Abstract
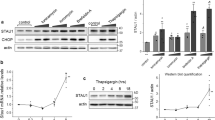
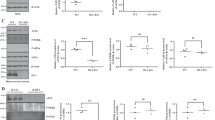
Previous studies have implicated the unfolded protein response (UPR) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We previously reported that DNA variants in the ubiquilin 1 (UBQLN1) gene increase the risk for AD. Since UBQLN1 has been shown to play a role in the UPR, we assessed the effects of overexpression and downregulation of UBQLN1 splice variants during tunicamycin-induced ER stress. In addition to previously described transcript variants, TV1 and TV2, we identified two novel transcript variants of UBQLN1 in brain: TV3 (lacking exons 2–4) and TV4 (lacking exon 4). Overexpression of TV1–3, but not TV4 significantly decreased the mRNA induction of UPR-inducible genes, C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), BiP/GRP78, and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) during the UPR. Stable overexpression of TV1–3, but not TV4, also significantly decreased the induction of CHOP protein and increased cell viability during the UPR. In contrast, downregulation of UBQLN1 did not affect CHOP mRNA induction, but instead increased PDI mRNA levels. These findings suggest that overexpression UBQLN1 transcript variants TV1–3, but not TV4, exert a protective effect during the UPR by attenuating CHOP induction and potentially increasing cell viability.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedford, F. K., Kittler, J. T., Muller, E., Thomas, P., Uren, J. M., Merlo, D., et al. (2001). GABA(A) receptor cell surface number and subunit stability are regulated by the ubiquitin-like protein Plic-1. Nature Neuroscience, 4, 908–916. doi:10.1038/nn0901-908.
Bertram, L., Hiltunen, M., Parkinson, M., Ingelsson, M., Lange, C., Ramasamy, K., et al. (2005). Family-based association between Alzheimer’s disease and variants in UBQLN1. The New England Journal of Medicine, 352, 884–894. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa042765.
Chen, G., Fan, Z., Wang, X., Ma, C., Bower, K. A., Shi, X., et al. (2007). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor suppresses tunicamycin-induced upregulation of CHOP in neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 85, 1674–1684. doi:10.1002/jnr.21292.
Corder, E. H., Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D. E., Gaskell, P. C., Small, G. W., et al. (1993). Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science, 261, 921–923. doi:10.1126/science.8346443.
Dorner, A. J., Wasley, L. C., Raney, P., Haugejorden, S., Green, M., & Kaufman, R. J. (1990). The stress response in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Regulation of ERp72 and protein disulfide isomerase expression and secretion. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 265, 22029–22034.
Funakoshi, M., Geley, S., Hunt, T., Nishimoto, T., & Kobayashi, H. (1999). Identification of XDRP1; a Xenopus protein related to yeast Dsk2p binds to the N-terminus of cyclin A and inhibits its degradation. The EMBO Journal, 18, 5009–5018. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.18.5009.
Gao, L., Tu, H., Shi, S. T., Lee, K. J., Asanaka, M., Hwang, S. B., et al. (2003). Interaction with a ubiquitin-like protein enhances the ubiquitination and degradation of hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Journal of Virology, 77, 4149–4159. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.7.4149-4159.2003.
Goate, A., Chartier-Harlin, M. C., Mullan, M., Brown, J., Crawford, F., Fidani, L., et al. (1991). Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature, 349, 704–706. doi:10.1038/349704a0.
Hansen, M. B., Nielsen, S. E., & Berg, K. (1989). Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell killing. Journal of Immunological Methods, 119, 203–210. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(89)90397-9.
Heir, R., Ablasou, C., Dumontier, E., Elliott, M., Fagotto-Kaufmann, C., & Bedford, F. K. (2006). The UBL domain of PLIC-1 regulates aggresome formation. EMBO Reports, 7, 1252–1258. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400823.
Hiltunen, M., Lu, A., Thomas, A. V., Romano, D. M., Kim, M., Jones, P. B., et al. (2006). Ubiquilin 1 modulates amyloid precursor protein trafficking and Abeta secretion. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 32240–32253. doi:10.1074/jbc.M603106200.
Ingelsson, M., Fukumoto, H., Newell, K. L., Growdon, J. H., Hedley-Whyte, E. T., Frosch, M. P., et al. (2004). Early Abeta accumulation and progressive synaptic loss, gliosis, and tangle formation in AD brain. Neurology, 62, 925–931.
