Abstract
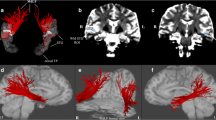
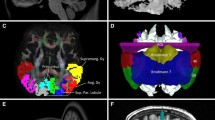
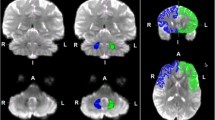
The middle longitudinal fascicle (MdLF) is a major fiber connection running principally between the superior temporal gyrus and the parietal lobe, neocortical regions of great biological and clinical interest. Although one of the most prominent cerebral association fiber tracts, it has only recently been discovered in humans. In this high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI) MRI study, we delineated the two major fiber connections of the human MdLF, by examining morphology, topography, cortical connections, biophysical measures, volume and length in seventy-four brains. These two fiber connections course together through the dorsal temporal pole and the superior temporal gyrus maintaining a characteristic topographic relationship in the mediolateral and ventrodorsal dimensions. As these pathways course towards the parietal lobe, they split to form separate fiber pathways, one following a ventrolateral trajectory and connecting with the angular gyrus and the other following a dorsomedial route and connecting with the superior parietal lobule. Based on the functions of their cortical affiliations, we suggest that the superior temporal-angular connection of the MdLF, i.e., STG(MdLF)AG plays a role in language and attention, whereas the superior temporal-superior parietal connection of the MdLF, i.e., STG(MdLF)SPL is involved in visuospatial and integrative audiovisual functions. Furthermore, the MdLF may have clinical implications in neurodegenerative disorders such as primary progressive aphasia, frontotemporal dementia, posterior cortical atrophy, corticobulbar degeneration and Alzheimer’s disease as well as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and schizophrenia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aja-Fernandez, S., Niethammer, M., Kubicki, M., Shenton, M. E., & Westin, C. F. (2008). Restoration of DWI data using a rician LMMSE estimator. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 27(10), 1389–1403. PubMed PMID: 18815091.
Alexander, A. L., Tsuruda, J. S., & Parker, D. L. (1997). Elimination of eddy current artifacts in diffusion-weighted echo-planar images: the use of bipolar gradients. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 38(6), 1016–1021. PubMed PMID: 9402204.
Asami, T., Saito, Y., Whitford, T. J., Makris, N., Niznikiewicz, M., McCarley, R. W., et al. (2013). Abnormalities of middle longitudinal fascicle and disorganization in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 143(2–3), 253–259. PubMed PMID: 23290607.
Avants, B. B., Epstein, C. L., Grossman, M., & Gee, J. C. (2008). Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical Image Analysis, 12(1), 26–41. PubMed PMID: 17659998.
Basser, P. J. (2004). Scaling laws for myelinated axons derived from an electrotonic core-conductor model. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience, 3(2), 227–244. PubMed PMID: 15285056.
Baumgartner, C., Micahilovich, O., Pasternak, O., Levitt, J., Weston, C.-F., Shenton, M. E., et al. (2012). A unified tractography framework for comparing diffusion models on clinical scans. Paper presented at the CDMRI-workshop (MICCAI'12), Londron, UK.
Boxer, A. L., Geschwind, M. D., Belfor, N., Gorno-Tempini, M. L., Schauer, G. F., Miller, B. L., et al. (2006). Patterns of brain atrophy that differentiate corticobasal degeneration syndrome from progressive supranuclear palsy. Archives of Neurology, 63(1), 81–86. PubMed PMID: 16401739.
Bruce, C., Desimone, R., & Gross, C. G. (1981). Visual properties of neurons in a polysensory area in superior temporal sulcus of the macaque. Journal of Neurophysiology, 46(2), 369–384. PubMed PMID: 6267219.
Cabeza, R., & Nyberg, L. (2000). Neural bases of learning and memory: functional neuroimaging evidence. Current Opinion in Neurology, 13(4), 415–421. PubMed PMID: 10970058.
Catani, M., Bodi, I., & Dell'Acqua, F. (2012). Comment on “the geometric structure of the brain fiber pathways”. Science, 337(6102), 1605. author reply 1605, PubMed PMID: 23019632.
