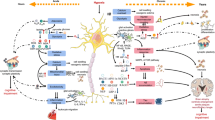
Abstract
Survivors from sepsis present long-term cognitive deficits and some of these alterations resemble the pathophysiological mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases. For this reason, we analyzed beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ) and synaptophysin levels in the brain of rats that survived from sepsis and their relation to cognitive dysfunction and to acute brain inflammation. Sepsis was induced in rats by cecal ligation and puncture, and 30 days after surgery, the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex were isolated just after cognitive evaluation by the inhibitory avoidance test. The immunocontent of Aβ and synaptophysin were analyzed by Western blot analysis. Aβ increased and synaptophysin decreased in septic animals both in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex concurrent with the presence of cognitive deficits. Prefrontal levels of synaptophysin correlated to the performance in the inhibitory avoidance. Two different treatments known to decrease brain inflammation and oxidative stress when administered at the acute phase of sepsis decreased Aβ levels both in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, increased synaptophysin levels only in the prefrontal cortex, and improved cognitive deficit in sepsis-survivor animals. In conclusion, we demonstrated that brain from sepsis-survivor animals presented an increase in Aβ content and a decrease in synaptophysin levels and cognitive impairment. These alterations can be prevented by treatments aimed to decrease acute brain inflammation and oxidative stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iacobone E, Bailly-Salin J, Polito A, Friedman D, Stevens RD, Sharshar T (2009) Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and its differential diagnosis. Crit Care Med 37:S331–S336
Semmler A, Widmann CN, Okulla T, Urbach H, Kaiser M, Widman G, Mormann F, Weide J, Floessbach K, Hoeft A, Jessen F, Putensen C, Heneka MT (2013) Persistent cognitive impairment, hippocampal atrophy and EEG changes in sepsis survivors. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84:62–69
Bozza F, D’Avila JC, Ritter C, Sonneville R, Sharshar T, Dal-Pizzol F (2013) Bioenergetics, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of septic encephalopathy. Shock 39:10–16
Barichello T, Martins MR, Reinke A, Feier G, Ritter C, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2005) Long-term cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors. Crit Care Med 33:1671
Barichello T, Machado RA, Constantino L, Valvassori SS, Reus GZ, Martins MR, Petronilho F, Ritter C, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2007) Antioxidant treatment prevented late memory impairment in an animal model of sepsis. Crit Care Med 35:2186–2190
Dal-Pizzol F, Rojas HA, dos Santos EM, Vuolo F, Constantino L, Feier G, Pasquali M, Comim CM, Petronilho F, Gelain DP, Quevedo J, Moreira JC, Ritter C (2013) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 activities are associated with blood–brain barrier dysfunction in an animal model of severe sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 48:62–70
van Gool WA, van de Beek D, Eikelenboom P (2010) Systemic infection and delirium: when cytokines and acetylcholine collide. Lancet 375:773–775
Buckingham SD, Jones AK, Brown LA, Sattelle DB (2009) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signalling: roles in Alzheimer’s disease and amyloid neuroprotection. Pharmacol Rev 61:39–61
Semmler A, Frisch C, Debeir T, Ramanathan M, Okulla T, Klockgether T, Heneka MT (2007) Long-term cognitive impairment, neuronal loss and reduced cortical cholinergic innervation after recovery from sepsis in a rodent model. Exp Neurol 204:733–740
Comim CM, Pereira JG, Steckert A, Petronilho F, Barichello T, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2009) Rivastigmine reverses habituation memory impairment observed in sepsis survivor rats. Shock 32:270–271
Tillement JP, Lecanu L, Papadopoulos V (2010) Amyloidosis and neurodegenerative diseases: current treatments and new pharmacological options. Pharmacology 85:1–17
Haapasalo A, Viswanathan J, Bertram L, Soininen H, Tanzi RE, Hiltunen M (2010) Emerging role of Alzheimer’s disease-associated ubiquilin-1 in protein aggregation. Biochem Soc Trans 38:150–155
Tan JM, Wong ES, Lim KL (2009) Protein misfolding and aggregation in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:2119–2134
Dal-Pizzol F, Pasquali M, Quevedo J, Gelain DP, Moreira JC (2012) Is there a role for high mobility group box 1 and the receptor for advanced glycation end products in the genesis of long-term cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors? Mol Med 18:1357–1358
Wichterman KA, Baue AE, Chaudry IH (1980) Sepsis and septic shock—a review of laboratory models and a proposal. J Surg Res 29:189–201