Iwatsubo, T. (2004). The gamma-secretase complex: machinery for intramembrane proteolysis. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 14, 379–383. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2004.05.010.
Kamboh, M. I., Minster, R. L., Feingold, E., & DeKosky, S. T. (2006). Genetic association of ubiquilin with Alzheimer’s disease and related quantitative measures. Molecular Psychiatry, 11, 273–279. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001775.
Katayama, T., Imaizumi, K., Sato, N., Miyoshi, K., Kudo, T., Hitomi, J., et al. (1999). Presenilin-1 mutations downregulate the signalling pathway of the unfolded-protein response. Nature Cell Biology, 1, 479–485. doi:10.1038/70265.
Ko, H. S., Uehara, T., & Nomura, Y. (2002). Role of ubiquilin associated with protein-disulfide isomerase in the endoplasmic reticulum in stress-induced apoptotic cell death. The Journal of Cell Biology, 277, 35386–35392.
Ko, H. S., Uehara, T., Tsuruma, K., & Nomura, Y. (2004). Ubiquilin interacts with ubiquitylated proteins and proteasome through its ubiquitin-associated and ubiquitin-like domains. FEBS Letters, 566, 110–114. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.031.
Kogel, D., Schomburg, R., Schurmann, T., Reimertz, C., Konig, H. G., Poppe, M., et al. (2003). The amyloid precursor protein protects PC12 cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Journal of Neurochemistry, 87, 248–256. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02000.x.
Levy-Lahad, E., Wasco, W., Poorkaj, P., Romano, D. M., Oshima, J., Pettingell, W. H., et al. (1995). Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus. Science, 269, 973–977. doi:10.1126/science.7638622.
Li, J., & Holbrook, N. J. (2004). Elevated gadd153/chop expression and enhanced c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase activation sensitizes aged cells to ER stress. Experimental Gerontology, 39, 735–744. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2004.02.008.
Mah, A. L., Perry, G., Smith, M. A., & Monteiro, M. J. (2000). Identification of ubiquilin, a novel presenilin interactor that increases presenilin protein accumulation. The Journal of Cell Biology, 151, 847–862. doi:10.1083/jcb.151.4.847.
Massey, L. K., Mah, A. L., Ford, D. L., Miller, J., Liang, J., Doong, H., et al. (2004). Overexpression of ubiquilin decreases ubiquitination and degradation of presenilin proteins. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 6, 79–92.
Murer, M. G., Yan, Q., & Raisman-Vozari, R. (2001). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the control human brain, and in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Progress in Neurobiology, 63, 71–124. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(00)00014-9.
Rogaev, E. I., Sherrington, R., Rogaeva, E. A., Levesque, G., Ikeda, M., Liang, Y., et al. (1995). Familial Alzheimer’s disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene. Nature, 376, 775–778. doi:10.1038/376775a0.
Sato, N., Urano, F., Yoon Leem, J., Kim, S. H., Li, M., Donoviel, D., et al. (2000). Upregulation of BiP and CHOP by the unfolded-protein response is independent of presenilin expression. Nature Cell Biology, 2, 863–870. doi:10.1038/35046500.
Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D., George-Hyslop, P. H., Pericak-Vance, M. A., Joo, S. H., et al. (1993). Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 43, 1467–1472.
Sherrington, R., Rogaev, E. I., Liang, Y., Rogaeva, E. A., Levesque, G., Ikeda, M., et al. (1995). Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature, 375, 754–760. doi:10.1038/375754a0.
Thomas, A. V., Herl, L., Spoelgen, R., Hiltunen, M., Jones, P. B., Tanzi, R. E., et al. (2006). Interaction between presenilin 1 and ubiquilin 1 as detected by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy and a high-throughput fluorescent plate reader. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 26400–26407. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601085200.
Uehara, T., Nakamura, T., Yao, D., Shi, Z. Q., Gu, Z., Ma, Y., et al. (2006). S-nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration. Nature, 441, 513–517. doi:10.1038/nature04782.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Extendicare Foundation, EVO grant 5772708 from Kuopio University Hospital, Finland, and the Finnish Academy (Mikko Hiltunen). We thank Petra Mäkinen for her excellent technical help.
Disclosure Statement
The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
A. Lu and M. Hiltunen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, A., Hiltunen, M., Romano, D.M. et al. Effects of Ubiquilin 1 on the Unfolded Protein Response. J Mol Neurosci 38, 19–30 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9155-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9155-6