Abstract
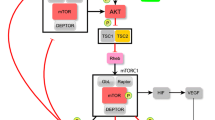
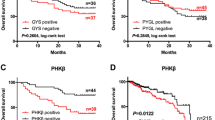
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT (PI3K/AKT) pathway plays a critical role in human cancer. We determined the expression patterns of class I PI3K catalytic subunits and evaluated their importance in the development or progression of colorectal cancer (CRC). For this purpose, expression of class I PI3K isoforms was evaluated in 82 primary CRC and paired non-cancerous mucosa samples by qRT-PCR. P-AKT-Ser473 and P-AKT-Thr308 expression were measured by western blot. We found that, compared with paired non-cancerous mucosa samples, mRNA expression of p110α and p110β in CRCs was significantly increased to 2.02-fold (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.25–3.28 fold) and 1.76-fold (95% CI 1.19–2.60 fold), respectively; while slight differences were found regarding the expression of p110δ (0.57-fold; 95% CI 0.31–1.07 fold) and p110γ (0.97-fold; 95% CI 0.50–1.88 fold). Increased p110α and p110β expression correlated with primary tumor size, regional lymph node metastases, and AJCC stage. Increased p110β expression also correlated with distant metastasis. P-AKT-Thr308 and P-AKT-Ser473 expression showed significant direct correlations with p110α and p110β mRNA expression. Besides, CRC patients with p110β mRNA overexpression had a worse disease-free survival after radical surgery compared with those with normal or decreased levels (P = 0.043). It was, therefore, concluded that the altered p110α and p110β expression might contribute to the CRC development or progression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Hao, Y., Xu, J., & Thun, M. J. (2009). Cancer statistics 2009. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 59, 225–249.
Moertel, C. G., Fleming, T. R., Macdonald, J. S., et al. (1990). Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. The New England Journal of Medicine, 322, 352–358.
Krook, J. E., Moertel, C. G., Gunderson, L. L., et al. (1991). Effective surgical adjuvant therapy for high-risk rectal carcinoma. The New England Journal of Medicine, 324, 709–715.
Hahn, W. C., & Weinberg, R. A. (2002). Rules for making human tumor cells. The New England Journal of Medicine, 347, 1593–1603.
Niedermeier, M., Hennessy, B. T., Knight, Z. A., et al. (2009). Isoform-selective phosphoinositide 3’-kinase inhibitors inhibit CXCR4 signaling and overcome stromal cell-mediated drug resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a novel therapeutic approach. Blood, 113, 5549–5557.
Bader, A. G., Kang, S., Zhao, L., & Vogt, P. K. (2005). Oncogenic PI3K deregulates transcription and translation. Nature Review Cancer, 5, 921–929.
Carracedo, A., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2008). The PTEN-PI3K pathway of feedbacks and cross-talks. Oncogene, 27, 5527–5541.
Liu, P., Cheng, H., Roberts, T. M., & Zhao, J. J. (2009). Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nature Review Drug Discovery, 8, 627–644.
Garcia-Echeverria, C., & Sellers, W. R. (2008). Drug discovery approaches targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer. Oncogene, 27, 5511–5526.
Chen, J. (2008). Is src the key to understanding metastasis and developing new treatments for colon cancer? Nature Clinical Practice Gastroenterology Hepatology, 5, 306–307.
Cantley, L. C. (2002). The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science, 296, 1655–1657.
Wymann, M. P., Zvelebil, M., & Laffargue, M. (2003). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling—which way to target? Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 24, 366–376.
Edgar, K. A., Wallin, J. J., Berry, M., et al. (2010). Isoform-specific phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors exert distinct effects in solid tumors. Cancer Research, 70, 1164–1172.
Vanhaesebroeck, B., Guillermet-Guibert, J., Graupera, M., & Bilanges, B. (2010). The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nature Review Molecular Cell Biology, 11, 329–341.
Graupera, M., Guillermet-Guibert, J., Foukas, L. C., et al. (2008). Angiogenesis selectively requires the p110alpha isoform of PI3K to control endothelial cell migration. Nature, 453, 662–666.
Guillermet-Guibert, J., Bjorklof, K., Salpekar, A., et al. (2008). The p110beta isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signals downstream of G protein-coupled receptors and is functionally redundant with p110gamma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 8292–8297.
Gilio, K., Munnix, I. C., Mangin, P., et al. (2009). Non-redundant roles of phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoforms alpha and beta in glycoprotein VI-induced platelet signaling and thrombus formation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 33750–33762.
Ghigo, A., & Hirsch, E. (2008). Isoform selective phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma and delta inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery, 2, 1–10.
