Abstract
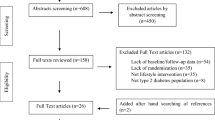
Obesity is a chronic disease characterized by excessive accumulation of body fat and the presence of metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance. In this sense, zinc is an important nutrient that stimulates insulin secretion and increases sensitivity to insulin. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance in obese subjects through a systematic review of the available clinical trials. The search for articles was conducted using the PubMed, SciVerse Scopus, SciVerse ScienceDirect, and Cochrane databases, on May 25, 2016, by two authors independently. The recommendations of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) were followed in the conduct of this review. The Cochrane Collaboration tool was used to assess the risk of bias of the trials included in this review. After screening of the articles, six clinical trials were included in this systematic review. The scientific evidence presented in this systematic review shows that zinc supplementation improves insulin resistance in obese individuals of both sexes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koliaki C, Roden M (2016) Alterations of mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity in human obesity and diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Nutr 36:337–367
Organization for economic co-operation and development. Obesity Update. Secretaria Geral da OECD, 2014. Disponível em: <http://www.oecd.org/els/health-systems/Obesity-Update-2014.pdf>. Acesso em: 20 Oct 2014
Parish RC, Todman S, Jain SK (2016) Resting heart rate variability, inflammation, and insulin resistance in overweight and obese adolescents. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 14(6):291–297
Kelishadi R, Hashemipour M, Adeli K, Tavakoli N, Movahedian-Attar A, Shapouri J, Poursafa P, Rouzbahani A (2010) Effect of zinc supplementation on markers of insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation among prepubescent children with metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 8(6):505–510. doi:10.1089/met.2010.0020
Ranasinghe P, Pigera S, Galappatthy P, Katulanda P, Constantine GR (2015) Zinc and diabetes mellitus: understanding molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Daru 23:44. doi:10.1186/s40199-015-0127-
Capdor J, Foster M, Petocz P, Samman S (2013) Zinc and glycemic control: a meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled supplementation trials in humans. J Trace Elem Med Biol 27(2):137–142. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.08.001
Jansen J, Rosenkranz E, Overbeck S, Warmuth S, Mocchegiani E, Giacconi R, Weiskirchen R, Karges W, Rink L (2012) Disturbed zinc homeostasis in diabetic patients by in vitro and in vivo analysis of insulinomimetic activity of zinc. J Nutr Biochem 23(11):1458–1466. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.09.008
Vardatsikos G, Pandey NR, Srivastava AK (2013) Insulino-mimetic and anti-diabetic effects of zinc. J Inorg Biochem 120:8–17. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.11.006
García OP, Ronquillo D, Caamaño MC, Martínez G, Camacho M, López V, Rosado JL (2013) Zinc, iron and vitamins a, C and E are associated with obesity, inflammation, lipid profile and insulin resistance in Mexican school-aged children. Nutrients 5(12):5012–5030. doi:10.3390/nu5125012
Suliburska J, Cofta S, Gajewska E, Kalmus G, Sobieska M, Samborski W, Krejpcio Z, Drzymala-Czyz S, Bogdanski P (2013) The evaluation of selected serum mineral concentrations and their association with insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17(17):2396–2400
Begin-Heick N, Dalpe-Scott M, Rowe J, Heick HM (1985) Zinc supplementation attenuates insulin secretory activity in pancreatic islets of the ob/ob mouse. Diabetes 34(2):179–184
Foster M, Samman S (2012) Zinc and regulation of inflammatory cytokines: implications for cardiometabolic disease. Nutrients 4(7):676–694. doi:10.3390/nu4070676
Feitosa MC, Lima VB, Moita Neto JM, Marreiro Ddo N (2013) Plasma concentration of IL-6 and TNF-α and its relationship with zincemia in obese women. Rev Assoc Med Bras 59(5):429–434. doi:10.1016/j.ramb.2013.03.003
Liuzzi JP, Lichten LA, Rivera S, Blanchard RK, Aydemir TB, Knutson MD, Ganz T, Cousins RJ (2005) Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(19):6843–6848
Noh H, Paik HY, Kim J, Chung J (2014) The alteration of zinc transporter gene expression is associated with inflammatory markers in obese women. Biol Trace Elem Res 158(1):1–8. doi:10.1007/s12011-014-9902-1
Noh H, Paik HY, Kim J, Chung J (2014) The changes of zinc transporter ZnT gene expression in response to zinc supplementation in obese women. Biol Trace Elem Res 162(1–3):38–45. doi:10.1007/s12011-014-0128-z
Moher A, Liberati J, Tetzlaff DG (2009) Altman PRISMA group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2535
Higgins JPT, Green S (eds) (2009) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.0.2. The Cochrane Collaboration, London
Kim J, Lee S (2012) Effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance and metabolic risk factors in obese Korean women. Nutr Res Pract 6(3):221–225. doi:10.4162/nrp.2012.6.3.221
Gómez-García A, Hernández-Salazar E, González-Ortiz M, Martínez-Abundis E (2006) Effect of oral zinc administration on insulin sensitivity, leptin and androgens in obese males. Rev Med Chil 134(3):279–284
Marreiro DN, Geloneze B, Tambascia MA, Lerário AC, Halpern A, Cozzolino SM (2006) Effect of zinc supplementation on serum leptin levels and insulin resistance of obese women. Biol Trace Elem Res 112(2):109–118
Hashemipour M, Kelishadi R, Shapouri J, Sarrafzadegan N, Amini M, Tavakoli N, Movahedian-Attar A, Mirmoghtadaee P, Poursafa P (2009) Effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance and components of the metabolic syndrome in prepubertal obese children. Hormones (Athens) 8(4):279–285
Payahoo L, Ostadrahimi A, Mobasseri M, Khaje Bishak Y, Farrin N, Asghari Jafarabadi M, Mahluji S (2013) Effects of zinc supplementation on the anthropometric measurements, lipid profiles and fasting blood glucose in the healthy obese adults. Adv Pharm Bull 3(1):161–165. doi:10.5681/apb.2013.027
Bellomo E, Massarotti A, Hogstrand C, Maret W (2014) Zinc ions modulate protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activity. Metallomics 6(7):1229–1239. doi:10.1039/c4mt00086b
Jansen J, Karges W, Rink L (2009) Zinc and diabetes—clinical links and molecular mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 20(6):399–417. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.01.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cruz, K.J.C., Morais, J.B.S., de Oliveira, A.R.S. et al. The Effect of Zinc Supplementation on Insulin Resistance in Obese Subjects: a Systematic Review. Biol Trace Elem Res 176, 239–243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0835-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0835-8