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (2002). Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(3), 201–215. PubMed PMID: 11994752.
Critchley, M. (1966). Is developmental dyslexia the expression of minor cerebral damage? Clinical Proceedings - Children’s Hospital of the District of Columbia, 22(8), 213–222. PubMed PMID: 5231793.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage, 9(2), 179–194. PubMed PMID: 9931268.
De Witt Hamer, P. C., Moritz-Gasser, S., Gatignol, P., & Duffau, H. (2011). Is the human left middle longitudinal fascicle essential for language? a brain electrostimulation study. Human Brain Mapping, 32(6), 962–973. PubMed PMID: 20578169.
Dejerine, J. (1895). Anatomie des Centres Nerveux. Tome 1 (1980, Masson ed.). Paris, France: Rueff et Cie.
Desikan, R. S., Segonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., et al. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980. PubMed PMID: 16530430.
Dickerson, B. C., Bakkour, A., Salat, D. H., Feczko, E., Pacheco, J., Greve, D. N., et al. (2009). The cortical signature of Alzheimer's disease: regionally specific cortical thinning relates to symptom severity in very mild to mild AD dementia and is detectable in asymptomatic amyloid-positive individuals. Cerebral Cortex, 19(3), 497–510. PubMed PMID: 18632739.
Duffy, F. H., & Burchfiel, J. L. (1971). Somatosensory system: organizational hierarchy from single units in monkey area 5. Science, 172(3980), 273–275. PubMed PMID: 4994137.
Duncan, J., & Owen, A. M. (2000). Common regions of the human frontal lobe recruited by diverse cognitive demands. Trends in Neurosciences, 23(10), 475–483. PubMed PMID: 11006464.
Evans, A. C., Collins, D. L., Mills, S. R., Brown, E. D., Kelly, R. L., & Peters, T. M. (1993). 3D statistical neuroanatomical model from 305 MRI volumes. Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, 1993 IEEE Conference Record, 3, 1813–1817.
First, M., Spitzer, R., Gibbon, M., & Williams, J. (1997). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Press.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11050–11055. PubMed PMID: 10984517.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. M. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. II: inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage, 9(2), 195–207. PubMed PMID: 9931269.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355. PubMed PMID: 11832223.
Fischl, B., van der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Segonne, F., Salat, D. H., et al. (2004). Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 14(1), 11–22. PubMed PMID: 14654453.
Galaburda, A. M., Corsiglia, J., Rosen, G. D., & Sherman, G. F. (1987). Planum temporale asymmetry, reappraisal since geschwind and levitsky. Neuropsychologia, 25(6), 853–868.
Galton, C. J., Patterson, K., Graham, K., Lambon-Ralph, M. A., Williams, G., Antoun, N., et al. (2001). Differing patterns of temporal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and semantic dementia. Neurology, 57(2), 216–225. PubMed PMID: 11468305.
Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1988). Topography of cognition: parallel distributed networks in primate association cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 11, 137–156. PubMed PMID: 3284439.
Gorno-Tempini, M. L., Brambati, S. M., Ginex, V., Ogar, J., Dronkers, N. F., Marcone, A., et al. (2008). The logopenic/phonological variant of primary progressive aphasia. Neurology, 71(16), 1227–1234. PubMed PMID: 18633132.
Heid, O. Eddy current-nulled diffusion weighted. In Proc Int Soc Mag Reson Med. Denver, Denver, CO, 2000 (p. 799)
Heilman, K. M., & Valenstein, E. (1985). Clinical neuropsychology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Heilman, K. M., & Van Den Abell, T. (1980). Right hemisphere dominance for attention: the mechanism underlying hemispheric asymmetries of inattention (neglect). Neurology, 30(3), 327–330. PubMed PMID: 7189037.
Heilman, K. M., Pandya, D. N., & Geschwind, N. (1970). Trimodal inattention following parietal lobe ablations. Transactions of the American Neurological Association, 95, 259–261. PubMed PMID: 4998763.
Heilman, K. M., Watson, R. T., Bower, D., & Valenstein, E. (1983). Right hemisphere dominance for attention. Revue Neurologique (Paris), 139(1), 15–17. PubMed PMID: 6407086.