Ogino, S., Nosho, K., Kirkner, G. J., et al. (2009). PIK3CA mutation is associated with poor prognosis among patients with curatively resected colon cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27, 1477–1484.
Barault, L., Veyrie, N., Jooste, V., et al. (2008). Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a population-based series of colon cancers. International Journal of Cancer, 122, 2255–2259.
Sujobert, P., Bardet, V., Cornillet-Lefebvre, P., et al. (2005). Essential role for the p110delta isoform in phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation and cell proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, 106, 1063–1066.
Hickey, F. B., & Cotter, T. G. (2006). BCR-ABL regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-p110gamma transcription and activation and is required for proliferation and drug resistance. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 2441–2450.
Mizoguchi, M., Nutt, C. L., Mohapatra, G., & Louis, D. N. (2004). Genetic alterations of phosphoinositide 3-kinase subunit genes in human glioblastomas. Brain Pathology, 14, 372–377.
Kang, S., Denley, A., Vanhaesebroeck, B., & Vogt, P. K. (2006). Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma, and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 1289–1294.
Bénistant, C., Chapuis, H., & Roche, S. (2000). A specific function for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha (p85alpha-p110alpha) in cell survival and for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase beta (p85alpha-p110beta) in de novo DNA synthesis of human colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 19, 5083–5090.
Yuan, T. L., & Cantley, L. C. (2008). PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene, 27, 5497–5510.
Martin-Berenjeno, I., & Vanhaesebroeck, B. (2009). PI3K regulatory subunits lose control in cancer. Cancer Cell, 16, 449–450.
Wee, S., Wiederschain, D., Maira, S. M., et al. (2008). PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 13057–13062.
Boller, D., Schramm, A., Doepfner, K. T., et al. (2008). Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoform p110delta impairs growth and survival in neuroblastoma cells. Clinical Cancer Research, 14, 1172–1181.
Ikenoue, T., Kanai, F., Hikiba, Y., et al. (2005). Functional analysis of PIK3CA gene mutations in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Research, 65, 4562–4567.
Sartore-Bianchi, A., Martini, M., Molinari, F., et al. (2009). PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Research, 69, 1851–1857.
Ekstrand, A. I., Jönsson, M., Lindblom, A., Borg, A., & Nilbert, M. (2010). Frequent alterations of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Familial Cancer, 9, 125–129.
Bader, A. G., Kang, S., & Vogt, P. K. (2006). Cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA are oncogenic. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 1475–1479.
Zhao, J. J., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Shin, E., Loda, M. F., & Roberts, T. M. (2005). The oncogenic properties of mutant p110alpha and p110beta phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases in human mammary epithelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 18443–18448.
Colakoglu, T., Yildirim, S., Kayaselcuk, F., et al. (2008). Clinicopathological significance of PTEN loss and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in sporadic colorectal neoplasms: Is PTEN loss predictor of local recurrence? American Journal of Surgery, 195, 719–725.
Bi, L., Okabe, I., Bernard, D. J., & Nussbaum, R. L. (2002). Early embryonic lethality in mice deficient in the p110beta catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase. Mammalian Genome, 13, 169–172.
Bi, L., Okabe, I., Bernard, D. J., Wynshaw-Boris, A., & Nussbaum, R. L. (1999). Proliferative defect and embryonic lethality in mice homozygous for a deletion in the p110alpha subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 10963–10968.
Ali, K., Bilancio, A., Thomas, M., et al. (2004). Essential role for the p110delta phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the allergic response. Nature, 431, 1007–1011.
Okkenhaug, K., Bilancio, A., Farjot, G., et al. (2002). Impaired B and T cell antigen receptor signaling in p110delta PI 3-kinase mutant mice. Science, 297, 1031–1034.
Sasaki, T., Irie-Sasaki, J., Horie, Y., et al. (2000). Colorectal carcinomas in mice lacking the catalytic subunit of PI(3)K-gamma. Nature, 406, 897–902.
Semba, S., Itoh, N., Ito, M., et al. (2002). Down-regulation of PIK3CG, a catalytic subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase, by CpG hypermethylation in human colorectal carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 8, 3824–3831.
Barbier, M., Attoub, S., Calvez, R., et al. (2001). Tumour biology. Weakening link to colorectal cancer? Nature, 413, 796.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (Grant # D2007-79), NSFC(30972561), Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Science-Research Foundation and Scientific Research Fund of Heilongjiang Provincial Education Department (Grant # 11541129) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Binbin Cui and Ji Tao have contributed equally to this work as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, B., Tao, J. & Yang, Y. Studies on the Expression Patterns of Class I PI3K Catalytic Subunits and Its Prognostic Significance in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys 62, 47–54 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9257-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-011-9257-6