Ritter C, Andrades M, Frota Júnior ML, Bonatto F, Pinho RA, Polydoro M, Klamt F, Pinheiro CT, Menna-Barreto SS, Moreira JC, Dal-Pizzol F (2003) Oxidative parameters and mortality in sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Intensive Care Med 29:1782–1789
Quevedo J, Vianna MR, Roesler R, Izquierdo I (1999) Two time windows of anisomycin-induced amnesia for inhibitory avoidance training in rats: protection from amnesia by pretraining but not pre-exposure to the task apparatus. Learn Mem 6:600–607
Ernst A, Morgenthaler NG, Buerger K, Dodel R, Noelker C, Sommer N, Schwarz M, Koehrle J, Bergmann A, Hampel H (2007) Procalcitonin is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia and acute neuroinflammation. J Neuroimmunol 189:169–174
Weberpals M, Hermes M, Hermann S, Kummer MP, Terwel D, Semmler A, Berger M, Schafers M, Heneka MT (2009) NOS2 gene deficiency protects from sepsis-induced long-term cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 29:14177–14184
Barichello T, Fortunato JJ, Vitali AM, Feier G, Reinke A, Moreira JC, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2006) Oxidative variables in the rat brain after sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Crit Care Med 34:886–889
Jeremias IC, Scaini G, Constantino L, Vuolo F, Ferreira AK, Scherer EB, Kolling J, da Silva DA, de Souza Wyse AT, Bogo MR, Dal-Pizzol F, Streck EL (2012) The decrease on Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in the cortex, but not in hippocampus, is reverted by antioxidants in an animal model of sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 46:467–474
Comim CM, Barichello T, Grandgirard D, Dal-Pizzol F, Quevedo J, Leib SL (2013) Caspase-3 mediates in part hippocampal apoptosis in sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 47:394–398
Tweedie D, Ferguson RA, Fishman K, Frankola KA, Van Praag H, Holloway HW, Luo W, Li Y, Caracciolo L, Russo I, Barlati S, Ray B, Lahiri DK, Bosetti F, Greig NH, Rosi S (2012) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis inhibitor 3,6′-dithiothalidomide attenuates markers of inflammation, Alzheimer pathology and behavioral deficits in animal models of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 9:106
Biff D, Petronilho F, Constantino L, Vuolo F, Zamora-Berridi GJ, Dall’Igna DM, Comim CM, Quevedo J, Kapczinski F, Dal-Pizzol F (2013) Correlation of acute phase inflammatory and oxidative markers with long-term cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors rats. Shock 40:45–48
Cras P, Kawai M, Siedlak S, Mulvihill P, Gambetti P, Lowery D, Gonzalez-DeWhitt P, Greenberg B, Perry G (1990) Neuronal and microglial involvement in beta-amyloid protein deposition in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 137:241–246
Good PF, Werner P, Hsu A, Olanow CW, Perl DP (1996) Evidence of neuronal oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 149:21–28
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
Fagiolo U, Cossarizza A, Scala E, Fanales-Belasio E, Ortolani C, Cozzi E, Monti D, Franceschi C, Paganelli R (1993) Increased cytokine production in mononuclear cells of healthy elderly people. Eur J Immunol 23:2375–2378
Nunomura A, Perry G, Aliev G, Hirai K, Takeda A, Balraj EK, Jones PK, Ghanbari H, Wataya T, Shimohama S, Chiba S, Atwood CS, Petersen RB, Smith MA (2001) Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:759–767
Baruch-Suchodolsky R, Fischer B (2009) Abeta40, either soluble or aggregated, is a remarkably potent antioxidant in cell-free oxidative systems. Biochemistry 48:4354–4370
Soscia SJ, Kirby JE, Washicosky KJ, Tucker SM, Ingelsson M, Hyman B, Burton MA, Goldstein LE, Duong S, Tanzi RE, Moir RD (2010) The Alzheimer’s disease-associated amyloid beta-protein is an antimicrobial peptide. PLoS One 5:e9505
Rao JS, Kellom M, Kim HW, Rapoport SI, Reese EA (2012) Neuroinflammation and synaptic loss. Neurochem Res 37:903–910
Garrido P, De Blas M, Giné E, Santos Á, Mora F (2012) Aging impairs the control of prefrontal cortex on the release of corticosterone in response to stress and on memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging 33:827.e1–827.9
Cassol-Jr OJ, Comim CM, Petronilho F, Constantino LS, Streck EL, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2010) Low dose dexamethasone reverses depressive-like parameters and memory impairment in rats submitted to sepsis. Neurosci Lett 473:126–130
Acknowledgments
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This work was funded by NENASC project (PRONEX program CNPq/FAPESC), INCT-TM, and PROCAD Sepse-CAPES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwalm, M.T., Pasquali, M., Miguel, S.P. et al. Acute Brain Inflammation and Oxidative Damage Are Related to Long-Term Cognitive Deficits and Markers of Neurodegeneration in Sepsis-Survivor Rats. Mol Neurobiol 49, 380–385 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8526-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8526-3