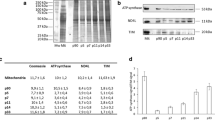
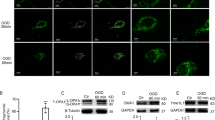
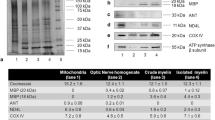
Abstract
FoF1-ATP synthase is the nanomotor responsible for most of ATP synthesis in the cell. In physiological conditions, it carries out ATP synthesis thanks to a proton gradient generated by the respiratory chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane. We previously reported that isolated myelin vesicles (IMV) contain functional FoF1-ATP synthase and respiratory chain complexes and are able to conduct an aerobic metabolism, to support the axonal energy demand. In this study, by biochemical assay, Western Blot (WB) analysis and immunofluorescence microscopy, we characterized the IMV FoF1-ATP synthase. ATP synthase activity decreased in the presence of the specific inhibitors (olygomicin, DCCD, FCCP, valynomicin/nigericin) and respiratory chain inhibitors (antimycin A, KCN), suggesting a coupling of oxygen consumption and ATP synthesis. ATPase activity was inhibited in low pH conditions. WB and microscopy analyses of both IMV and optic nerves showed that the Inhibitor of F1 (IF1), a small protein that binds the F1 moiety in low pH when of oxygen supply is impaired, is expressed in myelin sheath. Data are discussed in terms of the role of IF1 in the prevention of the reversal of ATP synthase in myelin sheath during central nervous system ischemic events. Overall, data are consistent with an energetic role of myelin sheath, and may shed light on the relationship among demyelination and axonal degeneration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyer, P. D. (2002). A research journey with ATP synthase. J Biol Chem, 277, 39045–39061.
von Ballmoos, C., Wiedenmann, A., & Dimroth, P. (2009). Essentials for ATP synthesis by F1F0 ATP synthases. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 78, 649–672.
Capaldi, R. A., Aggeler, R., Turina, P., & Wilkens, S. (1994). Coupling between catalytic sites and the proton channel in F1F0-type ATPases. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 19, 284–289.
Lebowitz, M. S., & Pedersen, P. L. (1996). Protein inhibitor of mitochondrial ATP synthase: relationship of inhibitor structure to pH-dependent regulation. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 330, 342–354.
Campanella, M., Casswell, E., Chong, S., Farah, Z., Wieckowski, M. R., Abramov, A. Y., et al. (2008). Regulation of mitochondrial structure and function by the F1Fo-ATPase inhibitor protein, IF1. Cell Metabolism, 8, 13–25.
Cabezon, E., Butler, P. J., Runswick, M. J., & Walker, J. E. (2000). Modulation of the oligomerization state of the bovine F1-ATPase inhibitor protein, IF1, by pH. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 25460–25464.
Gledhill, J. R., Montgomery, M. G., Leslie, A. G., & Walker, J. E. (2007). How the regulatory protein, IF(1), inhibits F(1)-ATPase from bovine mitochondria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 15671–15676.
Pullman, M. E., & Monroy, G. C. (1963). A naturally occurring inhibitor of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 238, 3762–3769.
Klein, G., Satre, M., Dianoux, A. C., & Vignais, P. V. (1980). Radiolabeling of natural adenosine triphosphatase inhibitor with phenyl (14C)isothiocyanate and study of its interaction with mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. Localization of inhibitor binding sites and stoichiometry of binding. Biochemistry, 19, 2919–2925.
Krull, K. W., & Schuster, S. M. (1981). Kinetic studies of beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase: interaction of the inhibitor protein and adenosine triphosphate analogues. Biochemistry, 20, 1592–1598.
Ames, A., I. I. I. (2000). CNS energy metabolism as related to function. Brain Research. Brain Research Reviews, 34, 42–68.
Veltri, K. L., Espiritu, M., & Singh, G. (1990). Distinct genomic copy number in mitochondria of different mammalian organs. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 143, 160–164.
