Abstract
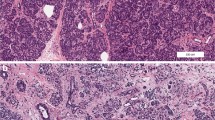
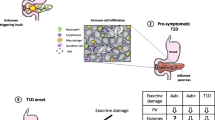
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is considered a pancreatic beta cell-specific disease that results in absolute insulin deficiency. Nevertheless, clinical studies from 1940 onwards showed that patients with T1D had an abnormal exocrine pancreas due to the presence of subclinical exocrine insufficiency and acinar atrophy. Exocrine abnormalities are an important, and mostly neglected, characteristic associated with T1D. It is however still unclear whether the exocrine dysfunction in T1D is a primary damage caused by the same pathogenic event that led to beta cell destruction or secondary to beta cell loss. In this review, we collect evidence supporting the hypothesis that T1D is a combined endocrine-exocrine disease in which the loss of functional beta cell mass is most clinically apparent.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Gale EAM. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes [internet]. Diapedia. 2014 Aug 13;2104085168 rev. no. 39.
Pollard HM, Miller L, Brewer WA. The external secretion of the pancreas and diabetes mellitus. Am J Dig Dis. 1943;10(1):20–3.
Perczak-Dudkowska B, Niewiedziol B. Exocrine function of the pancreas in juvenile onset diabetes mellitus. I. pH, duodenal content volume and bicarbonate concentration and secretion. Pediatr Pol. 1984;59(8):605–12.
Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965;14(10):619–33. The first report of decreased pancreatic size in patients with T1D.
Williams AJ, Thrower SL, Sequeiros IM, Ward A, Bickerton AS, Triay JM, et al. Pancreatic volume is reduced in adult patients with recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(11):E2109–13.
Tan GD. The pancreas. Anaesth Intensive Care Med. 2008;9(10):424–7.
Whitcomb DC, Lowe ME. Human pancreatic digestive enzymes. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52(1):1–17.
Chandra R, Liddle RA. Modulation of pancreatic exocrine and endocrine secretion. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2013;29(5):517–22.
Eberhard D, Lammert E. The pancreatic beta-cell in the islet and organ community. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19(5):469–75.
Pandiri AR. Overview of exocrine pancreatic pathobiology. Toxicol Pathol. 2014;42(1):207–16.
Pandol SJ. The exocrine pancreas. Colloquium series on integrated systems physiology: from molecule to function to disease. San Rafael (CA) 2010.
Piciucchi M, Capurso G, Archibugi L, Delle Fave MM, Capasso M, Delle FG. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in diabetic patients: prevalence, mechanisms, and treatment. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:595649.
Henderson JR, Daniel PM, Fraser PA. The pancreas as a single organ: the influence of the endocrine upon the exocrine part of the gland. Gut. 1981;22(2):158–67.
Whitcomb DC. Value of genetic testing in the management of pancreatitis. Gut. 2004;53(11):1710–7.
Parenti DM, Steinberg W, Kang P. Infectious causes of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1996;13(4):356–71.
Di Sebastiano P, di Mola FF, Bockman DE, Friess H, Buchler MW. Chronic pancreatitis: the perspective of pain generation by neuroimmune interaction. Gut. 2003;52(6):907–11.
Lankisch PG, Apte M, Banks PA. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2015.
Ewald N, Kaufmann C, Raspe A, Kloer HU, Bretzel RG, Hardt PD. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012;28(4):338–42.
Ewald NH, P.D. Alterations in exocrine pancreatic function in diabetes mellitus. The Pancreapedia. 2015;version 1.0.
Vacca JB, Henke WJ, Knight Jr WA. The exocrine pancreas in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1964;61:242–7.
Lankisch PG, Manthey G, Otto J, Koop H, Talaulicar M, Willms B, et al. Exocrine pancreatic function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Digestion. 1982;25(3):211–6.
Semakula C, Vandewalle CL, Van Schravendijk CF, Sodoyez JC, Schuit FC, Foriers A, et al. Abnormal circulating pancreatic enzyme activities in more than twenty-five percent of recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetic patients: association of hyperlipasemia with high-titer islet cell antibodies. Belgian Diabetes Registry. Pancreas. 1996;12(4):321–33.
Hardt PD, Krauss A, Bretz L, Porsch-Ozcurumez M, Schnell-Kretschmer H, Maser E, et al. Pancreatic exocrine function in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2000;37(3):105–10.
