Abstract
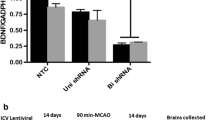
We have previously reported that angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT1R) blockade with candesartan exerts neurovascular protection after experimental cerebral ischemia. Here, we tested the hypothesis that a low, subhypotensive dose of candesartan enhances neuroplasticity and subsequent functional recovery through enhanced neurotrophic factor expression in rats subjected to ischemia reperfusion injury. Male Wistar rats (290–300 g) underwent 90 min of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and received candesartan (0.3 mg/kg) or saline at reperfusion and then once every 24 h for 7 days. Functional deficits were assessed in a blinded manner at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days after MCAO. Animals were sacrificed 14-day post-stroke and the brains perfused for infarct size by cresyl violet. Western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to assess the expression of growth factors and synaptic proteins. Candesartan-treated animals showed a significant reduction in the infarct size [t (13) = −5.5, P = 0.0001] accompanied by functional recovery in Bederson [F (1, 13) = 7.9, P = 0.015], beam walk [F (1, 13) = 6.7, P = 0.023], grip strength [F (1, 13) = 15.2, P = 0.0031], and rotarod performance [F (1, 14) = 29.8, P < 0.0001]. In addition, candesartan-treated animals showed significantly higher expression of active metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), laminin, and angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1). The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its receptor was significantly increased in the animals treated with candesartan. Also, we observed significant increases in neuroplasticity markers, synaptophysin, and PSD-95. These results indicate that low-dose candesartan had a large and enduring effect on measures of plasticity, and this accompanied the functional recovery after ischemic stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- Ang-1:
-
Angiopoietin-1
- AT1R:
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- MMP-3:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-3
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- PSD-95:
-
Postsynaptic density protein-95
- TrkB:
-
Tropomyosin-related kinase-B
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- ARBs:
-
Angiotensin receptor blockers
- MABP:
-
Mean arterial blood pressure
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
References
Lansberg MG, Albers GW, Wijman CA (2007) Symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage following thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke: a review of the risk factors. Cerebrovasc Dis 24(1):1–10. doi:10.1159/000103110
Marder VJ, Jahan R, Gruber T, Goyal A, Arora V (2010) Thrombolysis with plasmin: implications for stroke treatment. Stroke J Cereb Circ 41(10 Suppl):S45–S49. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.595157
Ishitsuka K, Kamouchi M, Hata J, Fukuda K, Matsuo R, Kuroda J, Ago T, Kuwashiro T, Sugimori H, Nakane H, Kitazono T (2014) High blood pressure after acute ischemic stroke is associated with poor clinical outcomes: Fukuoka Stroke Registry. Hypertension 63(1):54–60. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02189
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW Jr, Qureshi AI, Rosenfield K, Scott PA, Summers DR, Wang DZ, Wintermark M, Yonas H (2013) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke J Cereb Circ 44(3):870–947. doi:10.1161/STR.0b013e318284056a
Sandset EC, Bath PM, Boysen G, Jatuzis D, Korv J, Luders S, Murray GD, Richter PS, Roine RO, Terent A, Thijs V, Berge E (2011) The angiotensin-receptor blocker candesartan for treatment of acute stroke (SCAST): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Lancet 377(9767):741–750. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60104-9
He J, Zhang Y, Xu T, Zhao Q, Wang D, Chen CS, Tong W, Liu C, Ju Z, Peng Y, Peng H, Li Q, Geng D, Zhang J, Li D, Zhang F, Guo L, Sun Y, Wang X, Cui Y, Li Y, Ma D, Yang G, Gao Y, Yuan X, Bazzano LA, Chen J (2014) Effects of immediate blood pressure reduction on death and major disability in patients with acute ischemic stroke: the CATIS randomized clinical trial. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 311(5):479–489. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282543
Nishimura Y, Ito T, Saavedra JM (2000) Angiotensin II AT(1) blockade normalizes cerebrovascular autoregulation and reduces cerebral ischemia in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke J Cereb Circ 31(10):2478–2486
