Abstract
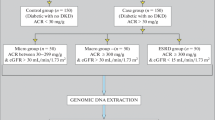
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an important public health problem. Patients with end-stage renal disease have a significant renalase deficiency, which could be one of the mechanisms explaining high prevalence of hypertension in these patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the possible association of renalase gene (rs2296545) polymorphism with normotensive and hypertensive CKD in sampled Egyptian patients and to determine the effect of such polymorphism on epinephrine level. Renalase gene (rs2296545) polymorphism was genotyped in 178 patients with CKD (83 normotensive and 95 hypertensive nephrosclerosis) and 178 normal healthy adults using polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). Epinephrine level was measured by HPLC method. We found an association of renalase (rs2296545) CC genotype and C allele with CKD. Also, the epinephrine level was significantly increased in normotensive and hypertensive nephrosclerosis patients as compared to controls. CKD patients with CC genotype showed significant high epinephrine level as compared to CG and GG genotypes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McClellan, W. M., Satko, S. G., Gladstone, E., Krisher, J. O., Narva, A. S., & Freedman, B. I. (2009). Individuals with a family history of ESRD are a high-risk population for CKD: implications for targeted surveillance and intervention activities. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 53(3), S100–S106.
Xu, J., Wang, G., Li, P., Velazquez, H., Yao, X., Li, Y., et al. (2005). Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115(5), 1275–1280.
Desir, G. V. (2009). Regulation of blood pressure and cardiovascular function by renalase. Kidney International, 76, 366–370.
Boomsma, F., & Tipton, K. F. (2007). Renalase, a catecholamine-metabolizing enzyme? Journal of Neural Transmission, 114, 775–776.
Xu, J., & Desir, G. V. (2007). Renalase, a new renal hormone: its role in health and disease. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 16, 373–378.
Haroun, M. K., Jaar, B. G., Hoffman, S. C., Comstock, G. W., Klag, M. J., & Coresh, J. (2003). Risk factors for chronic kidney disease: a prospective study of 23,534 men and women in Washington Country, Maryland. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 14(11), 2934–2941.
Toto, R. B. (2003). Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis in African Americans. Kidney International, 64(6), 2331–2341.
Hsu, C. Y., McCulloch, C. E., Darbinian, J., Go, A. S., & Iribarren, C. (2005). Elevated blood pressure and risk of end-stage renal disease in subjects without baseline kidney disease. Archives of Internal Medicine, 165(8), 923–928.
Farzaneh-Far, R., Desir, G. V., Na, B., Schiller, N. B., & Whooley, M. A. (2010). A functional polymorphism in renalase (Glu37Asp) is associated with cardiac hypertrophy, dysfunction, andischemia: data from the heart and soul study. PLoS One 20, 5(10) e13496.
Zhao, Q., Fan, Z., He, J., Chen, S., Li, H., Zhang, P., et al. (2007). Renalase gene is a novel susceptibility gene for essential hypertension: a two stage association study in northern Han Chinese population. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 85, 877–885.
Abdallah, E., & Sabry, D. (2013). Renalase gene polymorphisms in end-stage renal disease patients: an Egyptian study. Journal of American Science, 9(1), 346–349.
Freedman, B. I., Hicks, P. J., Bostrom, M. A., Cunningham, M. E., Liu, Y., Divers, J., et al. (2009). Polymorphisms in the non-muscle myosin heavy chain 9 Gene (MYH9) are strongly associated with end-stage renal disease historically attributed to hypertension in African Americans. Kidney International, 75(7), 736–745.
Fogo, A., Breyer, J. A., Smith, M. C., Cleveland, W. H., Agodoa, L., Kirk, K. A., et al. (1997). Accuracy of the diagnosis of hypertensive nephrosclerosis in African Americans: a report from the African American Study of Kidney Disease (AASK) Trial. AASK Pilot Study Investigators. Kidney International, 51(1), 244–252.
Buraczynska, M., Zukowski, P., Buraczynska, K., Mozul, S., & Ksiazek, A. (2011). Renalase gene polymorphisms in patients with type 2 diabetes, hypertension and stroke. Neuromolecular Medicine, 13(4), 321–327.
BauersfeldW, R. D., Knoll, E., & Wisser, H. (1986). Determination of catecholamines in plasma by hplc and amperometric detection. Comparison with a radioenzymatic method. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 24, 185–188.
SPSS for Windows Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 11.0.1.SPSS Inc, Chicago 2001
Coresh, J., Selvin, E., Stevens, L. A., Manzi, J., Kusek, J. W., Eggers, P., et al. (2007). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Journal of the American Medical Association, 298(17), 2038–2047.
Ahlawat, R. S., Gupta, S., Kapoor, S., & Kar, P. (2012). Polymorphism of renalase gene in patients of chronic kidney disease. Open Journal of Nephrology, 2, 136–143.
Peng, M., & Jiang, X. J. (2011). Novel renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system-related targets for antihypertensive therapy. Advance Cardiovascular Diseases, 32, 13–16.
Li, G., Xu, J., Wang, P., Velazquez, H., Li, Y., Wu, Y., et al. (2008). Catecholamines regulate the activity, secretion, and synthesis of renalase. Circulation, 117(10), 1277–1282.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezk, N.A., Zidan, H.E., Elnaggar, Y.A. et al. Renalase Gene Polymorphism and Epinephrine Level in Chronic Kidney Disease. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175, 2309–2317 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1433-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1433-x