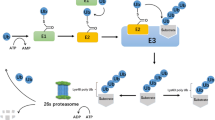
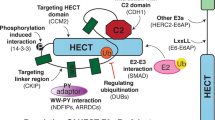
Abstract
The Siah ubiquitin ligases are members of the RING finger E3 ligases. The Siah E3s are conserved from fly to mammals. Primarily implicated in cellular stress responses, Siah ligases play a key role in hypoxia, through the regulation of HIF-1α transcription stability and activity. Concomitantly, physiological conditions associated with varying oxygen tension often highlight the importance of Siah, as seen in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Notably, recent studies also point to the role of these ligases in fundamental processes including DNA damage response, cellular organization and polarity. This review summarizes the current understanding of upstream regulators and downstream effectors of Siah.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hershko, A., & Ciechanover, A. (1998). The ubiquitin system. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 67, 425–479.
Schnell, J. D., & Hicke, L. (2003). Non-traditional functions of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-binding proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 35857–35860.
Reed, J. C., & Ely, K. R. (2002). Degrading liaisons: Siah structure revealed. Natural Structural Biology, 9, 8–10.
Genbacev, O., Zhou, Y., Ludlow, J. W., & Fisher, S. J. (1997). Regulation of human placental development by oxygen tension. Science, 277, 1669–1672.
Tang, A. H., Neufeld, T. P., Kwan, E., & Rubin, G. M. (1997). PHYL acts to down-regulate TTK88, a transcriptional repressor of neuronal cell fates, by a SINA-dependent mechanism. Cell, 90, 459–467.
Della, N. G., Senior, P. V., & Bowtell, D. D. (1993). Isolation and characterisation of murine homologues of the Drosophila seven in absentia gene (sina). Development, 117, 1333–1343.
Matsuzawa, S. I., & Reed, J. C. (2001). Siah-1, SIP, and Ebi collaborate in a novel pathway for beta-catenin degradation linked to p53 responses. Molecular Cell, 7, 915–926.
Li, S., Xu, C., & Carthew, R. W. (2002). Phyllopod acts as an adaptor protein to link the sina ubiquitin ligase to the substrate protein tramtrack. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 22, 6854–6865.
Frew, I. J., Hammond, V. E., Dickins, R. A., Quinn, J. M., Walkley, C. R., Sims, N. A., et al. (2003). Generation and analysis of Siah2 mutant mice. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 23, 9150–9161.
Liu, M., Hsu, J., Chan, C., Li, Z., & Zhou, Q. (2012). The ubiquitin ligase Siah1 controls ELL2 stability and formation of super elongation complexes to modulate gene transcription. Molecular Cell, 46, 325–334.
Grishina, I., Debus, K., Garcia-Limones, C., Schneider, C., Shresta, A., Garcia, C., et al. (2012). SIAH-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of acetyl-transferases regulate the p53 response and protein acetylation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1823, 2287–2296.
Kilroy, G., Kirk-Ballard, H., Carter, L. E., & Floyd, Z. E. (2012). The ubiquitin ligase Siah2 regulates PPARgamma activity in adipocytes. Endocrinology, 153, 1206–1218.
Zhao, H. L., Ueki, N., & Hayman, M. J. (2010). The Ski protein negatively regulates Siah2-mediated HDAC3 degradation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 399, 623–628.
Wu, H., Lin, Y., Shi, Y., Qian, W., Tian, Z., Yu, Y., et al. (2010). SIAH-1 interacts with mammalian polyhomeotic homologues HPH2 and affects its stability via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 397, 391–396.
Calzado, M. A., de la Vega, L., Moller, A., Bowtell, D. D., & Schmitz, M. L. (2009). An inducible autoregulatory loop between HIPK2 and Siah2 at the apex of the hypoxic response. Nature Cell Biology, 11, 85–91.
Winter, M., Sombroek, D., Dauth, I., Moehlenbrink, J., Scheuermann, K., Crone, J., et al. (2008). Control of HIPK2 stability by ubiquitin ligase Siah-1 and checkpoint kinases ATM and ATR. Nature Cell Biology, 10, 812–824.
Buchwald, M., Pietschmann, K., Brand, P., Gunther, A., Mahajan, NP., Heinze,l T., and Kramer OH (2012) SIAH ubiquitin ligases target the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase ACK1 for ubiquitinylation and proteasomal degradation. Oncogene. 2012.
Zhou, Y., Li, L., Liu, Q., Xing, G., Kuai, X., Sun, J., et al. (2008). E3 ubiquitin ligase SIAH1 mediates ubiquitination and degradation of TRB3. Cellular Signalling, 20, 942–948.