Hardt PD, Hauenschild A, Nalop J, Marzeion AM, Jaeger C, Teichmann J, et al. High prevalence of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in diabetes mellitus. A multicenter study screening fecal elastase 1 concentrations in 1,021 diabetic patients. Pancreatol : Off J Int Assoc Pancreatol. 2003;3(5):395–402.
Larger E, Philippe MF, Barbot-Trystram L, Radu A, Rotariu M, Nobecourt E, et al. Pancreatic exocrine function in patients with diabetes. Diabet Med : J Br Diabet Assoc. 2012;29(8):1047–54.
Dominguez-Munoz JE, Hieronymus C, Sauerbruch T, Malfertheiner P. Fecal elastase test: evaluation of a new noninvasive pancreatic function test. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90(10):1834–7.
Frier BM, Saunders JH, Wormsley KG, Bouchier IA. Exocrine pancreatic function in juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. Gut. 1976;17(9):685–91.
Ewald N, Raspe A, Kaufmann C, Bretzel RG, Kloer HU, Hardt PD. Determinants of exocrine pancreatic function as measured by fecal elastase-1 concentrations (FEC) in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14(3):118–22.
Bilgin M, Balci NC, Momtahen AJ, Bilgin Y, Klor HU, Rau WS. MRI and MRCP findings of the pancreas in patients with diabetes mellitus: compared analysis with pancreatic exocrine function determined by fecal elastase 1. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43(2):165–70.
Grippo PJ, Venkatasubramanian PN, Knop RH, Heiferman DM, Iordanescu G, Melstrom LG, et al. Visualization of mouse pancreas architecture using MR microscopy. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(2):610–8.
Sequeiros IM, Hester K, Callaway M, Williams A, Garland Z, Powell T, et al. MRI appearance of the pancreas in patients with cystic fibrosis: a comparison of pancreas volume in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Br J Radiol. 2010;83(995):921–6.
Campbell-Thompson M, Wasserfall C, Montgomery EL, Atkinson MA, Kaddis JS. Pancreas organ weight in individuals with disease-associated autoantibodies at risk for type 1 diabetes. JAMA. 2012;308(22):2337–9. The first demonstration in humans that pancreas weight is reduced in individuals at risk of developing T1D, thus suggesting that early atrophy of the organ may be an important sub-clinical feature of T1D pathogenesis.
Di Gialleonardo V, de Vries EF, Di Girolamo M, Quintero AM, Dierckx RA, Signore A. Imaging of β-cell mass and insulitis in insulin-dependent (type 1) diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev. 2012.
Cecil RL. A study of the pathological anatomy of the pancreas in ninety cases of diabetes mellitus. J Exp Med. 1909;11(2):266–90.
MacLean N, Ogilvie RF. Quantitative estimation of the pancreatic islet tissue in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1955;4(5):367–76.
Rahier J, Goebbels RM, Henquin JC. Cellular composition of the human diabetic pancreas. Diabetologia. 1983;24(5):366–71.
Foulis AK, Stewart JA. The pancreas in recent-onset type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: insulin content of islets, insulitis and associated changes in the exocrine acinar tissue. Diabetologia. 1984;26(6):456–61.
Altobelli E, Blasetti A, Verrotti A, Di Giandomenico V, Bonomo L, Chiarelli F. Size of pancreas in children and adolescents with type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes. J Clin Ultrasound. 1998;26(8):391–5.
Fonseca V, Berger LA, Beckett AG, Dandona P. Size of pancreas in diabetes mellitus: a study based on ultrasound. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1985;291(6504):1240–1.
Gilbeau JP, Poncelet V, Libon E, Derue G, Heller FR. The density, contour, and thickness of the pancreas in diabetics: CT findings in 57 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159(3):527–31.
Goda K, Sasaki E, Nagata K, Fukai M, Ohsawa N, Hahafusa T. Pancreatic volume in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2001;38(3):145–9.
Gaglia JL, Guimaraes AR, Harisinghani M, Turvey SE, Jackson R, Benoist C, et al. Noninvasive imaging of pancreatic islet inflammation in type 1A diabetes patients. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(1):442–5.
