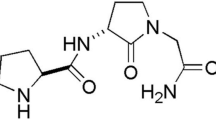
Abstract
Chronic administration of antipsychotics has been associated with dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) upregulation and tardive dyskinesia. We have previously shown that haloperidol, a first-generation antipsychotic (FGA), exerted an increase in D2R expression and oxidative stress and that (±)-α-lipoic acid reversed its effect. Previous studies have implicated the Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) signaling pathway in antipsychotic action. These findings led us to examine whether the Akt/GSK-3β pathway was involved in D2R upregulation and oxidative stress elicited by antipsychotics and, in (±)-α-lipoic acid-induced reversal of these phenomena, in SH-SY5Y cells. Antipsychotics increased phosphorylation of Akt and GSK-3β, and additive effects were observed with (±)-α-lipoic acid. GSK-3β inhibitors reversed haloperidol-induced overexpression of D2R mRNA levels but did not affect haloperidol-induced oxidative stress. Sustained antipsychotic treatment increased β-arrestin-2 and D2R receptor interaction. Regarding Akt/GSK-3β downstream targets, antipsychotics increased β-catenin levels, whereas (±)-α-lipoic acid induced an elevation of mTOR activation. These results suggest (1) that the effect of antipsychotics on the Akt/GSK-3β pathway in SH-SY5Y cells is reminiscent of their in vivo action, (2) that (±)-α-lipoic acid partially synergizes with antipsychotic drugs (APDs) on the same pathway, and (3) that the Akt/GSK-3β signaling cascade is not involved in the preventive effect of (±)-α-lipoic acid on antipsychotics-induced D2R upregulation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abilio VC, Araujo CC, Bergamo M, Calvente PR, D’Almeida V, Ribeiro RA, Frussa-Filho R (2003) Vitamin E attenuates reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia and striatal oxidized glutathione/reduced glutathione ratio (GSSG/GSH) enhancement in rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:109–114
Alimohamad H, Rajakumar N, Seah YH, Rushlow W (2005a) Antipsychotics alter the protein expression levels of beta-catenin and GSK-3 in the rat medial prefrontal cortex and striatum. Biol Psychiatry 57:533–542
Alimohamad H, Sutton L, Mouyal J, Rajakumar N, Rushlow WJ (2005b) The effects of antipsychotics on beta-catenin, glycogen synthase kinase-3 and dishevelled in the ventral midbrain of rats. J Neurochem 95:513–525
Allagui MS, Nciri R, Rouhaud MF, Murat JC, El FA, Croute F, Vincent C (2009) Long-term exposure to low lithium concentrations stimulates proliferation, modifies stress protein expression pattern and enhances resistance to oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res 34:453–462
Beasley C, Cotter D, Khan N, Pollard C, Sheppard P, Varndell I, Lovestone S, Anderton B, Everall I (2001) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta immunoreactivity is reduced in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 302:117–120
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Yao WD, Kockeritz L, Woodgett JR, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2004) Lithium antagonizes dopamine-dependent behaviors mediated by an AKT/glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5099–5104
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Marion S, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2005) An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell 122:261–273
Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2006) Paradoxical striatal cellular signaling responses to psychostimulants in hyperactive mice. J Biol Chem 281:32072–32080
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2007) The Akt-GSK-3 signaling cascade in the actions of dopamine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:166–172
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2009) Akt/GSK3 signaling in the action of psychotropic drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:327–347
Beom S, Cheong D, Torres G, Caron MG, Kim KM (2004) Comparative studies of molecular mechanisms of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors for the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J Biol Chem 279:28304–28314
Bhat R, Xue Y, Berg S, Hellberg S, Ormo M, Nilsson Y, Radesater AC, Jerning E, Markgren PO, Borgegard T, Nylof M, Gimenez-Cassina A, Hernandez F, Lucas JJ, Diaz-Nido J, Avila J (2003) Structural insights and biological effects of glycogen synthase kinase 3-specific inhibitor AR-A014418. J Biol Chem 278:45937–45945
Bishnoi M, Chopra K, Kulkarni SK (2008) Protective effect of Curcumin, the active principle of turmeric (Curcuma longa) in haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and associated behavioural, biochemical and neurochemical changes in rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:511–522