Yun, S., Moller, A., Chae, S. K., Hong, W. P., Bae, Y. J., Bowtell, D. D., et al. (2008). Siah proteins induce the epidermal growth factor-dependent degradation of phospholipase Cepsilon. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283, 1034–1042.
Nadeau, R. J., Toher, J. L., Kovalenko, D., & Friesel, R. (2007). Regulation of Sprouty2 stability by mammalian Seven-in-Absentia homolog 2. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 100, 151–160.
Famulski, J. K., Trivedi, N., Howell, D., Yang, Y., Tong, Y., Gilbertson, R., et al. (2010). Siah regulation of Pard3A controls neuronal cell adhesion during germinal zone exit. Science, 330, 1834–1838.
Nagano, Y., Fukushima, T., Okemoto, K., Tanaka, K., Bowtell, D. D., Ronai, Z., et al. (2011). Siah1/SIP regulates p27(kip1) stability and cell migration under metabolic stress. Cell Cycle, 10, 2592–2602.
Bhanot, M., & Smith, S. (2012). TIN2 stability is regulated by the E3 ligase Siah2. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 32, 376–384.
Sarkar, T. R., Sharan, S., Wang, J., Pawar, S. A., Cantwell, C. A., Johnson, P. F., et al. (2012). Identification of a Src tyrosine kinase/SIAH2 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway that regulates C/EBPdelta expression and contributes to transformation of breast tumor cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 32, 320–332.
Zhao, J., Wang, C., Wang, J., Yang, X., Diao, N., Li, Q., et al. (2011). E3 ubiquitin ligase Siah-1 facilitates poly-ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the hepatitis B viral X protein. FEBS Letters, 585, 2943–2950.
Wu, H., Shi, Y., Lin, Y., Qian, W., Yu, Y., & Huo, K. (2011). Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 delta inhibits the ubiquitin ligase activity of SIAH-1. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 357, 209–215.
Scortegagna, M., Subtil, T., Qi, J., Kim, H., Zhao, W., Gu, W., et al. (2011). USP13 enzyme regulates Siah2 ligase stability and activity via noncatalytic ubiquitin-binding domains. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 27333–27341.
Nagel, C. H., Albrecht, N., Milovic-Holm, K., Mariyanna, L., Keyser, B., Abel, B., et al. (2011). Herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP0 is targeted by SIAH-1 for proteasomal degradation. Journal of Virology, 85, 7644–7657.
Garrison, J. B., Correa, R. G., Gerlic, M., Yip, K. W., Krieg, A., Tamble, C. M., et al. (2011). ARTS and Siah collaborate in a pathway for XIAP degradation. Molecular Cell, 41, 107–116.
Twomey, E., Li, Y., Lei, J., Sodja, C., Ribecco-Lutkiewicz, M., Smith, B., et al. (2010). Regulation of MYPT1 stability by the E3 ubiquitin ligase SIAH2. Experimental Cell Research, 316, 68–77.
Ban, R., Matsuzaki, H., Akashi, T., Sakashita, G., Taniguchi, H., Park, S. Y., et al. (2009). Mitotic regulation of the stability of microtubule plus-end tracking protein EB3 by ubiquitin ligase SIAH-1 and Aurora mitotic kinases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 28367–28381.
Kim, H., Scimia, M. C., Wilkinson, D., Trelles, R. D., Wood, M. R., Bowtell, D., et al. (2011). Fine-tuning of Drp1/Fis1 availability by AKAP121/Siah2 regulates mitochondrial adaptation to hypoxia. Molecular Cell, 44, 532–544.
Carlucci, A., Adornetto, A., Scorziello, A., Viggiano, D., Foca, M., Cuomo, O., et al. (2008). Proteolysis of AKAP121 regulates mitochondrial activity during cellular hypoxia and brain ischaemia. EMBO Journal, 27, 1073–1084.
Szczepanowski, M., Adam-Klages, S., Kruse, M. L., Pollmann, M., Klapper, W., Parwaresch, R., et al. (2007). Regulation of repp 86 stability by human Siah2. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 362, 485–490.
Nakayama, K., Frew, I. J., Hagensen, M., Skals, M., Habelhah, H., Bhoumik, A., et al. (2004). Siah2 regulates stability of prolyl-hydroxylases, controls HIF1alpha abundance, and modulates physiological responses to hypoxia. Cell, 117, 941–952.
Yego, E. C., & Mohr, S. (2010). Siah-1 protein is necessary for high glucose-induced glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase nuclear accumulation and cell death in Muller cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010(285), 3181–3190.