Edgar, J. M., McCulloch, M. C., Thomson, C. E., & Griffiths, I. R. (2008). Distribution of mitochondria along small-diameter myelinated central nervous system axons. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 86, 2250–2257.
Ravera, S., Panfoli, I., Calzia, D., Aluigi, M. G., Bianchini, P., Diaspro, A., et al. (2009). Evidence for aerobic ATP synthesis in isolated myelin vesicles. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 41, 1581–1591.
Chi, S. L., & Pizzo, S. V. (2006). Cell surface F1Fo ATP synthase: a new paradigm? Annals of Medicine, 38, 429–438.
Panfoli, I., Calzia, D., Bianchini, P., Ravera, S., Diaspro, A., Candiano, G., et al. (2009). Evidence for aerobic metabolism in retinal rod outer segment disks. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 41, 2555–2565.
Haley, J. E., Samuels, F. G., & Ledeen, R. W. (1981). Study of myelin purity in relation to axonal contaminants. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 1, 175–187.
Norton, W. T., & Poduslo, S. E. (1973). Myelination in rat brain: method of myelin isolation. Journal of Neurochemistry, 21, 749–757.
Ravera, S., Calzia, D., Panfoli, I., Pepe, I. M., & Morelli, A. (2007). Simultaneous detection of molecular weight and activity of adenylate kinases after electrophoretic separation. Electrophoresis, 28, 291–300.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Bucher, T., & Pfleiderer, G. (1955). Pyruvate kinase from muscle. In S. Colowick & N.O. Kaplan (Eds.), Methods in enzymology (pp. 435–440). Academic Press: New york.
Taylor, C. M., Marta, C. B., Claycomb, R. J., Han, D. K., Rasband, M. N., Coetzee, T., et al. (2004). Proteomic mapping provides powerful insights into functional myelin biology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 4643–4648.
Vanrobaeys, F., Van Coster, R., Dhondt, G., Devreese, B., & Van Beeumen, J. (2005). Profiling of myelin proteins by 2D-gel electrophoresis and multidimensional liquid chromatography coupled to MALDI TOF-TOF mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research, 4, 2283–2293.
Werner, H. B., Kuhlmann, K., Shen, S., Uecker, M., Schardt, A., Dimova, K., et al. (2007). Proteolipid protein is required for transport of sirtuin 2 into CNS myelin. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 7717–7730.
Ishii, A., Dutta, R., Wark, G. M., Hwang, S. I., Han, D. K., Trapp, B. D., et al. (2009). Human myelin proteome and comparative analysis with mouse myelin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 14605–14610.
Jahn, O., Tenzer, S., & Werner, H. B. (2009). Myelin proteomics: molecular anatomy of an insulating sheath. Molecular Neurobiology, 40, 55–72.
Arakaki, N., Nagao, T., Niki, R., Toyofuku, A., Tanaka, H., Kuramoto, Y., et al. (2003). Possible role of cell surface H + -ATP synthase in the extracellular ATP synthesis and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Molecular Cancer Research, 1, 931–939.
Mangiullo, R., Gnoni, A., Leone, A., Gnoni, G. V., Papa, S., & Zanotti, F. (2008). Structural and functional characterization of F(o)F(1)-ATP synthase on the extracellular surface of rat hepatocytes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1777, 1326–1335.
Imamura, H., Nhat, K. P., Togawa, H., Saito, K., Iino, R., Kato-Yamada, Y., et al. (2009). Visualization of ATP levels inside single living cells with fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based genetically encoded indicators. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 15651–15656.
Green, D. W., & Grover, G. J. (2000). The IF(1) inhibitor protein of the mitochondrial F(1)F(0)-ATPase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1458, 343–355.
Van Raaij, M. T., Oortgiesen, M., Timmerman, H. H., Dobbe, C. J., & Van Loveren, H. (1996). Time-dependent differential changes of immune function in rats exposed to chronic intermittent noise. Physiology & Behavior, 60, 1527–1533.
