Abstract
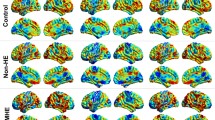
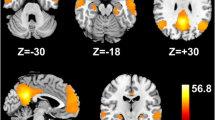
Resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is an important tool for understanding the functional reorganization of the brain in cirrhotic patients. Previous studies revealed that functional integration failure were observed in the whole brain. However, the whole-brain functional connectivity analysis methods used in these studies have the limitation that the result relied on a priori definition of network nodes. Moreover, the utility of resting state functional connectivity in the diagnosis and prediction of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is not well examined. In this study, we recruited 87 subjects consisting of patients without HE, with HE, and healthy controls. We employed a voxel-based, unbiased functional connectivity analysis and the functional connectivity density (FCD) metric to precisely study abnormalities in the intrinsic functional connectivity patterns of cirrhotic patients. FCD analyses showed that hub regions in the brain were less topologically important in cirrhotic patients, whereas non-hub regions became topologically important in the disease state. This trend was more apparent with the progression of cirrhosis severity. Most FCD abnormalities were associated with deficits in psychomotor function, executive control, or visual-spatial abilities (p < 0.05, AlphaSim corrected). FCD alterations in the left inferior parietal lobe and the right hippocampal gyrus/parahippocampal gyrus were significantly correlated with cognitive ability and blood ammonia level (p < 0.05, AlphaSim corrected). A pattern classification analysis indicated that whole-brain FCD differences distinguished cirrhotic patients from healthy controls and predicted disease severity with high accuracies. These findings suggest that voxel-based FCD analysis may be clinically important for the diagnosis and prediction of HE.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., Delon-Martin, C., Vertes, P. E., Renard, F., Schenck, M., Schneider, F., Heinrich, C., Kremer, S., & Bullmore, E. T. (2012). Hubs of brain functional networks are radically reorganized in comatose patients. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(50), 20608–20613.
Alonso, J., Cordoba, J., & Rovira, A. (2014). Brain magnetic resonance in hepatic encephalopathy. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MR, 35(2), 136–152.
Atterbury, C. E., Maddrey, W. C., & Conn, H. O. (1978). Neomycin-sorbitol and lactulose in the treatment of acute portal-systemic encephalopathy. A controlled, double-blind clinical trial. The American Journal of Digestive Diseases, 23(5), 398–406.
Buckner, R. L., Sepulcre, J., Talukdar, T., Krienen, F. M., Liu, H., Hedden, T., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Sperling, R. A., & Johnson, K. A. (2009). Cortical hubs revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity: mapping, assessment of stability, and relation to Alzheimer’s disease. The Journal of Neuroscience : The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 29(6), 1860–1873.
Chen, H. J., Zhu, X. Q., Shu, H., Yang, M., Zhang, Y., Ding, J., Wang, Y., & Teng, G. J. (2012). Structural and functional cerebral impairments in cirrhotic patients with a history of overt hepatic encephalopathy. European Journal of Radiology, 81(10), 2463–2469.
Chen, H. J., Jiang, L. F., Sun, T., Liu, J., Chen, Q. F., & Shi, H. B. (2015). Resting-state functional connectivity abnormalities correlate with psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score in cirrhosis. European Journal of Radiology, 84(11), 2287–2295.
Cheng, W., Rolls, E. T., Gu, H., Zhang, J., & Feng, J. (2015a). Autism: reduced connectivity between cortical areas involved in face expression, theory of mind, and the sense of self. Brain : A Journal of Neurology, 138(Pt 5), 1382–1393.
Cheng, Y., Huang, L. X., Zhang, X. D., Zhong, J. H., Ji, Q., Xie, S. S., Chen, L. H., Zuo, P. L., Zhang, L. J., & Shen, W. (2015b). Liver transplantation nearly normalizes brain spontaneous activity and cognitive function at 1 month: a resting-state functional MRI study. Metabolic Brain Disease, 30(4), 979–988.
Curtis, C. E. (2006). Prefrontal and parietal contributions to spatial working memory. Neuroscience, 139(1), 173–180.
Curtis, C. E., & D’Esposito, M. (2003). Persistent activity in the prefrontal cortex during working memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(9), 415–423.
Dai, Z., Yan, C., Li, K., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Cao, M., Lin, Q., Shu, N., Xia, M., Bi, Y., et al. (2015). Identifying and mapping connectivity patterns of brain network hubs in Alzheimer’s disease. Cerebral Cortex, 25(10), 3723–3742.
de Reus, M. A., & van den Heuvel, M. P. (2013). The parcellation-based connectome: limitations and extensions. NeuroImage, 80, 397–404.
Gotts, S. J., Simmons, W. K., Milbury, L. A., Wallace, G. L., Cox, R. W., & Martin, A. (2012). Fractionation of social brain circuits in autism spectrum disorders. Brain : A Journal of Neurology, 135(Pt 9), 2711–2725.
Hampson, M., Driesen, N. R., Skudlarski, P., Gore, J. C., & Constable, R. T. (2006). Brain connectivity related to working memory performance. The Journal of Neuroscience : The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 26(51), 13338–13343.