Fiucci, G., Beaucourt, S., Duflaut, D., Lespagnol, A., Stumptner-Cuvelette, P., Geant, A., et al. (2004). Siah-1b is a direct transcriptional target of p53: identification of the functional p53 responsive element in the siah-1b promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A., 101, 3510–3515.
Qi, J., Nakayama, K., Gaitonde, S., Goydos, J. S., Krajewski, S., Eroshkin, A., et al. (2008). The ubiquitin ligase Siah2 regulates tumorigenesis and metastasis by HIF-dependent and -independent pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 105, 16713–16718.
Qi, J., Nakayama, K., Cardiff, R. D., Borowsky, A. D., Kaul, K., Williams, R., et al. (2010). Siah2-dependent concerted activity of HIF and FoxA2 regulates formation of neuroendocrine phenotype and neuroendocrine prostate tumors. Cancer Cell, 18, 23–38.
Chan, P., Moller, A., Liu, M. C., Sceneay, J. E., Wong, C. S., Waddell, N., et al. (2011). The expression of the ubiquitin ligase SIAH2 (seven in absentia homolog 2) is mediated through gene copy number in breast cancer and is associated with a basal-like phenotype and p53 expression. Breast Cancer Research, 13, R19.
Ahmed, A. U., Schmidt, R. L., Park, C. H., Reed, N. R., Hesse, S. E., Thomas, C. F., et al. (2008). Effect of disrupting seven-in-absentia homolog 2 function on lung cancer cell growth. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 100, 1606–1629.
Schmidt, R. L., Park, C. H., Ahmed, A. U., Gundelach, J. H., Reed, N. R., Cheng, S., et al. (2007). Inhibition of RAS-mediated transformation and tumorigenesis by targeting the downstream E3 ubiquitin ligase seven in absentia homologue. Cancer Research, 67, 11798–11810.
Brauckhoff, A., Malz, M., Tschaharganeh, D., Malek, N., Weber, A., Riener, M. O., et al. (2011). Nuclear expression of the ubiquitin ligase seven in absentia homolog (SIAH)-1 induces proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells. Journal of Hepatology, 55, 1049–1057.
Malz, M., Aulmann, A., Samarin, J., Bissinger, M., Longerich, T., Schmitt, S., et al. (2012). Nuclear accumulation of seven in absentia homologue-2 supports motility and proliferation of liver cancer cells. International Journal of Cancer, 131, 2016–2026.
Frasor, J., Danes, J. M., Funk, C. C., & Katzenellenbogen, B. S. (2005). Estrogen down-regulation of the corepressor N-CoR: mechanism and implications for estrogen derepression of N-CoR-regulated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102, 13153–13157.
Maeda, A., Yoshida, T., Kusuzaki, K., & Sakai, T. (2002). The characterization of the human Siah-1 promoter(1). FEBS Letters, 512, 223–226.
Topol, L., Jiang, X., Choi, H., Garrett-Beal, L., Carolan, P. J., & Yang, Y. (2003). Wnt-5a inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting GSK-3-independent beta-catenin degradation. Journal of Cell Biology, 162, 899–908.
Xie, W., Mei, Y., & Wu, M. (2009). E2F1 represses beta-catenin/TCF activity by direct up-regulation of Siah1. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 13, 1719–1727.
MacLeod, R. J., Hayes, M., & Pacheco, I. (2007). Wnt5a secretion stimulated by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor inhibits defective Wnt signaling in colon cancer cells. American Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 293, G403–G411.
Xu, Z., Sproul, A., Wang, W., Kukekov, N., & Greene, L. A. (2006). Siah1 interacts with the scaffold protein POSH to promote JNK activation and apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 303–312.
Khurana, A., Nakayama, K., Williams, S., Davis, R. J., Mustelin, T., & Ronai, Z. (2006). Regulation of the ring finger E3 ligase Siah2 by p38 MAPK. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 35316–35326.
Perez, M., Garcia-Limones, C., Zapico, I., Marina, A., Schmitz, M. L., Munoz, E., et al. (2012). Mutual regulation between SIAH2 and DYRK2 controls hypoxic and genotoxic signaling pathways. J Mol Cell Biol, 4, 316–330.
Shah, M., Stebbins, J. L., Dewing, A., Qi, J., Pellecchia, M., & Ronai, Z. A. (2009). Inhibition of Siah2 ubiquitin ligase by vitamin K3 (menadione) attenuates hypoxia and MAPK signaling and blocks melanoma tumorigenesis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 22, 799–808.
