Abstract
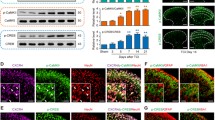
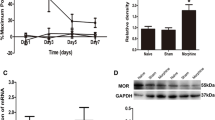
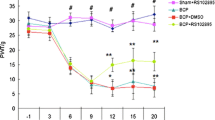
Morphine is a potent agonist of μ-opioid receptor and is widely used to relieve severe pain, including cancer pain. Some chemokines, for example, CX3CL1 and CCL2, participate in the regulation of opioid santinociception. In our previous study, we found overexpression of chemokine CXCL10/CXCR3 in spinal cord participated in the development of cancer-induced bone pain, so we supposed that CXCL10 may have influence in morphine analgesia in cancer pain relief. In this study, we found that a single dose of morphine could transiently increase the expression of CXCL10 in spinal cord. Blocking the function of CXCL10 enhanced morphine antinociception in cancer-induced bone pain rats. However, overexpression of CXCL10 induced acute algesia and decreased the analgesic effect of morphine in normal mice. The algesic effect of CXCL10 was blocked by inhibition of CXCR3 and Gi protein. These results suggested that CXCL10 in spinal cord serves as a novel negative regulator of morphine analgesia and provided evidence that activation of CXCL10/CXCR3 in spinal cord may attenuate antinociceptive potency of morphine in cancer pain relief.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akekawatchai C, Holland JD, Kochetkova M, Wallace JC, McColl SR (2005) Transactivation of CXCR4 by the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 280:39701–39708
Belkouch M, Dansereau MA, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, Van Steenwinckel J, Beaudet N, Chraibi A, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Sarret P (2011) The chemokine CCL2 increases Nav1.8 sodium channel activity in primary sensory neurons through a Gbetagamma-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci 31:18381–18390
Bovill JG (1997) Mechanisms of actions of opioids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Anaesthesiol Suppl 15:9–15
Bu H, Shu B, Gao F, Liu C, Guan X, Ke C, Cao F, Hinton AO, Jr., Xiang H, Yang H, Tian X, Tian Y (2013) Spinal IFN-gamma-induced protein-10 (CXCL10) mediates metastatic breast cancer-induced bone pain by activation of microglia in rat models. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2807-4
Cao F, Gao F, Xu AJ, Chen ZJ, Chen SS, Yang H, Yu HH, Mei W, Liu XJ, Xiao XP, Yang SB, Tian XB, Wang XR, Tian YK (2010) Regulation of spinal neuroimmune responses by prolonged morphine treatment in a rat model of cancer induced bone pain. Brain Res 1326:162–173
Chen X, Geller EB, Rogers TJ, Adler MW (2007) The chemokine CX3CL1/fractalkine interferes with the antinociceptive effect induced by opioid agonists in the periaqueductal grey of rats. Brain Res 1153:52–57
Dauvergne C, Molet J, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, Mauborgne A, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Boucher Y, Pohl M (2013) Implication of the chemokine CCL2 in trigeminal nociception and traumatic neuropathic orofacial pain. Eur J Pain. doi:10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00377.x
Davis RL, Buck DJ, Saffarian N, Stevens CW (2007) The opioid antagonist, beta-funaltrexamine, inhibits chemokine expression in human astroglial cells. J Neuroimmunol 186:141–149
Harris TH, Banigan EJ, Christian DA, Konradt C, Tait Wojno ED, Norose K, Wilson EH, John B, Weninger W, Luster AD, Liu AJ, Hunter CA (2012) Generalized Levy walks and the role of chemokines in migration of effector CD8+ T cells. Nature 486:545–548
Hidalgo A, Sanz-Rodriguez F, Rodriguez-Fernandez JL, Albella B, Blaya C, Wright N, Cabanas C, Prosper F, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Teixido J (2001) Chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha modulates VLA-4 integrin-dependent adhesion to fibronectin and VCAM-1 on bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp Hematol 29:345–355
Hu JH, Yang JP, Liu L, Li CF, Wang LN, Ji FH, Cheng H (2012) Involvement of CX3CR1 in bone cancer pain through the activation of microglia p38 MAPK pathway in the spinal cord. Brain Res 1465:1–9
Hylden JL, Wilcox GL (1980) Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol 67:313–316
Jackson KJ, Damaj MI (2013) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV mediates acute nicotine-induced antinociception in acute thermal pain tests. Behav Pharmacol 24:689–692
Ke C, Li C, Huang X, Cao F, Shi D, He W, Bu H, Gao F, Cai T, Hinton AO Jr, Tian Y (2013) Protocadherin20 promotes excitatory synaptogenesis in dorsal horn and contributes to bone cancer pain. Neuropharmacology 75C:181–190
Korniejewska A, McKnight AJ, Johnson Z, Watson ML, Ward SG (2011) Expression and agonist responsiveness of CXCR3 variants in human T lymphocytes. Immunology 132:503–515
Liu X, Bu H, Liu C, Gao F, Yang H, Tian X, Xu A, Chen Z, Cao F, Tian Y (2012) Inhibition of glial activation in rostral ventromedial medulla attenuates mechanical allodynia in a rat model of cancer-induced bone pain. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 32:291–298
