Abstract
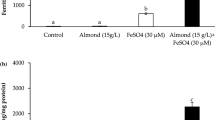
Calcium, phytic acid, polyphenols and fiber are major inhibitors of iron absorption and they could be found in excess in some diets, thereby altering or modifying the iron nutrition status. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of calcium, tannic acid, phytic acid, and pectin over iron uptake, using an in vitro model of epithelial cells (Caco-2 cell line). Caco-2 cells were incubated with iron (10–30 μM) with or without CaCl2 (500 and 1,000 μM) for 24 h. Then, cells were challenged with phytic acid (50–150 μM); pectin (50–150 nM) or tannic acid (100–500 μM) for another 24 h. Finally, 55Fe (10 μM) uptake was determined. Iron dialyzability was studied using an in vitro digestion method. Iron uptake in cells pre-incubated with 20 and 30 μM Fe was inhibited by CaCl2 (500 μM). Iron uptake decreased in cells cultured with tannic acid (300 μM) and CaCl2 (500–1,000 μM) (two-way ANOVA, p = 0.002). Phytic acid also decreased iron uptake mainly when cells were treated with CaCl2 (1,000 μM) (two-way ANOVA; p < 0.05). Pectin slightly decreased iron uptake (p = NS). Iron dialyzability decreased when iron was mixed with CaCl2 and phytic or tannic acid (T test p < 0.0001, for both) but not when mixed with pectin. Phytic acid combined with calcium is a strong iron uptake inhibitor. Pectin slightly decreased iron uptake with or without calcium. Tannic acid showed an unexpected behavior, inducing an increase on iron uptake, despite its low Fe dialyzability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheftel A, Stehling O, Lill R (2010) Iron-sulfur proteins in health and disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:302–314
Evstatiev R, Gasche C (2012) Iron sensing and signalling. Gut 61:933–952
Atanasova BD, Li AC, Bjarnason I, Tzatchev KN, Simpson RJ (2005) Duodenal ascorbate and ferric reductase in human iron deficiency. Am J Clin Nutr 81:130–133
Latunde-Dada GO, Simpson RJ, McKie AT (2008) Duodenal cytochrome B expression stimulates iron uptake by human intestinal epithelial cells. J Nutr 138:991–995
Hurrell R, Egli I (2010) Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1461S–1467S
Dudkowiak R, Neubauer K, Poniewierka E (2013) Hepcidin and its role in inflammatory bowel disease. Adv Clin Exp Med 22:585–591
Collings R, Harvey LJ, Hooper L, Hurst R, Brown TJ, Ansett J, King M, Fairweather-Tait SJ (2013) The absorption of iron from whole diets: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 98:65–81
Wienk KJ, Marx JJ, Lemmens AG, Brink EJ, Van Der Meer R, Beynen AC (1996) Mechanism underlying the inhibitory effect of high calcium carbonate intake on iron bioavailability from ferrous sulphate in anaemic rats. Br J Nutr 75:109–120
Thompson BA, Sharp PA, Elliott R, Fairweather-Tait SJ (2010) Inhibitory effect of calcium on non-heme iron absorption may be related to translocation of DMT-1 at the apical membrane of enterocytes. J Agric Food Chem 58:8414–8417
Egli I, Davidsson L, Zeder C, Walczyk T, Hurrell R (2004) Dephytinization of a complementary food based on wheat and soy increases zinc, but not copper, apparent absorption in adults. J Nutr 134:1077–1080
Hurrell RF, Juillerat MA, Reddy MB, Lynch SR, Dassenko SA, Cook JD (1992) Soy protein, phytate, and iron absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 56:573–578
Hurrell RF (2004) Phytic acid degradation as a means of improving iron absorption. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 74:445–452
Hurrell R, Ranum P, de Pee S, Biebinger R, Hulthen L, Johnson Q, Lynch S (2010) Revised recommendations for iron fortification of wheat flour and an evaluation of the expected impact of current national wheat flour fortification programs. Food Nutr Bull 31:S7–S21
Mandel S, Amit T, Reznichenko L, Weinreb O, Youdim MB (2006) Green tea catechins as brain-permeable, natural iron chelators-antioxidants for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Nutr Food Res 50:229–234
Kim MM, Atallah MT (1992) Structure of dietary pectin, iron bioavailability and hemoglobin repletion in anemic rats. J Nutr 122:2298–2305
Koester Weber T, Cássia Freitas K, Amancio OM, de Morais MB (2010) Effect of dietary fibre mixture on growth and intestinal iron absorption in rats recovering from iron-deficiency anaemia. BJN 104:1471–1476
Baig M, Burgin C, Cerda J (1983) Effect of dietary pectin on iron absorption and turnover in the rat. J Nutr 113:2385–2389
Brouns F, Theuwissen E, Adam A, Bell M, Berger A, Mensink RP (2012) Cholesterol-lowering properties of different pectin types in mildly hyper-cholesterolemic men and women. Eur J Clin Nutr 66:591–599
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr A, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Bosscher D, Van Caillie-Bertrand M, Deelstra H (2001) Effect of thickening agents, based on soluble dietary fiber, on the availability of calcium, iron, and zinc from infant formulas. Nutrition 17:614–618
Aarestrup J, Kyrø C, Christensen J, Kristensen M, Lund Wurtz AM, Johnsen NF, Overvad K, Tjønneland A, Olsen A (2012) Whole grain, dietary fiber, and incidence of endometrial cancer in a danish cohort study. Nutr Cancer 64:1160–1168
Timm DA, Slavin JL (2008) Dietary Fiber and the Relationship to Chronic Diseases. Am J Lifestyle Med 2:233–240
Miyada T, Nakajima A, Ebihara K (2011) Iron bound to pectin is utilised by rats. BJN 106:73–78
Miyada T, Nakajima A, Ebihara K (2012) Degradation of pectin in the caecum contributes to bioavailability of iron in rats. BJN 107:1452–1457
Serrano J, Puupponen-Pimiä R, Dauer A, Aura AM, Saura-Calixto F (2009) Tannins: current knowledge of food sources, intake, bioavailability and biological effects. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:S310–S329
Glahn RP, Wortley GM, South PK, Miller D (2002) Inhibition of iron uptake by phytic acid, tannic acid, and ZnCl 2: studies using an in vitro digestion/Caco-2 cell model. J Agric Food Chem 50:390–395
Kalgaonkar S, Lönnerdal B (2008) Effects of dietary factors on iron uptake from ferritin by Caco-2 cells. J Nutr Biochem 19:33–39
Ma G, Jin Y, Piao J, Kok F, Guusje B, Jacobsen E (2005) Phytate, calcium, iron, and zinc contents and their molar ratios in foods commonly consumed in China. J Agric Food Chem 53:10285–10290
Ma G, Li Y, Jin Y, Zhai F, Kok F, Yang X (2007) Phytate intake and molar ratios of phytate to zinc, iron and calcium in the diets of people in China. Eur J Clin Nutr 61:368–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrews, M., Briones, L., Jaramillo, A. et al. Effect of Calcium, Tannic Acid, Phytic Acid and Pectin over Iron Uptake in an In Vitro Caco-2 Cell Model. Biol Trace Elem Res 158, 122–127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9911-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9911-0