Abstract
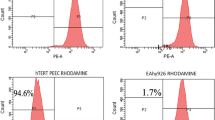
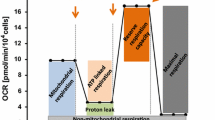
Chemotherapy is one of the common treatment modalities for cancer. Some of the antineoplastic drugs have, however, been found to be toxic for vascular endothelium, resulting in complications such as endothelial dysfunction, thromboembolism, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy. In this study, we investigated the cytotoxic effect of widely used antitumor agents doxorubicin, camptothecin, and thapsigargin on primary and immortalized porcine endocardial endothelial cells and compared with the effects of these agents on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, human aortic endothelial cells, and EA.hy926 cells. Our study revealed that endocardial endothelial cells are relatively resistant to apoptosis induced by these drugs. Interestingly, our study indicates that response to antitumor agents greatly differs depending on the site of origin of endothelial cells. Doxorubicin, camptothecin, and thapsigargin induce mitochondrial-dependent cell death following loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) in vascular endothelial cells, with subsequent increase in sub-G0 population. In endocardial endothelial cells, there was no MMP loss; and only cell cycle arrest either at G1 or S phases was observed when the cells were treated with doxorubicin, camptothecin, and thapsigargin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong, R. A., Iimura, T., Sumida, K. N., & Eager, R. M. (2010). Cardio-oncology/onco-cardiology. Clinical Cardiology, 33, 733–737.
Hunley, T. E., Iwasaki, S., Homma, T., & Kon, V. (1995). Nitric oxide and endothelin in pathophysiological settings. Pediatric Nephrology, 9, 235–244.
Baudin, B., Beneteau-Burnat, B., & Giboudeau, J. (1996). Cytotoxicity of amiodarone in cultured human endothelial cells. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 10, 557–560.
Brutsaert, D. L., Fransen, P., Andries, L. J., De Keulenaer, G. W., & Sys, S. U. (1998). Cardiac endothelium and myocardial function. Cardiovascular Research, 38, 281–290.
Kuruvilla, L., & Kartha, C. C. (2003). Molecular mechanisms in endothelial regulation of cardiac function. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 253, 113–123.
Tonini, T., Gabellini, C., Bagella, L., D’Andrilli, G., Masciullo, V., Romano, G., et al. (2004). pRb2/p130 decreases sensitivity to apoptosis induced by camptothecin and doxorubicin but not by taxol. Clinical Cancer Research, 10, 8085–8093.
Yamamoto, N., Watanabe, H., Kakizawa, H., Hirano, M., Kobayashi, A., & Ohno, R. (1995). A study on thapsigargin-induced calcium ion and cation influx pathways in vascular endothelial cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1266, 157–162.
Baudin, B., Bruneel, A., Bosselut, N., & Vaubourdolle, M. (2007). A protocol for isolation and culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Nature Protocols, 2, 481–485.
Andries, L. J., Kaluza, G., De Keulenaer, G. W., Mebazaa, A., Brutsaert, D. L., & Sys, S. U. (1996). Endocardial endothelial dysfunction and heart failure. Journal of Cardiac Failure, 2, S195–S202.
Kuruvilla, L., Santhosh Kumar, T. R., & Kartha, C. C. (2007). Immortalization and characterization of porcine ventricular endocardial endothelial cells. Endothelium, 14, 35–43.
Aird, W. C. (2007). Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circulation Research, 100, 158–173.
Kwok, J. C., & Richardson, D. R. (2003). Anthracyclines induce accumulation of iron in ferritin in myocardial and neoplastic cells: Inhibition of the ferritin iron mobilization pathway. Molecular Pharmacology, 63, 849–861.
Lock, R. B., & Stribinskiene, L. (1996). Dual modes of death induced by etoposide in human epithelial tumor cells allow Bcl-2 to inhibit apoptosis without affecting clonogenic survival. Cancer Research, 56, 4006–4012.
Walker, P. R., Smith, C., Youdale, T., Leblanc, J., Whitfield, J. F., & Sikorska, M. (1991). Topoisomerase II-reactive chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis in thymocytes. Cancer Research, 51, 1078–1085.
Mailloux, A., Grenet, K., Bruneel, A., Beneteau-Burnat, B., Vaubourdolle, M., & Baudin, B. (2001). Anticancer drugs induce necrosis of human endothelial cells involving both oncosis and apoptosis. European Journal of Cell Biology, 80, 442–449.
Schimmel, K. J., Richel, D. J., van den Brink, R. B., & Guchelaar, H. J. (2004). Cardiotoxicity of cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 30, 181–191.
Zunina, F., Gambetta, R., & Di Marco, A. (1975). The inhibition in vitro of DNA polymerase and RNA polymerases by daunomycin and adriamycin. Biochemical Pharmacology, 24, 309–311.