Hickok, G. (2001). Functional anatomy of speech perception and speech production: psycholinguistic implications. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 30(3), 225–235. PubMed PMID: 11523272.
Hickok, G., & Poeppel, D. (2000). Towards a functional neuroanatomy of speech perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(4), 131–138. PubMed PMID: 10740277.
Hickok, G., & Poeppel, D. (2007). The cortical organization of speech processing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(5), 393–402. PubMed PMID: 17431404.
Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. (2001). A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Medical Image Analysis, 5(2), 143–156. PubMed PMID: 11516708.
Karnath, H. O., Ferber, S., & Himmelbach, M. (2001). Spatial awareness is a function of the temporal not the posterior parietal lobe. Nature, 411(6840), 950–953. PubMed PMID: 11418859.
Lacquaniti, F., Guigon, E., Bianchi, L., Ferraina, S., & Caminiti, R. (1995). Representing spatial information for limb movement: role of area 5 in the monkey. Cerebral Cortex, 5(5), 391–409. PubMed PMID: 8547787.
Lehmann, M., Crutch, S. J., Ridgway, G. R., Ridha, B. H., Barnes, J., Warrington, E. K., et al. (2009). Cortical thickness and voxel-based morphometry in posterior cortical atrophy and typical Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging, PubMed PMID: 19781814.
Ludwig, E., & Klingler, J. (1956). Atlas cerebri humani. The inner structure of the brain demonstrated on the basis of macroscopical preparations. Boston: Little, Brown.
Makris, N. (1999). Delineation of human assocation fiber pathways using histologic and magnetic resonance methodologies. Dissertation, Dept. of Behavioral Neuroscience, Boston University, Boston, MA (http://www.cma.mgh.harvard.edu/staff/nm/Makris-PhD-THESIS.pdf).
Makris, N., & Pandya, D. N. (2009). The extreme capsule in humans and rethinking of the language circuitry. Brain Structure & Function, 213(3), 343–358. PubMed PMID: 19104833.
Makris, N., Meyer, J. W., Bates, J. F., Yeterian, E. H., Kennedy, D. N., & Caviness, V. S. (1999). MRI-based topographic parcellation of human cerebral white matter and nuclei II. Rationale and applications with systematics of cerebral connectivity. NeuroImage, 9(1), 18–45. PubMed PMID: 9918726.
Makris, N., Pandya, D. N., & Normandin, J. J. (2002). Quantitative DT-MRI investigations of the human cingulum bundle. Central Nervous System Spectrums, 7(7), 522–528.
Makris, N., Kennedy, D. N., McInerney, S., Sorensen, A. G., Wang, R., Caviness, V. S., Jr., et al. (2005). Segmentation of subcomponents within the superior longitudinal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 15(6), 854–869. PubMed PMID: 15590909.
Makris, N., Biederman, J., Valera, E. M., Bush, G., Kaiser, J., Kennedy, D. N., et al. (2007a). Cortical thinning of the attention and executive function networks in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Cerebral Cortex, 17(6), 1364–1375. PubMed PMID: 16920883.
Makris, N., Papadimitriou, G. M., Sorg, S., Kennedy, D. N., Caviness, V. S., & Pandya, D. N. (2007b). The occipitofrontal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. NeuroImage, 37(4), 1100–1111. PubMed PMID: 17681797.
Makris, N., Papadimitriou, G. M., Kaiser, J. R., Sorg, S., Kennedy, D. N., & Pandya, D. N. (2009). Delineation of the middle longitudinal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 19(4), 777–785. PubMed PMID: 18669591.
Makris, N., Seidman, L. J., Ahern, T., Kennedy, D. N., Caviness, V. S., Tsuang, M. T., et al. (2010). White matter volume abnormalities and associations with symptomatology in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 183(1), 21–29. PubMed PMID: 20538438.
Makris, N., Preti, M. G., Asami, T., Pelavin, P., Campbell, B., Papadimitriou, G. M., et al. (2012). Human middle longitudinal fascicle: variations in patterns of anatomical connections. Brain Struct Funct, PubMed PMID: 22782432.
