Abstract
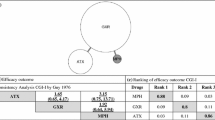
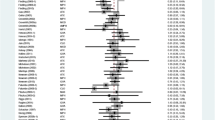
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common neurobehavioral disorders. We carried out this comparison of multiple treatments based on sufficient data in attempt to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ADHD medication for children and adolescents. PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Database were used to search for relevant articles. Changes in the ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS) scores and the Conners’ Parent Rating Scale-Revised (CPRS) scores were used as outcomes for efficacy. Withdrawals due to all-cause, adverse effects and lack of efficacy were defined as primary outcomes evaluating the safety of such medications. Both pair-wise and network meta-analyses were performed. Efficacy and safety of atomoxetine (ATX), bupropion (BUP), clonidine hydrochloride (CLON), guanfacine extended release (GXR), lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (LDX), and methylphenidate (MPH) were evaluated. LDX has the highest efficacy and a relatively lower rate of adverse effects compared to BUP, CLON and GXR. MPH has the lowest incidence rate of adverse effects and takes second place concerning ADHD-RS scores and third place concerning CPRS scores. ATX has the lowest incidence rate of all-cause withdrawals. The efficacy of ATX seems, however, to be lower than CLON, GXR, LDX and MPH. Adversely, BUP has the highest incidence rate of withdrawals and the second highest probability of causing adverse effects as well as lack of efficacy; therefore it should not be recommended as a treatment for ADHD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Limited ELAP (2013) STRATTERA® (atomoxetine hydrochloride)
Bangs ME, Wietecha LA, Wang S, Buchanan AS, Kelsey DK (2014) Meta-analysis of suicide-related behavior or ideation in child, adolescent, and adult patients treated with atomoxetine. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 24(8):426–434. doi:10.1089/cap.2014.0005
Stuhec M, Munda B, Svab V, Locatelli I (2015) Comparative efficacy and acceptability of atomoxetine, lisdexamfetamine, bupropion and methylphenidate in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis with focus on bupropion. J Affect Disord 178:149–159. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2015.03.006
Coghill DR, Banaschewski T, Lecendreux M, Johnson M, Zuddas A, Anderson CS, Civil R, Dauphin M et al (2014) Maintenance of efficacy of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: randomized-withdrawal study design. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 53(6):647–657 . doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2014.01.017e641
Ghuman JK, Hutchison SL (2014) Atomoxetine is a second-line medication treatment option for ADHD. Evid Based Ment Health 17(4):108. doi:10.1136/eb-2014-101805
Joseph A, Ayyagari R, Bischof M, Cai S, Xie M, Zhanabekova Z, Sikirica V (2014) Systematic literature review and mixed treatment comparison of GXR versus other treatments in children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Value Health 17(7):A454
Roskell NS, Setyawan J, Zimovetz EA, Hodgkins P (2014) Systematic evidence synthesis of treatments for ADHD in children and adolescents: indirect treatment comparisons of lisdexamfetamine with methylphenidate and atomoxetine. Curr Med Res Opin 30(8):1673–1685
Conners CK, Erhardt D, Sparrow EP Conners’ adult ADHD rating scales (CAARS): technical manual. In, 1999. MHS North Tonawanda
Faries DE, Yalcin I, Harder D, Heiligenstein JH (2001) Validation of the ADHD rating scale as a clirlician administered and scored instrument. J Atten Disord 5(2):107–115
Conners CK (2001) Conners’ rating scales revised. Multi-Health Systems, Incorporated
Abikoff HB, Vitiello B, Riddle MA, Cunningham C, Greenhill LL, Swanson JM, Chuang SZ, Davies M et al (2007) Methylphenidate effects on functional outcomes in the preschoolers with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder treatment study (PATS). J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 17(5):581–592. doi:10.1089/cap.2007.0068
Allen AJ, Kurlan RM, Gilbert DL, Coffey BJ, Linder SL, Lewis DW, Winner PK, Dunn DW et al (2005) Atomoxetine treatment in children and adolescents with ADHD and comorbid tic disorders. Neurology 65(12):1941–1949. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000188869.58300.a7
Bangs ME, Emslie GJ, Spencer TJ, Ramsey JL, Carlson C, Bartky EJ, Busner J, Duesenberg DA et al (2007) Efficacy and safety of atomoxetine in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and major depression. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 17(4):407–420. doi:10.1089/cap.2007.0066
Bangs ME, Hazell P, Danckaerts M, Hoare P, Coghill DR, Wehmeier PM, Williams DW, Moore RJ et al (2008) Atomoxetine for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder. Pediatrics 121(2):e314–e320. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1880
Biederman J, Krishnan S, Zhang Y, McGough JJ, Findling RL (2007) Efficacy and tolerability of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (NRP-104) in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, forced-dose, parallel-group study. Clin Ther 29(3):450–463
Biederman J, Melmed RD, Patel A, McBurnett K, Konow J, Lyne A, Scherer N (2008) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of guanfacine extended release in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 121(1):e73–e84. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-3695
Biederman J, Quinn D, Weiss M, Markabi S, Weidenman M, Edson K, Karlsson G, Pohlmann H et al (2003) Efficacy and safety of Ritalin LA, a new, once daily, extended-release dosage form of methylphenidate, in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Paediatric drugs 5(12):833–841
