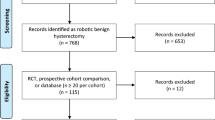
Abstract
Single-site hysterectomy (SSH) laparoscopic or robotic presented distinct advantages with regards to postoperative cosmetic outcome, wound-related complications and morbidity. We aimed to evaluate the feasibility of robotic and laparoscopic SSH in patients with benign or early-stage malignant gynecological conditions and to compare the two approaches. A systematic search of four electronic databases for articles published up to September 2019 was performed. Studies reporting outcomes for women who underwent robotic or laparoscopic SSH were considered eligible. A total of 6 studies with 412 patients were included. Among them, 150 women had robotic SSH, whereas 262 had laparoscopic SSH. Neither total operative time nor total hysterectomy time were found different among the 2 groups (355 patients MD 17.47 min, 95% CI − 5.82 to 40.76, p = 0.14 and 285 patients MD 6.41 min, 95% CI − 10.24 to 23.06, p = 0.45, respectively). Robotic approach presented significantly lower blood loss and hospital stay compared to laparoscopic (287 patients MD − 10.84 ml 95% CI − 20.35 to − 1.32, p = 0.03, 328 patients MD − 0.32 days, 95% CI − 0.44 to − 0.19, p < 0.00001, respectively). No difference was found with regards to major or overall postoperative complications. The present meta-analysis supports the use of robotic SSH, since it was related to faster recovery and comparable operative times and complication rates compared to laparoscopic. Nonetheless, due to the limited number of the included studies and their retrospective nature, the aforementioned outcomes must be interpreted with caution and further larger volume studies are needed in the field.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouquet de Joliniere J, Librino A, Dubuisson JB, Khomsi F, Ben Ali N, Fadhlaoui A, Ayoubi JM, Feki A (2016) Robotic surgery in gynecology. Front Surgy 3:26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2016.00026
Sandberg EM, la Chapelle CF, van den Tweel MM, Schoones JW, Jansen FW (2017) Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery versus conventional laparoscopy for hysterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 295(5):1089–1103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4323-y
Song T, Cho J, Kim TJ, Kim IR, Hahm TS, Kim BG, Bae DS (2013) Cosmetic outcomes of laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy compared with multi-port surgery: randomized controlled trial. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 20(4):460–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2013.01.010
Daniilidis A, Chatzistamatiou K, Assimakopoulos E (2017) Is there a role for single-port laparoscopy in the treatment of endometriosis? Minerva Ginecol 69(5):488–503. https://doi.org/10.23736/s0026-4784.17.04036-9
Boruta DM (2016) Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery in gynecologic oncology: an update. Gynecol Oncol 141(3):616–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.03.014
Fader AN, Escobar PF (2009) Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS) in gynecologic oncology: technique and initial report. Gynecol Oncol 114(2):157–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2009.05.020
Sendag F, Akdemir A, Oztekin MK (2014) Robotic single-incision transumbilical total hysterectomy using a single-site robotic platform: initial report and technique. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 21(1):147–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2013.07.004
Scheib SA, Fader AN (2015) Gynecologic robotic laparoendoscopic single-site surgery: prospective analysis of feasibility, safety, and technique. Am J Obstet Gynecol 212(2):179.e171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2014.07.057
Moukarzel LA, Fader AN, Tanner EJ (2017) Feasibility of robotic-assisted laparoendoscopic single-site surgery in the gynecologic oncology setting. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 24(2):258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2016.10.013
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73(9):712–716
DerSimonian R, Kacker R (2007) Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trial 28(2):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cct.2006.04.004
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
El Hachem L, Andikyan V, Mathews S, Friedman K, Poeran J, Shieh K, Geoghegan M, Gretz HF 3rd (2016) Robotic single-site and conventional laparoscopic surgery in gynecology: clinical outcomes and cost analysis of a matched case-control study. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 23(5):760–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2016.03.005