Malcolm, J. G., Shenton, M. E., & Rathi, Y. (2010). Filtered multitensor tractography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(9), 1664–1675. PubMed PMID: 20805043.
Menjot de Champfleur, N., Lima Maldonado, I., Moritz-Gasser, S., Machi, P., Le Bars, E., Bonafe, A., et al. (2013). Middle longitudinal fasciculus delineation within language pathways: a diffusion tensor imaging study in human. European Journal of Radiology, 82(1), 151–157. PubMed PMID: 23084876.
Mesulam, M. M. (1990). Large-scale neurocognitive networks and distributed processing for attention, language, and memory. Annals of Neurology, 28(5), 597–613. PubMed PMID: 2260847.
Mesulam, M. M. (1998). From sensation to cognition. Brain, 121(Pt 6), 1013–1052. PubMed PMID: 9648540.
Molholm, S., Sehatpour, P., Mehta, A. D., Shpaner, M., Gomez-Ramirez, M., Ortigue, S., et al. (2006). Audio-visual multisensory integration in superior parietal lobule revealed by human intracranial recordings. Journal of Neurophysiology, 96(2), 721–729. PubMed PMID: 16687619.
Mountcastle, V. B., Lynch, J. C., Georgopoulos, A., Sakata, H., & Acuna, C. (1975). Posterior parietal association cortex of the monkey: command functions for operations within extrapersonal space. Journal of Neurophysiology, 38(4), 871–908. PubMed PMID: 808592.
Poremba, A., Saunders, R. C., Crane, A. M., Cook, M., Sokoloff, L., & Mishkin, M. (2003). Functional mapping of the primate auditory system. Science, 299(5606), 568–572. PubMed PMID: 12543977.
Posner, M. I., & Petersen, S. E. (1990). The attention system of the human brain. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 13, 25–42. PubMed PMID: 2183676.
Rajarethinam, R., Sahni, S., Rosenberg, D. R., & Keshavan, M. S. (2004). Reduced superior temporal gyrus volume in young offspring of patients with schizophrenia. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 161(6), 1121–1124. PubMed PMID: 15169705.
Rathi, Y., Malcolm, J. G., Bouix, S., Westin, C.-F., & Shenton, M. E. False Positive Detection using Filtered Tractography. In International Society For Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Scientific Meeting (ISMRM), 2010.
Rilling, J. K., Glasser, M. F., Preuss, T. M., Ma, X., Zhao, T., Hu, X., et al. (2008). The evolution of the arcuate fasciculus revealed with comparative DTI. Nature Neuroscience, 11(4), 426–428. PubMed PMID: 18344993.
Rohrer, J. D., Warren, J. D., Omar, R., Mead, S., Beck, J., Revesz, T., et al. (2008). Parietal lobe deficits in frontotemporal lobar degeneration caused by a mutation in the progranulin gene. Archives of Neurology, 65(4), 506–513. PubMed PMID: 18413474.
Sakata, H., Takaoka, Y., Kawarasaki, A., & Shibutani, H. (1973). Somatosensory properties of neurons in the superior parietal cortex (area 5) of the rhesus monkey. Brain Research, 64, 85–102. PubMed PMID: 4360893.
Sapolsky, D., Bakkour, A., Negreira, A., Nalipinski, P., Weintraub, S., Mesulam, M. M., et al. (2010). Cortical neuroanatomic correlates of symptom severity in primary progressive aphasia. Neurology, 75(4), 358–366. PubMed PMID: 20660866.
Saur, D., Kreher, B. W., Schnell, S., Kummerer, D., Kellmeyer, P., Vry, M. S., et al. (2008). Ventral and dorsal pathways for language. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(46), 18035–18040. PubMed PMID: 19004769.
Schmahmann, J. D., & Pandya, D. N. (2006). Fiber pathways of the brain. New York: Oxford University Press.
Schmahmann, J. D., Pandya, D. N., Wang, R., Dai, G., D'Arceuil, H. E., de Crespigny, A. J., et al. (2007). Association fibre pathways of the brain: parallel observations from diffusion spectrum imaging and autoradiography. Brain, 130(Pt 3), 630–653. PubMed PMID: 17293361.
