Abstract
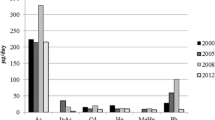
The concentrations of arsenic (As), beryllium (Be), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), mercury (Hg), manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), tin (Sn), thallium (Tl), and vanadium (V) were determined in a number of foodstuffs purchased during 2006 in various localities of Tarragona County (Catalonia, Spain), near a hazardous waste incinerator, which has been operating since 1999. The dietary intake of the above elements by the population of the area was subsequently estimated. The results were compared with those obtained in previous surveys (baseline 1997 and 2002) performed in the same area. The levels of Be, Tl, and V were under their respective limits of detection in all samples. The estimated dietary intakes of the elements analyzed in the current survey by an adult man of 70 kg were the following: 351 μg/day for As, 4.6 μg/day for Cd, 57.5 μg/day for Cr, 7.1 μg/day for Hg, 2,229 μg/day for Mn, 78.0 μg/day for Ni, 39.9 μg/day for Pb, and 37.9 μg/day for Sn. On average, fish and seafood were the main contributor to the total dietary intake of As, Cd, and Hg and one of the most important for Pb. In general terms, the differences on metal exposure through dietary intake between the present and our two previous surveys were not particularly relevant. The current intake of the most toxic elements (As, Cd, Hg, and Pb) remains under the respective Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intakes established by the Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hart A, Smith GC, Macarthur R, Rose M. Application of uncertainty analysis in assessing dietary exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2003;140–141:437–442.
Kiviranta H, Vartiainen T, Tuomisto J. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls in fishermen in Finland. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002;110:355–361.
Chen HL, Lee CC, Liao PC, Guo YL, Chen CH, Su HJ. Associations between dietary intake and serum polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran (PCDD/F) levels in Taiwanese. Environ. Res. 2003;91:172–178.
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Müller L, Sünderhauf W, Jager J. Baseline levels of PCDD/Fs in vegetation samples collected in the vicinity of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere. 1998;36:2581–2591.
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Lindström G, Wingfors H. Dioxin and dibenzofuran concentrations in blood of a general population from Tarragona, Spain. Chemosphere. 1999;38:1123–1133.
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Kiviranta H, Vartiainen T. PCDD/F concentrations in milk of non-occupationally exposed women living in southern Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere. 1999;38:995–1004.
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Lindström G, Wingfors H. Dioxin and dibenzofuran concentrations in adipose tissue of a general population from Tarragona, Spain. Chemosphere. 1999;38:2475–2487.
Schuhmacher M, Granero S, Llobet JM, de Kok HA, Domingo JL. Assessment of baseline levels of PCDD/F in soils in the neighbourhood of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere. 1997;35:1947–1958.
Biegalski S, Landsberger S. An evaluation of atmospheric deposition of trace elements into the Great Lakes. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1999;71–72:247–256.
Cook AG, Weinstein P, Centeno JA. Health effects of natural dust: Role of trace elements and compounds. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2005;103:1–15.
Bocio A, Nadal M, Domingo JL. Human exposure to metals through the diet in Tarragona, Spain: Temporal trend. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2005;104:193–201.
Granero S, Llobet JM, Schuhmacher M, Corbella J, Domingo JL. Biological monitoring of environmental pollution and human exposure to metals in Tarragona, Spain. I. Levels in hair of school children. Trace Elem. Electrolytes. 1998;15:39–43.
Leblanc JC, Guérin T, Noël L, Calamassi-Tran G, Volatier JL, Verger P. Dietary exposure estimates of 18 elements from the 1st French Total Diet Study. Food Addit. Contam. 2005;22:624–641.
Ferré-Huguet N, Martí-Cid R, Schuhmacher M, Domingo J. Risk Assessment of Metals from Consuming Vegetables, Fruits and Rice Grown on Soils Irrigated with Waters of the Ebro River in Catalonia, Spain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008;123:66–79.
Zukowska J, Biziuk M. Methodological evaluation of method for dietary heavy metal intake. J. Food Sci. 2008;73:21–29.
Llobet JM, Granero S, Schuhmacher M, Corbella J, Domingo JL. Biological monitoring of environmental pollution and human exposure to metals in Tarragona, Spain. IV. Estimation of the dietary intake. Trace Elem. Electrolytes. 1998;15:136–141.
Llobet JM, Granero S, Torres A, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL. Biological monitoring of environmental pollution and human exposure to metals in Tarragona, Spain. III. Blood levels. Trace Elem. Electrolytes. 1998;15:76–80.