Le Moan, N., Houslay, D. M., Christian, F., Houslay, M. D., & Akassoglou, K. (2011). Oxygen-dependent cleavage of the p75 neurotrophin receptor triggers stabilization of HIF-1alpha. Molecular Cell, 44, 476–490.
Liao Y, Zhang M and Lonnerdal B (2012) Growth factor TGF-beta induces intestinal epithelial cell (IEC-6) differentiation: miR-146b as a regulatory component in the negative feedback loop. Genes Nutr. 2012.
Imig, J., Motsch, N., Zhu, J. Y., Barth, S., Okoniewski, M., Reineke, T., et al. (2011). microRNA profiling in Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoma. Nucleic Acids Research, 39, 1880–1893.
Pang, R. T., Liu, W. M., Leung, C. O., Ye, T. M., Kwan, P. C., Lee, K. F., et al. (2011). miR-135A regulates preimplantation embryo development through down-regulation of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Seven In Absentia Homolog 1A (SIAH1A) expression. PLoS ONE, 6, e27878.
Tofaris, G. K., Razzaq, A., Ghetti, B., Lilley, K. S., & Spillantini, M. G. (2003). Ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies is a pathological event not associated with impairment of proteasome function. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 44405–44411.
Liani, E., Eyal, A., Avraham, E., Shemer, R., Szargel, R., Berg, D., et al. (2004). Ubiquitylation of synphilin-1 and alpha-synuclein by SIAH and its presence in cellular inclusions and Lewy bodies imply a role in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101, 5500–5505.
Anderson, J. P., Walker, D. E., Goldstein, J. M., de Laat, R., Banducci, K., Caccavello, R. J., et al. (2006). Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 29739–29752.
Lee, J. T., Wheeler, T. C., Li, L., & Chin, L. S. (2008). Ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein by Siah-1 promotes alpha-synuclein aggregation and apoptotic cell death. Human Molecular Genetics, 17, 906–917.
Engelender, S., Kaminsky, Z., Guo, X., Sharp, A. H., Amaravi, R. K., Kleiderlein, J. J., et al. (1999). Synphilin-1 associates with alpha-synuclein and promotes the formation of cytosolic inclusions. Nature Genetics, 22, 110–114.
Nagano, Y., Yamashita, H., Takahashi, T., Kishida, S., Nakamura, T., Iseki, E., et al. (2003). Siah-1 facilitates ubiquitination and degradation of synphilin-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 51504–51514.
Eyal, A., Szargel, R., Avraham, E., Liani, E., Haskin, J., Rott, R., et al. (2006). Synphilin-1A: an aggregation-prone isoform of synphilin-1 that causes neuronal death and is present in aggregates from alpha-synucleinopathy patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103, 5917–5922.
Szargel, R., Rott, R., Eyal, A., Haskin, J., Shani, V., Balan, L., et al. (2009). Synphilin-1A inhibits seven in absentia homolog (SIAH) and modulates alpha-synuclein monoubiquitylation and inclusion formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284, 11706–11716.
Fukuba, H., Takahashi, T., Jin, H. G., Kohriyama, T., & Matsumoto, M. (2008). Abundance of aspargynyl-hydroxylase FIH is regulated by Siah-1 under normoxic conditions. Neuroscience Letters, 433, 209–214.
Calzado, M. A., de la Vega, L., Munoz, E., & Schmitz, M. L. (2009). Autoregulatory control of the p53 response by Siah-1L-mediated HIPK2 degradation. Biological Chemistry, 390, 1079–1083.
Merrill, R. A., Dagda, R. K., Dickey, A. S., Cribbs, J. T., Green, S. H., Usachev, Y. M., et al. (2011). Mechanism of neuroprotective mitochondrial remodeling by PKA/AKAP1. PLoS Biology, 9, e1000612.
Ong, S. B., Subrayan, S., Lim, S. Y., Yellon, D. M., Davidson, S. M., & Hausenloy, D. J. (2010). Inhibiting mitochondrial fission protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation, 121, 2012–2022.
D’Orazi, G., Cecchinelli, B., Bruno, T., Manni, I., Higashimoto, Y., Saito, S., et al. (2002). Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 phosphorylates p53 at Ser 46 and mediates apoptosis. Nature Cell Biology, 4, 11–19.
Hofmann, T. G., Moller, A., Sirma, H., Zentgraf, H., Taya, Y., Droge, W., et al. (2002). Regulation of p53 activity by its interaction with homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2. Nature Cell Biology, 4, 1–10.
Zhang, Q., Yoshimatsu, Y., Hildebrand, J., Frisch, S. M., & Goodman, R. H. (2003). Homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 promotes apoptosis by downregulating the transcriptional corepressor CtBP. Cell, 115, 177–186.