Block SL, Kelsey D, Coury D, Lewis D, Quintana H, Sutton V, Schuh K, Allen AJ et al (2009) Once-daily atomoxetine for treating pediatric attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: comparison of morning and evening dosing. Clin Pediatr 48(7):723–733. doi:10.1177/0009922809335321
Buitelaar JK, Michelson D, Danckaerts M, Gillberg C, Spencer TJ, Zuddas A, Faries DE, Zhang S et al (2007) A randomized, double-blind study of continuation treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder after 1 year. Biol Psychiatry 61(5):694–699. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.066
Coghill D, Banaschewski T, Lecendreux M, Soutullo C, Johnson M, Zuddas A, Anderson C, Civil R et al (2013) European, randomized, phase 3 study of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. European neuropsychopharmacology: the journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 23(10):1208–1218. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.11.012
Coghill DR, Banaschewski T, Lecendreux M, Zuddas A, Dittmann RW, Otero IH, Civil R, Bloomfield R et al (2014) Efficacy of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate throughout the day in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: results from a randomized, controlled trial. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 23(2):61–68. doi:10.1007/s00787-013-0421-y
Conners CK, Casat CD, Gualtieri CT, Weller E, Reader M, Reiss A, Weller RA, Khayrallah M et al (1996) Bupropion hydrochloride in attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 35(10):1314–1321. doi:10.1097/00004583-199610000-00018
Connor DF, Findling RL, Kollins SH, Sallee F, Lopez FA, Lyne A, Tremblay G (2010) Effects of guanfacine extended release on oppositional symptoms in children aged 6-12 years with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and oppositional symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. CNS drugs 24(9):755–768. doi:10.2165/11537790-000000000-00000
Cutler AJ, Brams M, Bukstein O, Mattingly G, McBurnett K, White C, Rubin J (2014) Response/remission with guanfacine extended-release and psychostimulants in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 53(10):1092–1101. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2014.08.001
De Jong CGW, Van De Voorde S, Roeyers H, Raymaekers R, Allen AJ, Knijff S, Verhelst H, Temmink AH et al (2009) Differential effects of atomoxetine on executive functioning and lexical decision in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and reading disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 19(6):699–707
Dell’Agnello G, Maschietto D, Bravaccio C, Calamoneri F, Masi G, Curatolo P, Besana D, Mancini F et al (2009) Atomoxetine hydrochloride in the treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and comorbid oppositional defiant disorder: a placebo-controlled Italian study. European neuropsychopharmacology: the journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 19(11):822–834. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2009.07.008
Dittmann RW, Schacht A, Helsberg K, Schneider-Fresenius C, Lehmann M, Lehmkuhl G, Wehmeier PM (2011) Atomoxetine versus placebo in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and comorbid oppositional defiant disorder: a double-blind, randomized, multicenter trial in Germany. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 21(2):97–110. doi:10.1089/cap.2009.0111
Findling RL, Bukstein OG, Melmed RD, Lopez FA, Sallee FR, Arnold LE, Pratt RD (2008) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of methylphenidate transdermal system in pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. The Journal of clinical psychiatry 69(1):149–159
Findling RL, Childress AC, Cutler AJ, Gasior M, Hamdani M, Ferreira-Cornwell MC, Squires L (2011) Efficacy and safety of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 50(4):395–405. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.01.007
Findling RL, McBurnett K, White C, Youcha S (2014) Guanfacine extended release adjunctive to a psychostimulant in the treatment of comorbid oppositional symptoms in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 24(5):245–252. doi:10.1089/cap.2013.0103
Garg J, Arun P, Chavan BS (2014) Comparative short term efficacy and tolerability of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Indian Pediatr 51(7):550–554
Gau SS, Huang YS, Soong WT, Chou MC, Chou WJ, Shang CY, Tseng WL, Allen AJ et al (2007) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial on once-daily atomoxetine in Taiwanese children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 17(4):447–460. doi:10.1089/cap.2007.0091
Geller D, Donnelly C, Lopez F, Rubin R, Newcorn J, Sutton V, Bakken R, Paczkowski M et al (2007) Atomoxetine treatment for pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with comorbid anxiety disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46(9):1119–1127. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e3180ca8385
Greenhill LL, Findling RL, Swanson JM (2002) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of modified-release methylphenidate in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 109(3):E39
Handen BL, Aman MG, Arnold LE, Hyman SL, Tumuluru RV, Lecavalier L, Corbett-Dick P, Pan X et al (2015) Atomoxetine, parent training, and their combination in children with autism Spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 54(11):905–915. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2015.08.013
Harfterkamp M, van de Loo-Neus G, Minderaa RB, van der Gaag RJ, Escobar R, Schacht A, Pamulapati S, Buitelaar JK et al (2012) A randomized double-blind study of atomoxetine versus placebo for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51(7):733–741. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.04.011