Wilms H, Rosenstiel P, Unger T, Deuschl G, Lucius R (2005) Neuroprotection with angiotensin receptor antagonists: a review of the evidence and potential mechanisms. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs Drugs Devices Other Interv 5(4):245–253
Elewa HF, Kozak A, Johnson MH, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2007) Blood pressure lowering after experimental cerebral ischemia provides neurovascular protection. J Hypertens 25(4):855–859. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3280149708
Chen J, Zhang C, Jiang H, Li Y, Zhang L, Robin A, Katakowski M, Lu M, Chopp M (2005) Atorvastatin induction of VEGF and BDNF promotes brain plasticity after stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(2):281–290. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600034
Morris DC, Chopp M, Zhang L, Zhang ZG (2010) Thymosin beta4: a candidate for treatment of stroke? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1194:112–117. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05469.x
Cui X, Chopp M, Zacharek A, Cui Y, Roberts C, Chen J (2013) The neurorestorative benefit of GW3965 treatment of stroke in mice. Stroke J Cereb Circ 44(1):153–161. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.677682
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111(12):1843–1851. doi:10.1172/JCI17977
Greenberg ME, Xu B, Lu B, Hempstead BL (2009) New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release: implications in CNS function. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29(41):12764–12767. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3566-09.2009
Aguado F, Carmona MA, Pozas E, Aguilo A, Martinez-Guijarro FJ, Alcantara S, Borrell V, Yuste R, Ibanez CF, Soriano E (2003) BDNF regulates spontaneous correlated activity at early developmental stages by increasing synaptogenesis and expression of the K+/Cl- co-transporter KCC2. Development 130(7):1267–1280
Gorski JA, Zeiler SR, Tamowski S, Jones KR (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for the maintenance of cortical dendrites. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 23(17):6856–6865
Alhusban A, Kozak A, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2013) AT1 receptor antagonism is proangiogenic in the brain: BDNF a novel mediator. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344(2):348–359. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.197483
Guan W, Somanath PR, Kozak A, Goc A, El-Remessy AB, Ergul A, Johnson MH, Alhusban A, Soliman S, Fagan SC (2011) Vascular protection by angiotensin receptor antagonism involves differential VEGF expression in both hemispheres after experimental stroke. PLoS One 6(9):e24551. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024551
Soliman S, Ishrat T, Pillai A, Somanath PR, Ergul A, El-Remessy AB, Fagan SC (2014) Candesartan induces a prolonged proangiogenic effect and augments endothelium-mediated neuroprotection after oxygen and glucose deprivation: role of vascular endothelial growth factors a and B. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 349(3):444–457. doi:10.1124/jpet.113.212613
Ishrat T, Sayeed I, Atif F, Hua F, Stein DG (2012) Progesterone is neuroprotective against ischemic brain injury through its effects on the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway. Neuroscience 210:442–450. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.008
Kozak A, Ergul A, El-Remessy AB, Johnson MH, Machado LS, Elewa HF, Abdelsaid M, Wiley DC, Fagan SC (2009) Candesartan augments ischemia-induced proangiogenic state and results in sustained improvement after stroke. Stroke J Cereb Circ 40(5):1870–1876. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.537225
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke J Cereb Circ 20(1):84–91
Watanabe T, Okuda Y, Nonoguchi N, Zhao MZ, Kajimoto Y, Furutama D, Yukawa H, Shibata MA, Otsuki Y, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S (2004) Postischemic intraventricular administration of FGF-2 expressing adenoviral vectors improves neurologic outcome and reduces infarct volume after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(11):1205–1213. doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000136525.75839.41
Ishrat T, Sayeed I, Atif F, Stein DG (2009) Effects of progesterone administration on infarct volume and functional deficits following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1257:94–101. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.12.048