Löhr M, Klöppel G. Residual insulin positivity and pancreatic atrophy in relation to duration of chronic type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and microangiopathy. Diabetologia. 1987;30(10):757–62.
Muniraj T, Aslanian HR, Farrell J, Jamidar PA. Chronic pancreatitis, a comprehensive review and update. Part I: epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, genetics, pathophysiology, and clinical features. Dis Mon : DM. 2014;60(12):530–50.
Beger HG, Buchler M, Kozarek R, Lerch M, Neoptolemos JP, Warshaw A, et al. The pancreas: an integrated textbook of basic science, medicine, and surgery: Wiley; 2 edition; 2008. p. 1024.
Comfort MW, Gambill EE, Baggenstoss AH. Chronic relapsing pancreatitis; a study of 29 cases without associated disease of the biliary or gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1946;6:376–408.
Foulis AK, Liddle CN, Farquharson MA, Richmond JA, Weir RS. The histopathology of the pancreas in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: a 25-year review of deaths in patients under 20 years of age in the United Kingdom. Diabetologia. 1986;29(5):267–74.
Rodriguez-Calvo T, Ekwall O, Amirian N, Zapardiel-Gonzalo J, von Herrath MG. Increased immune cell infiltration of the exocrine pancreas: a possible contribution to the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2014;63(11):3880–90. The first demonstration that immune infiltrates in the pancreas of patients with T1D occurs also in the exocrine area.
Willcox A, Richardson S, Bone A, Foulis A, Morgan N. Analysis of islet inflammation in human type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;155(2):173–81.
Coppieters KT, Dotta F, Amirian N, Campbell PD, Kay TW, Atkinson MA, et al. Demonstration of islet-autoreactive CD8 T cells in insulitic lesions from recent onset and long-term type 1 diabetes patients. J Exp Med. 2012;209(1):51–60.
Valle A, Giamporcaro GM, Scavini M, Stabilini A, Grogan P, Bianconi E, et al. Reduction of circulating neutrophils precedes and accompanies type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(6):2072–7. The first demonstration that neutrophils accumulate in the pancreas of patients with T1D especially in the exocrine area.
Korsgren S, Molin Y, Salmela K, Lundgren T, Melhus A, Korsgren O. On the etiology of type 1 diabetes: a new animal model signifying a decisive role for bacteria eliciting an adverse innate immunity response. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(5):1735–48.
Kloppel G. Islet histopathology in diabetes mellitus. Kloppel G, Heitz P, editors. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1984. 239 p.
Panicot L, Mas E, Thivolet C, Lombardo D. Circulating antibodies against an exocrine pancreatic enzyme in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48(12):2316–23.
Endo T, Takizawa S, Tanaka S, Takahashi M, Fujii H, Kamisawa T, et al. Amylase alpha-2A autoantibodies: novel marker of autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009;58(3):732–7.
Taniguchi T, Okazaki K, Okamoto M, Seko S, Tanaka J, Uchida K, et al. High prevalence of autoantibodies against carbonic anhydrase II and lactoferrin in type 1 diabetes: concept of autoimmune exocrinopathy and endocrinopathy of the pancreas. Pancreas. 2003;27(1):26–30.
Kobayashi T, Nakanishi K, Kajio H, Morinaga S, Sugimoto T, Murase T, et al. Pancreatic cytokeratin: an antigen of pancreatic exocrine cell autoantibodies in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1990;33(6):363–70.
di Cesare E, Previti M, Lombardo F, Mazzù N, di Benedetto A, Cucinotta D. Prevalence of autoantibodies to carbonic anhydrase II and lactoferrin in patients with type 1 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1037:131–2.
Hardt PD, Ewald N, Bröckling K, Tanaka S, Endo T, Kloer HU, et al. Distinct autoantibodies against exocrine pancreatic antigens in European patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. JOP. 2008;9(6):683–9.
Rowe P, Wasserfall C, Croker B, Campbell-Thompson M, Pugliese A, Atkinson M, et al. Increased complement activation in human type 1 diabetes pancreata. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(11):3815–7.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Martha Campbell-Thompson, Teresa Rodriguez-Calvo, and Manuela Battaglia declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell-Thompson, M., Rodriguez-Calvo, T. & Battaglia, M. Abnormalities of the Exocrine Pancreas in Type 1 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 15, 79 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-015-0653-y
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-015-0653-y