Hsu, T. W., Wu, C. W., Cheng, Y. F., Chen, H. L., Lu, C. H., Cho, K. H., Lin, W. C., & Lin, C. P. (2012). Impaired small-world network efficiency and dynamic functional distribution in patients with cirrhosis. PLoS ONE, 7(5), e35266.
Jao, T., Schroter, M., Chen, C. L., Cheng, Y. F., Lo, C. Z., Chou, K. H., Patel, A. X., Lin, W. C., Lin, C. P., & Bullmore, E. T. (2015). Functional brain network changes associated with clinical and biochemical measures of the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. NeuroImage, 122, 332–344.
Ledberg, A., Akerman, S., & Roland, P. E. (1998). Estimation of the probabilities of 3D clusters in functional brain images. NeuroImage, 8(2), 113–128.
Liang, X., Zou, Q., He, Y., & Yang, Y. (2013). Coupling of functional connectivity and regional cerebral blood flow reveals a physiological basis for network hubs of the human brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(5), 1929–1934.
Lin, W. C., Hsu, T. W., Chen, C. L., Lu, C. H., Chen, H. L., & Cheng, Y. F. (2015). Resting State-fMRI with ReHo analysis as a non-invasive modality for the prognosis of cirrhotic patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS ONE, 10(5), e0126834.
McPhail, M. J., Patel, N. R., & Taylor-Robinson, S. D. (2012). Brain imaging and hepatic encephalopathy. Clinics in Liver Disease, 16(1), 57–72.
Ni, L., Qi, R., Zhang, L. J., Zhong, J., Zheng, G., Zhang, Z., Zhong, Y., Xu, Q., Liao, W., Jiao, Q., et al. (2012). Altered regional homogeneity in the development of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a resting-state functional MRI study. PLoS ONE, 7(7), e42016.
Pessoa, L., Gutierrez, E., Bandettini, P., & Ungerleider, L. (2002). Neural correlates of visual working memory: fMRI amplitude predicts task performance. Neuron, 35(5), 975–987.
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2142–2154.
Power, J. D., Mitra, A., Laumann, T. O., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2014). Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 84, 320–341.
Pugh, R. N., Murray-Lyon, I. M., Dawson, J. L., Pietroni, M. C., & Williams, R. (1973). Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. The British Journal of Surgery, 60(8), 646–649.
Qi, R., Zhang, L. J., Xu, Q., Zhong, J., Wu, S., Zhang, Z., Liao, W., Ni, L., Zhang, Z., Chen, H., et al. (2012). Selective impairments of resting-state networks in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS ONE, 7(5), e37400.
Qi, R., Zhang, L. J., Zhong, J., Zhang, Z., Ni, L., Zheng, G., & Lu, G. M. (2013). Disrupted thalamic resting-state functional connectivity in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. European Journal of Radiology, 82(5), 850–856.
Qi, R., Zhang, L. J., Chen, H. J., Zhong, J., Luo, S., Ke, J., Xu, Q., Kong, X., Liu, C., & Lu, G. M. (2015). Role of local and distant functional connectivity density in the development of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Scientific Reports, 5, 13720.
Sepulcre, J., Liu, H., Talukdar, T., Martincorena, I., Yeo, B. T., & Buckner, R. L. (2010). The organization of local and distant functional connectivity in the human brain. PLoS Computational Biology, 6(6), e1000808.
Silk, T. J., Bellgrove, M. A., Wrafter, P., Mattingley, J. B., & Cunnington, R. (2010). Spatial working memory and spatial attention rely on common neural processes in the intraparietal sulcus. NeuroImage, 53(2), 718–724.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2010). Functional connectivity density mapping. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(21), 9885–9890.
Vapnik (1995). The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York Inc.
Wu, X., Zou, Q., Hu, J., Tang, W., Mao, Y., Gao, L., Zhu, J., Jin, Y., Wu, X., Lu, L., et al. (2015). Intrinsic functional connectivity patterns predict consciousness level and recovery outcome in acquired brain injury. The Journal of Neuroscience : The official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 35(37), 12932–12946.
Zhang, L., Qi, R., Wu, S., Zhong, J., Zhong, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., & Lu, G. (2012a). Brain default-mode network abnormalities in hepatic encephalopathy: a resting-state functional MRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 33(6), 1384–1392.
Zhang, L., Zheng, G., Zhang, L., Zhong, J., Wu, S., Qi, R., Li, Q., Wang, L., & Lu, G. (2012b). Altered brain functional connectivity in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a functional MR imaging study. Radiology, 265(2), 528–536.
Zhang, L., Wu, S., Ren, J., & Lu, G. M. (2014). Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging in hepatic encephalopathy: current status and perspectives. Metabolic Brain Disease, 29(3), 569–582.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (No. 2013CB329301 and No. 2012CB316301) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61271128, No.61571327 and No. 61503278).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Gaoyan Zhang, Yue Cheng and Baolin Liu declare that they have no actual or potential conflict of interest including any financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work. All of the authors declare that the work described in the manuscript was original research that has not been published previously, and was not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Informed consent
This study was approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee of Tianjin First Central Hospital. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects for being included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Cheng, Y. & Liu, B. Abnormalities of voxel-based whole-brain functional connectivity patterns predict the progression of hepatic encephalopathy. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 784–796 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9553-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9553-2