Paek J, Lee JD, Kong TW, Chang SJ, Ryu HS (2016) Robotic single-site versus laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery for adnexal tumours: a propensity score-matching analysis. MRCAS 12(4):694–700. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1707
Moon HS, Shim JE, Lee SR, Jeong K (2018) The comparison of robotic single-site surgery to single-port laparoendoscopic surgery for the treatment of advanced-stage endometriosis. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Technique Part A. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2018.0118
Cela V, Marrucci E, Angioni S, Freschi L (2018) Robot-assisted laparoscopic single-site hysterectomy: our experience and multicentric comparison with single-port laparoscopy. Minerva Ginecol 70(5):621–628
Gungor M, Kahraman K, Dursun P, Ozbasli E, Genim C (2018) Single-port hysterectomy: robotic versus laparoscopic. J Robot Surg 12(1):87–92
Paek J, Lee J-D, Kong TW, Chang S-J, Ryu H-S (2016) Robotic single-site versus laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy: a propensity score matching study. Surg Endosc 30(3):1043–1050
Lopez S, Mulla ZD, Hernandez L, Garza DM, Payne TN, Farnam RW (2016) A comparison of outcomes between robotic-assisted, single-site laparoscopy versus laparoendoscopic single site for benign hysterectomy. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 23(1):84–88
Akdemir A, Yildirim N, Zeybek B, Karaman S, Sendag F (2015) Single incision trans-umbilical total hysterectomy: robotic or laparoscopic? Gynecol Obstet Invest 80(2):93–98
Fagotti A, Corrado G, Fanfani F, Mancini M, Paglia A, Vizzielli G, Sindico S, Scambia G, Vizza E (2013) Robotic single-site hysterectomy (RSS-H) vs. laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy (LESS-H) in early endometrial cancer: a double-institution case–control study. Gynecol Oncol 130 (1):219–223
Albright BB, Witte T, Tofte AN, Chou J, Black JD, Desai VB, Erekson EA (2016) Robotic versus laparoscopic hysterectomy for benign disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 23(1):18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2015.08.003
Park D, Lee D, Kim S, Lee S (2016) Comparative safety and effectiveness of robot-assisted laparoscopic hysterectomy versus conventional laparoscopy and laparotomy for endometrial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol (EJSO) 42(9):1303–1314
Park DA, Yun JE, Kim SW, Lee SH (2017) Surgical and clinical safety and effectiveness of robot-assisted laparoscopic hysterectomy compared to conventional laparoscopy and laparotomy for cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 43(6):994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2016.07.017
Pelosi MA, Pelosi MA 3rd (1991) Laparoscopic hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy using a single umbilical puncture. New Jersey Med 88(10):721–726
Uppal S, Frumovitz M, Escobar P, Ramirez PT (2011) Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery in gynecology: review of literature and available technology. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 18(1):12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2010.07.013
Fader AN, Cohen S, Escobar PF, Gunderson C (2010) Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery in gynecology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 22(4):331–338
Kane S, Stepp KJ (2010) Laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery hysterectomy using robotic lightweight endoscope assistants. J Robot Surg 3(4):253–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-010-0170-6
Iavazzo C, Minis EE, Gkegkes ID (2018) Single-site port robotic-assisted hysterectomy: an update. J Robot Surg 12(2):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-018-0789-2
Akdemir A, Zeybek B, Ozgurel B, Oztekin MK, Sendag F (2015) Learning curve analysis of intracorporeal cuff suturing during robotic single-site total hysterectomy. J Minimal Invasive Gynecol 22(3):384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2014.06.006
Jayakumaran J, Wiercinski K, Buffington C, Caceres A (2018) Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site benign gynecologic surgery: a single-center experience. J Robot Surg 12(3):447–454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Prodromidou, E. Spartalis, G. Tsourouflis, D Dimitroulis and N. Nikiteas declare they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prodromidou, A., Spartalis, E., Tsourouflis, G. et al. Robotic versus laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Robotic Surg 14, 679–686 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01042-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01042-1