Bundey RA, Nahorski SR (2001) Homologous and heterologous uncoupling of muscarinic M(3) and alpha(1B) adrenoceptors to Galpha(q/11) in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Br J Pharmacol 134:257–264
Burger ME, Fachinetto R, Zeni G, Rocha JB (2005) Ebselen attenuates haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and oxidative stress in rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:608–615
Chen Z, Dupre DJ, Le Gouill C, Rola-Pleszczynski M, Stankova J (2002) Agonist-induced internalization of the platelet-activating factor receptor is dependent on arrestins but independent of G-protein activation. Role of the C terminus and the (D/N)PXXY motif. J Biol Chem 277:7356–7362
Cobos EJ, del Pozo E, Baeyens JM (2007) Irreversible blockade of sigma-1 receptors by haloperidol and its metabolites in guinea pig brain and SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 102:812–825
Correll CU, Schenk EM (2008) Tardive dyskinesia and new antipsychotics. Curr Opin Psychiatry 21:151–156
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378:785–789
Cui J, Shao L, Young LT, Wang JF (2007) Role of glutathione in neuroprotective effects of mood stabilizing drugs lithium and valproate. Neuroscience 144:1447–1453
Dakhale G, Khanzode S, Saoji A, Khobragade L, Turankar A (2004) Oxidative damage and schizophrenia: the potential benefit by atypical antipsychotics. Neuropsychobiology 49:205–209
Deslauriers J, Lefrancois M, Larouche A, Sarret P, Grignon S (2011) Antipsychotic-induced DRD2 upregulation and its prevention by alpha-lipoic acid in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Synapse 65:321–331
Doble BW, Woodgett JR (2003) GSK-3: tricks of the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci 116:1175–1186
Emamian ES (2012) AKT/GSK3 signaling pathway and schizophrenia. Front Mol Neurosci 5:33
Emamian ES, Hall D, Birnbaum MJ, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA (2004) Convergent evidence for impaired AKT1-GSK3beta signaling in schizophrenia. Nat Genet 36:131–137
Gainetdinov RR, Jones SR, Caron MG (1999) Functional hyperdopaminergia in dopamine transporter knock-out mice. Biol Psychiatry 46:303–311
Giros B, Jaber M, Jones SR, Wightman RM, Caron MG (1996) Hyperlocomotion and indifference to cocaine and amphetamine in mice lacking the dopamine transporter. Nature 379:606–612
Grimes CA, Jope RS (2001) The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol 65:391–426
Harrison PJ (1999) The neuropathological effects of antipsychotic drugs. Schizophr Res 40:87–99
Iizuka Y, Sei Y, Weinberger DR, Straub RE (2007) Evidence that the BLOC-1 protein dysbindin modulates dopamine D2 receptor internalization and signaling but not D1 internalization. J Neurosci 27:12390–12395
Jenner P, Rupniak NM, Marsden CD (1985) Differential alteration of striatal D-1 and D-2 receptors induced by the long-term administration of haloperidol, sulpiride or clozapine to rats. Psychopharmacology Suppl 2:174–181
Jeste DV, Lacro JP, Bailey A, Rockwell E, Harris MJ, Caligiuri MP (1999) Lower incidence of tardive dyskinesia with risperidone compared with haloperidol in older patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 47:716–719
Jia Z, Hallur S, Zhu H, Li Y, Misra HP (2008) Potent upregulation of glutathione and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 by alpha-lipoic acid in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: protection against neurotoxicant-elicited cytotoxicity. Neurochem Res 33:790–800
Kapur S, Langlois X, Vinken P, Megens AA, De Coster R, Andrews JS (2002) The differential effects of atypical antipsychotics on prolactin elevation are explained by their differential blood–brain disposition: a pharmacological analysis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:1129–1134
Kihara T, Shimohama S, Sawada H, Honda K, Nakamizo T, Kanki R, Yamashita H, Akaike A (2002) Protective effect of dopamine D2 agonists in cortical neurons via the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase cascade. J Neurosci Res 70:274–282
Kim E, Park DW, Choi SH, Kim JJ, Cho HS (2008) A preliminary investigation of alpha-lipoic acid treatment of antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain in patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28:138–146
Kozlovsky N, Belmaker RH, Agam G (2000) Low GSK-3beta immunoreactivity in postmortem frontal cortex of schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 157:831–833
Kozlovsky N, Belmaker RH, Agam G (2002) GSK-3 and the neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 12:13–25
Kropp S, Kern V, Lange K, Degner D, Hajak G, Kornhuber J, Ruther E, Emrich HM, Schneider U, Bleich S (2005) Oxidative stress during treatment with first- and second-generation antipsychotics. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 17:227–231
Kruck S, Bedke J, Hennenlotter J, Ohneseit PA, Kuehs U, Senger E, Sievert KD, Stenzl A (2010) Activation of mTOR in renal cell carcinoma is due to increased phosphorylation rather than protein overexpression. Oncol Rep 23:159–163