Ishrat T, Sayeed I, Atif F, Hua F, Stein DG (2010) Progesterone and allopregnanolone attenuate blood-brain barrier dysfunction following permanent focal ischemia by regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases. Exp Neurol 226(1):183–190. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.08.023
Fouda A, Kozak A, Alhusban A, Switzer J, Fagan S (2013) Anti-inflammatory IL-10 is upregulated in both hemispheres after experimental ischemic stroke: hypertension blunts the response. Exp Transl Stroke Med 5(1):12
Miyata S, Nakatani Y, Hayashi N, Nakashima T (2005) Matrix-degrading enzymes tissue plasminogen activator and matrix metalloprotease-3 in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Brain Res 1058(1–2):1–9. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.07.027
Wright JW, Meighan SE, Murphy ES, Holtfreter KL, Davis CJ, Olson ML, Benoist CC, Muhunthan K, Harding JW (2006) Habituation of the head-shake response induces changes in brain matrix metalloproteinases-3 (MMP-3) and -9. Behav Brain Res 174(1):78–85. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.07.006
Dityatev A, Schachner M (2003) Extracellular matrix molecules and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(6):456–468. doi:10.1038/nrn1115
Falo MC, Fillmore HL, Reeves TM, Phillips LL (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression profile differentiates adaptive and maladaptive synaptic plasticity induced by traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res 84(4):768–781. doi:10.1002/jnr.20986
Valable S, Montaner J, Bellail A, Berezowski V, Brillault J, Cecchelli R, Divoux D, Mackenzie ET, Bernaudin M, Roussel S, Petit E (2005) VEGF-induced BBB permeability is associated with an MMP-9 activity increase in cerebral ischemia: both effects decreased by Ang-1. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(11):1491–1504. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600148
Brdon J, Kaiser S, Hagemann F, Zhao Y, Culman J, Gohlke P (2007) Comparison between early and delayed systemic treatment with candesartan of rats after ischaemic stroke. J Hypertens 25(1):187–196. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000254376.80864.d3
Kozak W, Kozak A, Johnson MH, Elewa HF, Fagan SC (2008) Vascular protection with candesartan after experimental acute stroke in hypertensive rats: a dose-response study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326(3):773–782. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.139618
Rosenberg GA, Mun-Bryce S (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral ischemia. Ernst Schering Res Found Work 47:1–16
Lo EH (2008) A new penumbra: transitioning from injury into repair after stroke. Nat Med 14(5):497–500. doi:10.1038/nm1735
Pham LD, Hayakawa K, Seo JH, Nguyen MN, Som AT, Lee BJ, Guo S, Kim KW, Lo EH, Arai K (2012) Crosstalk between oligodendrocytes and cerebral endothelium contributes to vascular remodeling after white matter injury. Glia 60(6):875–881. doi:10.1002/glia.22320
Zhao BQ, Wang S, Kim HY, Storrie H, Rosen BR, Mooney DJ, Wang X, Lo EH (2006) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in delayed cortical responses after stroke. Nat Med 12(4):441–445. doi:10.1038/nm1387
Rivera S, Ogier C, Jourquin J, Timsit S, Szklarczyk AW, Miller K, Gearing AJ, Kaczmarek L, Khrestchatisky M (2002) Gelatinase B and TIMP-1 are regulated in a cell- and time-dependent manner in association with neuronal death and glial reactivity after global forebrain ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 15(1):19–32
Van Hove I, Lemmens K, Van de Velde S, Verslegers M, Moons L (2012) Matrix metalloproteinase-3 in the central nervous system: a look on the bright side. J Neurochem 123(2):203–216. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07900.x
Thurston G, Suri C, Smith K, McClain J, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD, McDonald DM (1999) Leakage-resistant blood vessels in mice transgenically overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 286(5449):2511–2514
Thurston G, Rudge JS, Ioffe E, Zhou H, Ross L, Croll SD, Glazer N, Holash J, McDonald DM, Yancopoulos GD (2000) Angiopoietin-1 protects the adult vasculature against plasma leakage. Nat Med 6(4):460–463. doi:10.1038/74725
Davis S, Yancopoulos GD (1999) The angiopoietins: Yin and Yang in angiogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 237:173–185
Zacharek A, Chen J, Cui X, Li A, Li Y, Roberts C, Feng Y, Gao Q, Chopp M (2007) Angiopoietin1/Tie2 and VEGF/Flk1 induced by MSC treatment amplifies angiogenesis and vascular stabilization after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(10):1684–1691. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600475
