychology, 58(1), 1.
Meltzoff, A. N., & Decety, J. (2003). What imitation tells us about social cognition: a rapprochement between developmental psychology and cognitive neuroscience. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 358(1431), 491–500.
Nahab, F. B., Hattori, N., Saad, Z. S., & Hallett, M. (2009). Contagious yawning and the frontal lobe: an fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 30(5), 1744–1751.
Nietlisbach, G., Maercker, A., Rössler, W., & Haker, H. (2010). Are empathic abilities impaired in posttraumatic stress disorder? Psychological Reports, 106(3), 832–844.
Ohnishi, T., Moriguchi, Y., Matsuda, H., Mori, T., Hirakata, M., Imabayashi, E., et al. (2004). The neural network for the mirror system and mentalizing in normally developed children: an fMRI study. Neuroreport, 15(9), 1483–1487.
Palagi, E., Leone, A., Mancini, G., & Ferrari, P. F. (2009). Contagious yawning in gelada baboons as a possible expression of empathy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(46), 19262–19267.
Paukner, A., & Anderson, J. R. (2006). Video-induced yawning in stumptail macaques (Macaca arctoides). Biology Letters, 2(1), 36–38.
Piaget, J. (1951). Play, Dreams and Imitation in Childhood. New York: Norton.
Platek, S. M., Critton, S. R., Myers, T. E., & Gallup, G. G. (2003). Contagious yawning: the role of self-awareness and mental state attribution. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 17(2), 223–227.
Platek, S. M., Mohamed, F. B., & Gallup, G. G., Jr. (2005). Contagious yawning and the brain. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 23(2–3), 448–452.
Preston, S. D., & de Waal, F. B. (2002). Empathy: its ultimate and proximate bases. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 25(1), 1–20.
Provine, R. R. (1986). Yawning as a stereotyped action pattern and releasing stimulus. Ethology, 72, 109–122.
Provine, R. R. (1989). Faces as releasers of contagious yawning: an approach to face detection using normal human subjects. Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 27(3), 211–214.
Provine, R. R. (2005). Yawning. American Scientist, 93(6), 532–539.
Puce, A., Allison, T., Bentin, S., Gore, J. C., & McCarthy, G. (1998). Temporal cortex activation in humans viewing eye and mouth movements. Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 18(6), 2188–2199.
Rizzolatti, G., & Craighero, L. (2004). The mirror neuron system. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 27(1), 169–192.
Rizzolatti, G., & Sinigaglia, C. (2010). The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11(4), 264–274.
Rizzolatti, G., Fadiga, L., Gallese, V., & Fogassi, L. (1996). Premotor cortex and the recognition of motor actions. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 3(2), 131–141.
Rizzolatti, G., Fogassi, L., & Gallese, V. (2001). Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying the understanding and imitation of action. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(9), 661–670.
Rowe, J. B., & Siebner, H. R. (2012). The motor system and its disorders. NeuroImage, 61(2), 464–477.
Schürmann, M., Hesse, M. D., Stephan, K. E., Saarela, M., Zilles, K., Hari, R., et al. (2005). Yearning to yawn: the neural basis of contagious yawning. NeuroImage, 24(4), 1260–1264.
Senju, A. (2010). Developmental and comparative perspectives of contagious yawning. Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience, 28, 113–119.
Senju, A., Maeda, M., Kikuchi, Y., Hasegawa, T., Tojo, Y., & Osanai, H. (2007). Absence of contagious yawning in children with autism spectrum disorder. Biology Letters, 3(6), 706–708.
Senju, A., Kikuchi, Y., Akechi, H., Hasegawa, T., Tojo, Y., & Osanai, H. (2009). Brief report: does eye contact induce contagious yawning in children with autism spectrum disorder? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(11), 1598–1602.
Sepulveda, W., & Mangiamarchi, M. (1995). Fetal yawning. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology, 5(1), 57–59.
Siegal, M., & Varley, R. (2002). Neural systems involved in “theory of mind”. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(6), 463–471.
Talairach, P., & Tournoux, J. A. (1988). Stereotactic Coplanar Atlas of Human Brain. Stuttgart: Thieme.
Uddin, L. Q., Iacoboni, M., Lange, C., & Keenan, J. P. (2007). The self and social cognition: the role of cortical midline structures and mirror neurons. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(4), 153–157.
Vischer, A. L. (1959). About yawning and it’s spontaneous associated movements. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift, 89, 1356–1359.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mengia Dosch, Thomas Loenneker, and Ernst Martin for their support in data acquisition and analysis.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haker, H., Kawohl, W., Herwig, U. et al. Mirror neuron activity during contagious yawning—an fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 7, 28–34 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9189-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9189-9