Kulkarni SK, Naidu PS (2001) Animal models of tardive dyskinesia—a review. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 45:148–160
Laruelle M, Jaskiw GE, Lipska BK, Kolachana B, Casanova MF, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR (1992) D1 and D2 receptor modulation in rat striatum and nucleus accumbens after subchronic and chronic haloperidol treatment. Brain Res 575:47–56
Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK (2005) Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science 308:512–517
Li XM, Xu H (2007) Evidence for neuroprotective effects of antipsychotic drugs: implications for the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. Int Rev Neurobiol 77:107–142
Lieberman JA (2004) Dopamine partial agonists: a new class of antipsychotic. CNS Drugs 18:251–267
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Bracha HS, Moir M, Jeste DV (1990) Increased indices of free radical activity in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tardive dyskinesia. Biol Psychiatry 28:535–539
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Niculescu AB (2003) Oxidative mechanisms and tardive dyskinesia. CNS Drugs 17:47–62
Mailman RB, Murthy V (2010) Third generation antipsychotic drugs: partial agonism or receptor functional selectivity? Curr Pharm Des 16:488–501
Marchese G, Bartholini F, Ruiu S, Casti P, Saba P, Gessa G, Pani L (2002) Effect of the amisulpride isomers on rat catalepsy. Eur J Pharmacol 444:69–74
Masri B, Salahpour A, Didriksen M, Ghisi V, Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2008) Antagonism of dopamine D2 receptor/beta-arrestin 2 interaction is a common property of clinically effective antipsychotics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13656–13661
Meltzer HY (1995) The role of serotonin in schizophrenia and the place of serotonin–dopamine antagonist antipsychotics. J Clin Psychopharmacol 15:2S–3S
Mi R, Ma J, Zhang D, Li L, Zhang H (2009) Efficacy of combined inhibition of mTOR and ERK/MAPK pathways in treating a tuberous sclerosis complex cell model. J Genet Genomics 36:355–361
Morgenstern H, Glazer WM (1993) Identifying risk factors for tardive dyskinesia among long-term outpatients maintained with neuroleptic medications. Results of the Yale Tardive Dyskinesia Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:723–733
Muller MJ, Regenbogen B, Hartter S, Eich FX, Hiemke C (2007) Therapeutic drug monitoring for optimizing amisulpride therapy in patients with schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 41:673–679
Murer MG, Moratalla R (2011) Striatal signaling in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: common mechanisms with drug abuse and long term memory involving D1 dopamine receptor stimulation. Front Neuroanat 5:51
Nadri C, Lipska BK, Kozlovsky N, Weinberger DR, Belmaker RH, Agam G (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta levels and activity in a neurodevelopmental rat model of schizophrenia. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 141:33–37
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2003) Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, attenuates haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia. Neuropharmacology 44:1100–1106
Nair VD, Sealfon SC (2003) Agonist-specific transactivation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway mediated by the dopamine D2 receptor. J Biol Chem 278:47053–47061
Nave BT, Ouwens M, Withers DJ, Alessi DR, Shepherd PR (1999) Mammalian target of rapamycin is a direct target for protein kinase B: identification of a convergence point for opposing effects of insulin and amino-acid deficiency on protein translation. Biochem J 344(Pt 2):427–431
Nciri R, Desmoulin F, Allagui MS, Murat JC, Feki AE, Vincent C, Croute F (2012) Neuroprotective effects of chronic exposure of SH-SY5Y to low lithium concentration involve glycolysis stimulation, extracellular pyruvate accumulation and resistance to oxidative stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 1–12
Packer L, Tritschler HJ (1996) Alpha-lipoic acid: the metabolic antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med 20:625–626
Pal A, Fontanilla D, Gopalakrishnan A, Chae YK, Markley JL, Ruoho AE (2012) The sigma-1 receptor protects against cellular oxidative stress and activates antioxidant response elements. Eur J Pharmacol 682:12–20
Pan T, Xie W, Jankovic J, Le W (2005) Biological effects of pramipexole on dopaminergic neuron-associated genes: relevance to neuroprotection. Neurosci Lett 377:106–109
Paulson GW (2005) Historical comments on tardive dyskinesia: a neurologist’s perspective. J Clin Psychiatry 66:260–264
Peet M, Laugharne J, Rangarajan N, Reynolds GP (1993) Tardive dyskinesia, lipid peroxidation, and sustained amelioration with vitamin E treatment. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 8:151–153