Bocio A, Llobet JM, Domingo JL, Corbella J, Teixidó A, Casas C. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in foodstuffs: Human exposure through the diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003;51:3191–3195.
Martí-Cid R, Llobet JM, Castell V, Domingo JL. Dietary intake of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead by the population of Catalonia, Spain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008;125:120–132.
Serra-Majem L, Ribas L, Salvador G, Castells C, Serra J, Jover L, et al. Avaluació de l’estat nutricional de la població catalana 2002–2003. Evolució dels hàbits alimentaris i del consum d’aliments i nutrients a Catalunya (1992–2003). Barcelona, Spain: Direcció General de Salut Pública. Departament de Sanitat i Seguretat Social. Generalitat de Catalunya; 2003 (in Catalan).
Falcó G, Llobet JM, Bocio A, Domingo JL. Daily intake of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead by consumption of edible marine species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006;54:6106–6112.
Bordajandi LR, Gómez G, Abad E, Rivera J, Del Mar Fernández-Bastón M, Blasco J, et al. Survey of persistent organochlorine contaminants (PCBs, PCDD/Fs, and PAHs), heavy metals (Cu, Cd, Zn, Pb, and Hg), and arsenic in food samples from Huelva (Spain): levels and health implications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004;52:992–1001.
Jalón M, Urieta I, Macho ML, Azpiri M (1997) Metales Pesados y Arsénico. In: Vigilancia de la Contaminación Química de los Alimentos en la Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco 1990–1995. Servicio Central de Publicaciones del Gobierno Vasco, Vitoria, Spain 29–43 (in Spanish).
Tsuda T, Inoue T, Kojima M, Aoki S. Market basket and duplicate portion estimation of dietary intakes of cadmium, mercury, arsenic, copper, manganese and zinc by Japanese adults. J. AOAC Int. 1995;78:1363–1368.
Rubio C, Hardisson A, Reguera JI, Revert C, Lafuente MA, González-Iglesias T. Cadmium dietary intake in the Canary Islands, Spain. Environ. Res. 2006;100:123–129.
Ysart G, Miller P, Croasdale M, Crews H, Robb P, Baxter M, et al. UK total diet study—dietary exposures to aluminium, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, mercury, nickel, selenium, tin and zinc. Food Addit. Contam. 1997;17:775–786.
Urieta I, Jalón M, Equileror I. Food surveillance in the Basque Country (Spain). II. Estimation of the dietary intake of organochlorine pesticides, heavy metals, arsenic, aflatoxin M1, iron and zinc through the Total Diet Study, 1990/1991. Food Addit. Contam. 1996;13:29–52.
Leblanc JC, Malmauret L, Guérin T, Bordet F, Boursier B, Verger P. Estimation of the dietary intake of pesticide residues, lead, cadmium, arsenic and radionuclides in France. Food Addit. Contam. 2000;17:925–932.
Larsen EH, Andersen NL, Møller A, Petersen A, Mortensen GK, Petersen J. Monitoring the content and intake of trace elements from food in Denmark. Food Addit. Contam. 2002;19:33–46.
Wilhelm M, Wittsiepe J, Schrey P, Budde U, Idel H. Dietary intake of cadmium by children and adults from Germany using duplicate portion sampling. Sci. Total Environ. 2002;285:11–19.
Zheng N, Wang Q, Zhang X, Zheng D, Zhang Z, Zhang S. Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2007;387:96–104.
Karita K, Suzuki T. Fish eating and variations in selenium and mercury levels in plasma and erythrocytes in free-living healthy Japanese men. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2002;90:71–81.
Llobet JM, Falcó G, Casas C, Teixidó A, Domingo JL. Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead in common foods and estimated daily intake by children, adolescents, adults, and seniors of Catalonia, Spain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003;51:838–842.
Ferré-Huguet N, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo J (2009) Monitoring metals in blood and hair of the population living near a hazardous waste incinerator: temporal trend. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. In press
Schuhmacher M, Bosque MA, Domingo JL, Corbella J. Dietary intake of lead and cadmium from foods in Tarragona Province, Spain. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991;46:320–328.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the Agència of Residus, Generalitat de Catalunya, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martí-Cid, R., Perelló, G. & Domingo, J.L. Dietary Exposure to Metals by Individuals Living Near a Hazardous Waste Incinerator in Catalonia, Spain: Temporal Trend. Biol Trace Elem Res 131, 245–254 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8368-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8368-z