Abstract
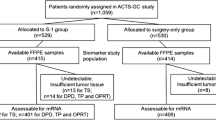
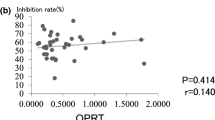
This study was performed to analyze the impact of protein expression related to fluoropyrimidine and cisplatin metabolism (thymidylate synthase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, thymidine phosphorylase, orotate phosphoribosyltransferase [OPRT], excision repair cross-complementation 1, Fanconi anemia complementation group D2, glutathione S-transferase P1, and X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1) on treatment outcomes in patients with metastatic or relapsed gastric cancer (MRGC) receiving S-1/cisplatin chemotherapy. Protein expression was measured by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Of the 43 patients who had received S-1 (80 mg/m2/day; days 1–14) and cisplatin (60 mg/m2; day 1) every 3 weeks and had available tissue blocks, IHC was successfully performed in 41 patients. Patients with high OPRT levels in tumor tissues (IHC score ≥6) had superior progression-free survival (PFS) (23.3 vs. 14.1 weeks [median]) and overall survival (OS) (72.4 vs. 55.4 weeks [median]) to those with low OPRT levels (IHC score ≤5; P-values <.05). Expression levels of other proteins were not predictive of treatment outcomes. In multivariate analysis, both a good performance status and a high OPRT level were independently associated with prolonged PFS and OS. The OPRT expression level may be a good predictive marker in S-1/cisplatin-treated patients with MRGC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Vanhoefer U, et al. Final results of a randomized phase III trial of sequential high-dose methotrexate, fluorouracil, and doxorubicin versus etoposide, leucovorin, and fluorouracil versus infusional fluorouracil and cisplatin in advanced gastric cancer: a trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2648–57.
Cunningham D, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:36–46.
Kang YK, et al. Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomised phase III noninferiority trial. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:666–73.
Choi IS, et al. Oxaliplatin, 5-FU, folinic acid as first-line palliative chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2007;39:99–103.
Koizumi W, et al. Phase I/II study of S-1 combined with cisplatin in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:2207–12.
Ajani JA, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of S-1 plus cisplatin in patients with untreated advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:663–7.
Lee JL, et al. Phase I/II study of 3-week combination of S-1 and cisplatin chemotherapy for metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008;61:837–45.
Koizumi W, et al. S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:215–21.
Boku N, et al. Biological markers as a predictor for response and prognosis of unresectable gastric cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil and cis-platinum. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:1469–74.
Metzger R, et al. ERCC1 mRNA levels complement thymidylate synthase mRNA levels in predicting response and survival for gastric cancer patients receiving combination cisplatin and fluorouracil chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:309–16.
Miyamoto S. et al. Clinical implications of immunoreactivity of thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in gastric cancer treated with oral fluoropyrimidine (S-1). Study Group of S-1 for Gastric Cancer. Int J Oncol. 2000;17:653–8.
Ichikawa W, et al. Thymidylate synthase predictive power is overcome by irinotecan combination therapy with S-1 for gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:1245–50.
Ichikawa W, et al. Simple combinations of 5-FU pathway genes predict the outcome of metastatic gastric cancer patients treated by S-1. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:1927–33.
Napieralski R, et al. Combined GADD45A and thymidine phosphorylase expression levels predict response and survival of neoadjuvant-treated gastric cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3025–31.
Koizumi W, et al. Impacts of fluorouracil-metabolizing enzymes on the outcomes of patients treated with S-1 alone or S-1 plus cisplatin for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:162–70.
Liu B, et al. Polymorphism of XRCC1 predicts overall survival of gastric cancer patients receiving oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in Chinese population. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007;15:1049–53.
Olaussen KA, et al. Bio Investigators: DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:983–91.
D’Andrea AD, Grompe M. The Fanconi anaemia/BRCA pathway. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:23–34.
Goto S, et al. Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase pi enhances the adduct formation of cisplatin with glutathione in human cancer cells. Free Radic Res. 1999;31:549–58.
Lee HS, et al. MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 expressions in gastric carcinomas: their roles as prognostic indicators. Cancer. 2001;92:1427–34.
Choi IS, et al. Three-weekly S-1 plus cisplatin chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2010; doi:10.1007/s12032-009-9321-x.
Fujii R, Seshimo A, Kameoka S. Relationships between the expression of thymidylate synthase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, and orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and cell proliferative activity and 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 2003;8:72–8.
Kodera Y, et al. Gene expression of 5-fluorouracil metabolic enzymes in primary gastric cancer: correlation with drug sensitivity against 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Lett. 2007;252:307–13.
Ichikawa W, et al. Both gene expression for orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and its ratio to dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase influence outcome following fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:1486–92.
Shimizu T, Yamada Y, Yasui H, Shirao K, Fukuoka M. Clinical application of immunoreactivity of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) in gastric scirrhous carcinoma treated with S-1, a new DPD inhibitory fluoropyrimidine. Anticancer Res. 2005;25:2997–3001.
Koizumi W, Saigenji K, Nakamaru N, Okayasu I, Kurihara M. Prediction of response to 5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine (5′-DFUR) in patients with inoperable advanced gastric cancer by immunostaining of thymidine phosphorylase/platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor. Oncology. 1999;56:215–22.
Shirota Y, et al. ERCC1 and thymidylate synthase mRNA levels predict survival for colorectal cancer patients receiving combination oxaliplatin and fluorouracil chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:4298–304.
Kwon HC, et al. Prognostic value of expression of ERCC1, thymidylate synthase, and glutathione S-transferase P1 for 5-fluorouracil/oxaliplatin chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:504–9.
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by grants from Korean Cancer Research Foundation, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund (11-2008-034), and Seoul Municipal Boramae Hospital Clinical Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors In Sil Choi and Hye Seung Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, I.S., Lee, H.S., Lee, KW. et al. Biomarker analysis in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with S-1 plus cisplatin chemotherapy: orotate phosphoribosyltransferase expression is associated with treatment outcomes. Med Oncol 28, 991–998 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9590-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9590-4