Seeley, W. W., Crawford, R. K., Zhou, J., Miller, B. L., & Greicius, M. D. (2009). Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks. Neuron, 62(1), 42–52. PubMed PMID: 19376066.
Seltzer, B., & Pandya, D. N. (1978). Afferent cortical connections and architectonics of the superior temporal sulcus and surrounding cortex in the rhesus monkey. Brain Research, 149(1), 1–24. PubMed PMID: 418850.
Seltzer, B., & Pandya, D. N. (1984). Further observations on parieto-temporal connections in the rhesus monkey. Experimental Brain Research, 55(2), 301–312. PubMed PMID: 6745368.
Seltzer, B., & Pandya, D. N. (1991). Post-rolandic cortical projections of the superior temporal sulcus in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 312(4), 625–640. PubMed PMID: 1761745.
Song, S. K., Sun, S. W., Ramsbottom, M. J., Chang, C., Russell, J., & Cross, A. H. (2002). Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. NeuroImage, 17(3), 1429–1436. PubMed PMID: 12414282.
Song, S. K., Sun, S. W., Ju, W. K., Lin, S. J., Cross, A. H., & Neufeld, A. H. (2003). Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage, 20(3), 1714–1722. PubMed PMID: 14642481.
Suchan, J., Umarova, R., Schnell, S., Himmelbach, M., Weiller, C., Karnath, H. O., et al. (2013). Fiber pathways connecting cortical areas relevant for spatial orienting and exploration. Hum Brain Mapp, PubMed PMID: 23283834.
Talairach, J., & Tournoux, P. (1988). Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.
Thiebaut de Schotten, M., Dell'Acqua, F., Forkel, S. J., Simmons, A., Vergani, F., Murphy, D. G., et al. (2011). A lateralized brain network for visuospatial attention. Nature Neuroscience, 14(10), 1245–1246. PubMed PMID: 21926985.
Tuch, D. S., Reese, T. G., Wiegell, M. R., Makris, N., Belliveau, J. W., & Wedeen, V. J. (2002). High angular resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 48(4), 577–582. PubMed PMID: 12353272.
Turken, A. U., & Dronkers, N. F. (2011). The neural architecture of the language comprehension network: converging evidence from lesion and connectivity analyses. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 5, 1. PubMed PMID: 21347218.
Wang, Y., Fernandez-Miranda, J. C., Verstynen, T., Pathak, S., Schneider, W., & Yeh, F. C. (2012). Rethinking the Role of the Middle Longitudinal Fascicle in Language and Auditory Pathways. Cereb Cortex, PubMed PMID: 22875865.
Wedeen, V. J., Wang, R. P., Schmahmann, J. D., Benner, T., Tseng, W. Y., Dai, G., et al. (2008). Diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging (DSI) tractography of crossing fibers. NeuroImage, 41(4), 1267–1277. PubMed PMID: 18495497.
Yeh, F. C., & Tseng, W. Y. (2011). NTU-90: a high angular resolution brain atlas constructed by q-space diffeomorphic reconstruction. NeuroImage, 58(1), 91–99. PubMed PMID: 21704171.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported, in part, by grants from: NIDA 1R01DA027804-01 (NM), NINDS R21NS077059 (NM and BCD); the National Institute of Health (K05 MH070047 and R01 MH 50740 (MES), P50MH 080272-CIDAR award (MES and MK), R01 M074794 (MK), the Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Award (MES), the VA Schizophrenia Center Grant (MES); the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NA-MIC), the latter a grant supported through the National Institutes of Health Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149 (MK, MES); Progetto Roberto Rocca Foundation (MGP). The authors would like to thank Dr. Lichen Liang for his contribution to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. G. Preti and D. Wassermann contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 151 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makris, N., Preti, M.G., Wassermann, D. et al. Human middle longitudinal fascicle: segregation and behavioral-clinical implications of two distinct fiber connections linking temporal pole and superior temporal gyrus with the angular gyrus or superior parietal lobule using multi-tensor tractography. Brain Imaging and Behavior 7, 335–352 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-013-9235-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-013-9235-2