Pillai A, Parikh V, Terry AV Jr, Mahadik SP (2007) Long-term antipsychotic treatments and crossover studies in rats: differential effects of typical and atypical agents on the expression of antioxidant enzymes and membrane lipid peroxidation in rat brain. J Psychiatr Res 41:372–386
Presgraves SP, Ahmed T, Borwege S, Joyce JN (2004) Terminally differentiated SH-SY5Y cells provide a model system for studying neuroprotective effects of dopamine agonists. Neurotox Res 5:579–598
Richelson E (1999) Receptor pharmacology of neuroleptics: relation to clinical effects. J Clin Psychiatry 60(Suppl 10):5–14
Schoemaker H, Claustre Y, Fage D, Rouquier L, Chergui K, Curet O, Oblin A, Gonon F, Carter C, Benavides J, Scatton B (1997) Neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:83–97
Schroder J, Silvestri S, Bubeck B, Karr M, Demisch S, Scherrer S, Geider FJ, Sauer H (1998) D2 dopamine receptor up-regulation, treatment response, neurological soft signs, and extrapyramidal side effects in schizophrenia: a follow-up study with 123I-iodobenzamide single photon emission computed tomography in the drug-naive state and after neuroleptic treatment. Biol Psychiatry 43:660–665
Seeman P, Corbett R, Van Tol HH (1997) Atypical neuroleptics have low affinity for dopamine D2 receptors or are selective for D4 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 16:93–110, discussion 111-35
Shamir E, Barak Y, Shalman I, Laudon M, Zisapel N, Tarrasch R, Elizur A, Weizman R (2001) Melatonin treatment for tardive dyskinesia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:1049–1052
Shaul U, Ben-Shachar D, Karry R, Klein E (2003) Modulation of frequency and duration of repetitive magnetic stimulation affects catecholamine levels and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in human neuroblastoma cells: implication for the antidepressant effect of rTMS. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 6:233–241
Silvestri S, Seeman MV, Negrete JC, Houle S, Shammi CM, Remington GJ, Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Wilson AA, Christensen BK, Seeman P (2000) Increased dopamine D2 receptor binding after long-term treatment with antipsychotics in humans: a clinical PET study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:174–180
Soares KV, McGrath JJ (1999) The treatment of tardive dyskinesia—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 39:1–16, discussion 17-8
Sternberg DE, Bowers MB Jr, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1983) Lithium prevents adaptation of brain dopamine systems to haloperidol in schizophrenic patients. Psychiatry Res 10:79–86
Thaakur S, Himabindhu G (2009) Effect of alpha lipoic acid on the tardive dyskinesia and oxidative stress induced by haloperidol in rats. J Neural Transm 116:807–814
Tsai G, Goff DC, Chang RW, Flood J, Baer L, Coyle JT (1998) Markers of glutamatergic neurotransmission and oxidative stress associated with tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 155:1207–1213
Vernaleken I, Siessmeier T, Buchholz HG, Hartter S, Hiemke C, Stoeter P, Rosch F, Bartenstein P, Grunder G (2004) High striatal occupancy of D2-like dopamine receptors by amisulpride in the brain of patients with schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7:421–430
Wang Y, Li X, Guo Y, Chan L, Guan X (2010) Alpha-lipoic acid increases energy expenditure by enhancing adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha signaling in the skeletal muscle of aged mice. Metabolism 59:967–976
Zhang L, Yu J, Pan H, Hu P, Hao Y, Cai W, Zhu H, Yu AD, Xie X, Ma D, Yuan J (2007a) Small molecule regulators of autophagy identified by an image-based high-throughput screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19023–19028
Zhang WJ, Wei H, Hagen T, Frei B (2007b) Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:4077–4082
Zhao Z, Robinson RG, Barnett SF, Defeo-Jones D, Jones RE, Hartman GD, Huber HE, Duggan ME, Lindsley CW (2008) Development of potent, allosteric dual Akt1 and Akt2 inhibitors with improved physical properties and cell activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:49–53
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Novartis Pharma Canada to the Department of Psychiatry, Université de Sherbrooke and by the Centre des Neurosciences de Sherbrooke. Philippe Sarret, PhD is a CIHR investigator. Philippe Sarret, PhD and Sylvain Grignon, MD, PhD are members of the FRSQ-funded Centre de Recherche Clinique Étienne Lebel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deslauriers, J., Desmarais, C., Sarret, P. et al. α-Lipoic Acid Interaction with Dopamine D2 Receptor-Dependent Activation of the Akt/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway Induced by Antipsychotics: Potential Relevance for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. J Mol Neurosci 50, 134–145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9884-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9884-4