Lippe, G., Sorgato, M. C., & Harris, D. A. (1988). The binding and release of the inhibitor protein are governed independently by ATP and membrane potential in ox-heart submitochondrial vesicles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 933, 12–21.
Lippe, G., Sorgato, M. C., & Harris, D. A. (1988). Kinetics of the release of the mitochondrial inhibitor protein. Correlation with synthesis and hydrolysis of ATP. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 933, 1–11.
Panchenko, M. V., & Vinogradov, A. D. (1985). Interaction between the mitochondrial ATP synthetase and ATPase inhibitor protein. Active/inactive slow pH-dependent transitions of the inhibitor protein. FEBS Letters, 184, 226–230.
Crompton, M., Ellinger, H., & Costi, A. (1988). Inhibition by cyclosporin A of a Ca2 + -dependent pore in heart mitochondria activated by inorganic phosphate and oxidative stress. Biochemical Journal, 255, 357–360.
Mitchell, P. (1961). Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature, 191, 144–148.
Boyer, P. D. (1997). The ATP synthase–a splendid molecular machine. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 66, 717–749.
Beutner, G., Ruck, A., Riede, B., Welte, W., & Brdiczka, D. (1996). Complexes between kinases, mitochondrial porin and adenylate translocator in rat brain resemble the permeability transition pore. FEBS Letters, 396, 189–195.
Rouslin, W. (1986). Myocardial acidosis and the mitigation of tissue ATP depletion in ischemic cardiac muscle: the role of the mitochondrial ATPase. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 194, 355–373.
Kann, O., & Kovacs, R. (2007). Mitochondria and neuronal activity. American journal of physiology. Cell physiology, 292, C641–C657.
Silver, I., & Erecinska, M. (1998). Oxygen and ion concentrations in normoxic and hypoxic brain cells. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 454, 7–16.
Aliev, G., Palacios, H. H., Walrafen, B., Lipsitt, A. E., Obrenovich, M. E., & Morales, L. (2009). Brain mitochondria as a primary target in the development of treatment strategies for Alzheimer disease. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 41, 1989–2004.
Schmidt, C., Lepsverdize, E., Chi, S. L., Das, A. M., Pizzo, S. V., Dityatev, A., et al. (2008). Amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta-peptide bind to ATP synthase and regulate its activity at the surface of neural cells. Molecular Psychiatry, 13, 953–969.
Sergeant, N., Wattez, A., Galvan-valencia, M., Ghestem, A., David, J. P., Lemoine, J., et al. (2003). Association of ATP synthase alpha-chain with neurofibrillary degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience, 117, 293–303.
Trapp, B. D., & Nave, K. A. (2008). Multiple sclerosis: an immune or neurodegenerative disorder? Annual Review of Neuroscience, 31, 247–269.
Correale, J., Meli, F., & Ysrraelit, C. (2006). Neuronal injury in multiple sclerosis. Medicina (B Aires), 66, 472–485.
Mutsaers, S. E., & Carroll, W. M. (1998). Focal accumulation of intra-axonal mitochondria in demyelination of the cat optic nerve. Acta Neuropathologica, 96, 139–143.
Dutta, R., & Trapp, B. D. (2006). Pathology and definition of multiple sclerosis. La Revue du praticien, 56, 1293–1298.
Lin, M. T., & Beal, M. F. (2006). Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature, 443, 787–795.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by a Grant from the “Compagnia di San Paolo”- Neuroscience Program, for the research project entitled: “Energetic metabolism in myelinated axon: a new trophic role of myelin sheath”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Silvia Ravera and Isabella Panfoli have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravera, S., Panfoli, I., Aluigi, M.G. et al. Characterization of Myelin Sheath FoF1-ATP Synthase and its Regulation by IF1 . Cell Biochem Biophys 59, 63–70 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-010-9112-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-010-9112-1