Loram LC, Grace PM, Strand KA, Taylor FR, Ellis A, Berkelhammer D, Bowlin M, Skarda B, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2012) Prior exposure to repeated morphine potentiates mechanical allodynia induced by peripheral inflammation and neuropathy. Brain Behav Immun 26:1256–1264
Mao-Ying QL, Wang XW, Yang CJ, Li X, Mi WL, Wu GC, Wang YQ (2012) Robust spinal neuroinflammation mediates mechanical allodynia in Walker 256 induced bone cancer rats. Mol Brain 5:16
Nguyen KD, Vanichsarn C, Fohner A, Nadeau KC (2009) Selective deregulation in chemokine signaling pathways of CD4 + CD25(hi)CD127(lo)/(−) regulatory T cells in human allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(933–9):e10
Petreaca ML, Do D, Dhall S, McLelland D, Serafino A, Lyubovitsky J, Schiller N, Martins-Green MM (2012) Deletion of a tumor necrosis superfamily gene in mice leads to impaired healing that mimics chronic wounds in humans. Wound Repair Regen 20:353–366
Qin X, Wan Y, Wang X (2005) CCL2 and CXCL1 trigger calcitonin gene-related peptide release by exciting primary nociceptive neurons. J Neurosci Res 82:51–62
Rivat C, Sebaihi S, Steenwinckel JV, Fouquet S, Kitabgi P, Pohl M, Parsadaniantz SM, Goazigo AR (2013) Src family kinases involved in CXCL12-induced loss of acute morphine analgesia. Brain Behav Immun. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2013.11.010
Sanchez-Sanchez N, Riol-Blanco L, de la Rosa G, Puig-Kroger A, Garcia-Bordas J, Martin D, Longo N, Cuadrado A, Cabanas C, Corbi AL, Sanchez-Mateos P, Rodriguez-Fernandez JL (2004) Chemokine receptor CCR7 induces intracellular signaling that inhibits apoptosis of mature dendritic cells. Blood 104:619–625
Sano R, Tessitore A, Ingrassia A, d'Azzo A (2005) Chemokine-induced recruitment of genetically modified bone marrow cells into the CNS of GM1-gangliosidosis mice corrects neuronal pathology. Blood 106:2259–2268
Schwarz JM, Smith SH, Bilbo SD (2013) FACS analysis of neuronal–glial interactions in the nucleus accumbens following morphine administration. Psychopharmacology (Berl). doi:10.1007/s00213-013-3180-z
Smit MJ, Verdijk P, van der Raaij-Helmer EM, Navis M, Hensbergen PJ, Leurs R, Tensen CP (2003) CXCR3-mediated chemotaxis of human T cells is regulated by a Gi- and phospholipase C-dependent pathway and not via activation of MEK/p44/p42 MAPK nor Akt/PI-3 kinase. Blood 102:1959–1965
Suzuki M, Narita M, Hasegawa M, Furuta S, Kawamata T, Ashikawa M, Miyano K, Yanagihara K, Chiwaki F, Ochiya T, Suzuki T, Matoba M, Sasaki H, Uezono Y (2012) Sensation of abdominal pain induced by peritoneal carcinomatosis is accompanied by changes in the expression of substance P and mu-opioid receptors in the spinal cord of mice. Anesthesiology 117:847–856
Szabo I, Chen XH, Xin L, Adler MW, Howard OM, Oppenheim JJ, Rogers TJ (2002) Heterologous desensitization of opioid receptors by chemokines inhibits chemotaxis and enhances the perception of pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:10276–10281
Wang LN, Yang JP, Ji FH, Zhan Y, Jin XH, Xu QN, Wang XY, Zuo JL (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor activation in a rat model of cancer-induced bone pain. J Neurosci Res 90:1249–1260
Weibel R, Reiss D, Karchewski L, Gardon O, Matifas A, Filliol D, Becker JA, Wood JN, Kieffer BL, Gaveriaux-Ruff C (2013) Mu opioid receptors on primary afferent nav1.8 neurons contribute to opiate-induced analgesia: insight from conditional knockout mice. PLoS One 8:e74706
Willox I, Mirkina I, Westwick J, Ward SG (2010) Evidence for PI3K-dependent CXCR3 agonist-induced degranulation of human cord blood-derived mast cells. Mol Immunol 47:2367–2377
Yaksh TL, Rudy TA (1976) Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav 17:1031–1036
Yoon Y, Liang Z, Zhang X, Choe M, Zhu A, Cho HT, Shin DM, Goodman MM, Chen ZG, Shim H (2007) CXC chemokine receptor-4 antagonist blocks both growth of primary tumor and metastasis of head and neck cancer in xenograft mouse models. Cancer Res 67:7518–7524
Zhao CM, Guo RX, Hu F, Meng JL, Mo LQ, Chen PX, Liao XX, Cui Y, Feng JQ (2012) Spinal MCP-1 contributes to the development of morphine antinociceptive tolerance in rats. Am J Med Sci 344:473–479
Zhuang ZY, Kawasaki Y, Tan PH, Wen YR, Huang J, Ji RR (2007) Role of the CX3CR1/p38 MAPK pathway in spinal microglia for the development of neuropathic pain following nerve injury-induced cleavage of fractalkine. Brain Behav Immun 21:642–651
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of the People's Republic of China (No. 81171259, No. 81371250, and No. 81070890) and also supported by 2010 Clinical Key Disciplines Construction Grant from the Ministry of Health of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dawei Ye and Huilian Bu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, D., Bu, H., Guo, G. et al. Activation of CXCL10/CXCR3 Signaling Attenuates Morphine Analgesia: Involvement of Gi Protein. J Mol Neurosci 53, 571–579 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0223-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0223-1