Longhese, M. P., Anbalagan, S., Martina, M., & Bonetti, D. (2012). The role of shelterin in maintaining telomere integrity. Frontiers in Bioscience, 17, 1715–1728.
Fujita, K., Horikawa, I., Mondal, A. M., Jenkins, L. M., Appella, E., Vojtesek, B., et al. (2010). Positive feedback between p53 and TRF2 during telomere-damage signalling and cellular senescence. Nature Cell Biology, 12, 1205–1212.
Karlseder, J., Smogorzewska, A., & de Lange, T. (2002). Senescence induced by altered telomere state, not telomere loss. Science, 295, 2446–2449.
Liu, D., Safari, A., O’Connor, M. S., Chan, D. W., Laegeler, A., Qin, J., et al. (2004). PTOP interacts with POT1 and regulates its localization to telomeres. Nature Cell Biology, 6, 673–680.
Wong, C. S., Sceneay, J., House, C. M., Halse, H. M., Liu, M. C., George, J., et al. (2012). Vascular normalization by loss of Siah2 results in increased chemotherapeutic efficacy. Cancer Research, 72, 1694–1704.
Moller, A., House, C. M., Wong, C. S., Scanlon, D. B., Liu, M. C., Ronai, Z., et al. (2009). Inhibition of Siah ubiquitin ligase function. Oncogene, 28, 289–296.
Liao, D., Corle, C., Seagroves, T. N., & Johnson, R. S. (2007). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is a key regulator of metastasis in a transgenic model of cancer initiation and progression. Cancer Research, 67, 563–572.
Matsuo, K., Satoh, S., Okabe, H., Nomura, A., Maeda, T., Yamaoka, Y., et al. (2003). SIAH1 inactivation correlates with tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinomas. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer, 36, 283–291.
Kim, C. J., Cho, Y. G., Park, C. H., Jeong, S. W., Nam, S. W., Kim, S. Y., et al. (2004). Inactivating mutations of the Siah-1 gene in gastric cancer. Oncogene, 23, 8591–8596.
Wen, Y. Y., Yang, Z. Q., Song, M., Li, B. L., Yao, X. H., Chen, X. L., et al. (2010). The expression of SIAH1 is downregulated and associated with Bim and apoptosis in human breast cancer tissues and cells. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 49, 440–449.
Wen, Y. Y., Yang, Z. Q., Song, M., Li, B. L., Zhu, J. J., & Wang, E. H. (2010). SIAH1 induced apoptosis by activation of the JNK pathway and inhibited invasion by inactivation of the ERK pathway in breast cancer cells. Cancer Science, 101, 73–79.
He, H. T., Fokas, E., You, A., Engenhart-Cabillic, R., & An, H. X. (2010). Siah1 proteins enhance radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer, 10, 403.
Kramer, O. H., Muller, S., Buchwald, M., Reichardt, S., & Heinzel, T. (2008). Mechanism for ubiquitylation of the leukemia fusion proteins AML1-ETO and PML-RARalpha. FASEB J., 22, 1369–1379.
Fanelli, M., Fantozzi, A., De Luca, P., Caprodossi, S., Matsuzawa, S., Lazar, M. A., et al. (2004). The coiled-coil domain is the structural determinant for mammalian homologues of Drosophila Sina-mediated degradation of promyelocytic leukemia protein and other tripartite motif proteins by the proteasome. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 5374–5379.
Bursen, A., Moritz, S., Gaussmann, A., Moritz, S., Dingermann, T., & Marschalek, R. (2004). Interaction of AF4 wild-type and AF4.MLL fusion protein with SIAH proteins: indication for t(4;11) pathobiology? Oncogene, 23, 6237–6249.
Buchwald, M., Pietschmann, K., Muller, J. P., Bohmer, F. D., Heinzel, T., & Kramer, O. H. (2010). Ubiquitin conjugase UBCH8 targets active FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 for proteasomal degradation. Leukemia, 24, 1412–1421.
Qi, J., Pellecchia, M., & Ronai, Z. A. (2010). The Siah2-HIF-FoxA2 axis in prostate cancer—new markers and therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget, 5, 379–385.
Acknowledgments
Support by NCI Grants CA099961 and CA128814 (to ZR) and CA154888 (to JQ) is gratefully acknowledged. We thank Allan Weisman and Serge Fuchs for the critical reading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jianfei Qi and Hyungsoo Kim contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, J., Kim, H., Scortegagna, M. et al. Regulators and Effectors of Siah Ubiquitin Ligases. Cell Biochem Biophys 67, 15–24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9636-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9636-2