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Tsang W, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Morris D, Zhang R, Goussev A, Powers C, Yeich T, Chopp M (2002) Correlation of VEGF and angiopoietin expression with disruption of blood-brain barrier and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22(4):379–392. doi:10.1097/00004647-200204000-00002
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Croll SD, Chopp M (2002) Angiopoietin-1 reduces cerebral blood vessel leakage and ischemic lesion volume after focal cerebral embolic ischemia in mice. Neuroscience 113(3):683–687
Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Zhou H, Oldmixon EH, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1998) Increased vascularization in mice overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 282(5388):468–471
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, Kumar S, Wang JM (1994) Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Stroke J Cereb Circ 25(9):1794–1798
Krupinski J, Stroemer P, Slevin M, Marti E, Kumar P, Rubio F (2003) Three-dimensional structure and survival of newly formed blood vessels after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroreport 14(8):1171–1176. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000075304.76650.29
Chen YH, Wu HL, Chen CK, Huang YH, Yang BC, Wu LW (2003) Angiostatin antagonizes the action of VEGF-A in human endothelial cells via two distinct pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310(3):804–810
Jin K, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Xie L, Greenberg DA (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(18):11946–11950. doi:10.1073/pnas.182296499
Wang Y, Jin K, Mao XO, Xie L, Banwait S, Marti HH, Greenberg DA (2007) VEGF-overexpressing transgenic mice show enhanced post-ischemic neurogenesis and neuromigration. J Neurosci Res 85(4):740–747. doi:10.1002/jnr.21169
Ergul A, Alhusban A, Fagan SC (2012) Angiogenesis: a harmonized target for recovery after stroke. Stroke J Cereb Circ 43(8):2270–2274. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.642710
Zhang ZG, Chopp M (2009) Neurorestorative therapies for stroke: underlying mechanisms and translation to the clinic. Lancet Neurol 8(5):491–500. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70061-4
Jahn R, Schiebler W, Ouimet C, Greengard P (1985) A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82(12):4137–4141
Ujike H, Takaki M, Kodama M, Kuroda S (2002) Gene expression related to synaptogenesis, neuritogenesis, and MAP kinase in behavioral sensitization to psychostimulants. Ann N Y Acad Sci 965:55–67
Lin Y, Jover-Mengual T, Wong J, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2006) PSD-95 and PKC converge in regulating NMDA receptor trafficking and gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(52):19902–19907. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609924104
Lin Y, Skeberdis VA, Francesconi A, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2004) Postsynaptic density protein-95 regulates NMDA channel gating and surface expression. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 24(45):10138–10148. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3159-04.2004
Sans N, Petralia RS, Wang YX, Blahos J 2nd, Hell JW, Wenthold RJ (2000) A developmental change in NMDA receptor-associated proteins at hippocampal synapses. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 20(3):1260–1271
Yan BC, Park JH, Ahn JH, Lee JC, Won MH, Kang IJ (2013) Postsynaptic density protein (PSD)-95 expression is markedly decreased in the hippocampal CA1 region after experimental ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Neurol Sci 330(1–2):111–116. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2013.04.023
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the Veterans Affairs Merit Review (SCF, BX000891 and AE, BX000347) and NIH–NINDS (SCF, NS063965 and AE, NS054688). Adviye Ergul is a research career scientist at the Charlie Norwood Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Augusta, Georgia.
Conflict of Interest
SCF is a consultant for and has received funding from Pfizer. The contents do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 292 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishrat, T., Pillai, B., Soliman, S. et al. Low-Dose Candesartan Enhances Molecular Mediators of Neuroplasticity and Subsequent Functional Recovery After Ischemic Stroke in Rats. Mol Neurobiol 51, 1542–1553 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8830-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8830-6