Iwamoto, Y., Hansen, I. L., Porter, T. H., & Folkers, K. (1974). Inhibition of coenzyme Q10-enzymes, succinoxidase and NADH-oxidase, by adriamycin and other quinones having antitumor activity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 58, 633–638.
Corna, G., Santambrogio, P., Minotti, G., & Cairo, G. (2004). Doxorubicin paradoxically protects cardiomyocytes against iron-mediated toxicity: Role of reactive oxygen species and ferritin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 13738–13745.
L’Ecuyer, T., Sanjeev, S., Thomas, R., Novak, R., Das, L., Campbell, W., et al. (2006). DNA damage is an early event in doxorubicin-induced cardiac myocyte death. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 291, H1273–H1280.
Pantazis, P. (1995). Preclinical studies of water-insoluble camptothecin congeners: Cytotoxicity, development of resistance, and combination treatments. Clinical Cancer Research, 1, 1235–1244.
Ryan, A. J., Squires, S., Strutt, H. L., & Johnson, R. T. (1991). Camptothecin cytotoxicity in mammalian cells is associated with the induction of persistent double strand breaks in replicating DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 19, 3295–3300.
Hsiang, Y. H., Liu, L. F., Wall, M. E., Wani, M. C., Nicholas, A. W., Manikumar, G., et al. (1989). DNA topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage and cytotoxicity of camptothecin analogues. Cancer Research, 49, 4385–4389.
O’Leary, J. J., Shapiro, R. L., Ren, C. J., Chuang, N., Cohen, H. W., & Potmesil, M. (1999). Antiangiogenic effects of camptothecin analogues 9-amino-20(S)-camptothecin, topotecan, and CPT-11 studied in the mouse cornea model. Clinical Cancer Research, 5, 181–187.
Feng, X. Q., You, Y., Xiao, J., & Zou, P. (2006). Thapsigargin-induced apoptosis of K562 cells and its mechanism. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 14, 25–30.
Crow, M. T., Mani, K., Nam, Y. J., & Kitsis, R. N. (2004). The mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circulation Research, 95, 957–970.
Sarkar, S., Chawla-Sarkar, M., Young, D., Nishiyama, K., Rayborn, M. E., Hollyfield, J. G., et al. (2004). Myocardial cell death and regeneration during progression of cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 52630–52642.
Bernecker, O. Y., Huq, F., Heist, E. K., Podesser, B. K., & Hajjar, R. J. (2003). Apoptosis in heart failure and the senescent heart. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 3, 183–190.
Umansky, S. R., & Tomei, L. D. (2003). Apoptosis in the myocardium: Much is still expected. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 7, 61–69.
deBlois, D., Orlov, S. N., & Hamet, P. (2001). Apoptosis in cardiovascular remodeling–effect of medication. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 15, 539–545.
Mercie, P., Garnier, O., Lascoste, L., Renard, M., Closse, C., Durrieu, F., et al. (2000). Homocysteine-thiolactone induces caspase-independent vascular endothelial cell death with apoptotic features. Apoptosis, 5, 403–411.
Kuruvilla, L., Nair, R. R., Umashankar, P. R., Lal, A. V., & Kartha, C. C. (2007). Endocardial endothelial cells stimulate proliferation and collagen synthesis of cardiac fibroblasts. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 47, 65–72.
Fransen, P., Hendrickx, J., Brutsaert, D. L., & Sys, S. U. (2001). Distribution and role of Na(+)/K(+) ATPase in endocardial endothelium. Cardiovascular Research, 52, 487–499.
Flens, M. J., Zaman, G. J., van der Valk, P., Izquierdo, M. A., Schroeijers, A. B., Scheffer, G. L., et al. (1996). Tissue distribution of the multidrug resistance protein. American Journal of Pathology, 148, 1237–1247.
Cordon-Cardo, C., O’Brien, J. P., Boccia, J., Casals, D., Bertino, J. R., & Melamed, M. R. (1990). Expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 38, 1277–1287.
Sugawara, I., Kataoka, I., Morishita, Y., Hamada, H., Tsuruo, T., Itoyama, S., et al. (1988). Tissue distribution of P-glycoprotein encoded by a multidrug-resistant gene as revealed by a monoclonal antibody, MRK 16. Cancer Research, 48, 1926–1929.
Acknowledgments
Sathish Kumar Maney and Ann Mary Johnson were supported with Junior Research Fellowship from Council of Scientific Industrial Research, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maney, S.K., Johnson, A.M., Sampath Kumar, A. et al. Effect of Apoptosis-Inducing Antitumor Agents on Endocardial Endothelial Cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol 11, 253–262 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-011-9119-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-011-9119-x