Hazell PL, Stuart JE (2003) A randomized controlled trial of clonidine added to psychostimulant medication for hyperactive and aggressive children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42(8):886–894. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000046908.27264.00
Hervas A, Huss M, Johnson M, McNicholas F, van Stralen J, Sreckovic S, Lyne A, Bloomfield R et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of extended-release guanfacine hydrochloride in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, controlled, phase III trial. European neuropsychopharmacology: the journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 24(12):1861–1872. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2014.09.014
Jain R, Segal S, Kollins SH, Khayrallah M (2011) Clonidine extended-release tablets for pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 50(2):171–179. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2010.11.005
Kaplan S, Heiligenstein J, West S, Busner J, Harder D, Dittmann R, Casat C, Wernicke JF (2004) Efficacy and safety of atomoxetine in childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with comorbid oppositional defiant disorder. J Atten Disord 8(2):45–52
Kelsey DK, Sumner CR, Casat CD, Coury DL, Quintana H, Saylor KE, Sutton VK, Gonzales J et al (2004) Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, including an assessment of evening and morning behavior: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics 114(1):e1–e8
Kollins SH, Jain R, Brams M, Segal S, Findling RL, Wigal SB, Khayrallah M (2011) Clonidine extended-release tablets as add-on therapy to psychostimulants in children and adolescents with ADHD. Pediatrics 127(6):e1406–e1413. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1260
Kollins SH, Lopez FA, Vince BD, Turnbow JM, Farrand K, Lyne A, Wigal SB, Roth T (2011) Psychomotor functioning and alertness with guanfacine extended release in subjects with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 21(2):111–120. doi:10.1089/cap.2010.0064
Kratochvil CJ, Vaughan BS, Stoner JA, Daughton JM, Lubberstedt BD, Murray DW, Chrisman AK, Faircloth MA et al (2011) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of atomoxetine in young children with ADHD. Pediatrics 127(4):e862–e868. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-0825
Martenyi F, Zavadenko NN, Jarkova NB, Yarosh AA, Soldatenkova VO, Bardenstein LM, Kozlova IA, Neznanov NG et al (2010) Atomoxetine in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a 6-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial in Russia. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 19(1):57–66. doi:10.1007/s00787-009-0042-7
Michelson D, Allen AJ, Busner J, Casat C, Dunn D, Kratochvil C, Newcorn J, Sallee FR et al (2002) Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry 159(11):1896–1901
Michelson D, Faries D, Wernicke J, Kelsey D, Kendrick K, Sallee FR, Spencer T (2001) Atomoxetine in the treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-response study. Pediatrics 108(5):E83
Nagy P, Hage A, Coghill DR, Caballero B, Adeyi B, Anderson CS, Sikirica V, Cardo E (2016) Functional outcomes from a head-to-head, randomized, double-blind trial of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate and atomoxetine in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and an inadequate response to methylphenidate. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 25(2):141–149. doi:10.1007/s00787-015-0718-0
Newcorn JH, Harpin V, Huss M, Lyne A, Sikirica V, Johnson M, Ramos-Quiroga JA, van Stralen J et al (2016) Extended-release guanfacine hydrochloride in 6-17-year olds with ADHD: a randomised-withdrawal maintenance of efficacy study. Journal of child psychology and psychiatry, and allied disciplines. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12492
Newcorn JH, Kratochvil CJ, Allen AJ, Casat CD, Ruff DD, Moore RJ, Michelson D, Bailey CE et al (2008) Atomoxetine and osmotically released methylphenidate for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: acute comparison and differential response. Am J Psychiatr 165(6):721–730
Newcorn JH, Stein MA, Childress AC, Youcha S, White C, Enright G, Rubin J (2013) Randomized, double-blind trial of guanfacine extended release in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: morning or evening administration. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 52(9):921–930. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.06.006
Rugino TA (2014) Effect on primary sleep disorders when children with ADHD are administered guanfacine extended release. J Atten Disord. doi:10.1177/1087054714554932
Sallee FR, McGough J, Wigal T, Donahue J, Lyne A, Biederman J (2009) Guanfacine extended release in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a placebo-controlled trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48(2):155–165. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e318191769e
Sangal RB, Owens J, Allen AJ, Sutton V, Schuh K, Kelsey D (2006) Effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate on sleep in children with ADHD. Sleep 29(12):1573–1585
Scahill L, Chappell PB, Kim YS, Schultz RT, Katsovich L, Shepherd E, Arnsten AF, Cohen DJ et al (2001) A placebo-controlled study of guanfacine in the treatment of children with tic disorders and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 158(7):1067–1074
Shang CY, Pan YL, Lin HY, Huang LW, Gau SS (2015) An open-label, randomized trial of methylphenidate and atomoxetine treatment in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 25(7):566–573. doi:10.1089/cap.2015.0035
Soutullo C, Banaschewski T, Lecendreux M, Johnson M, Zuddas A, Anderson C, Civil R, Higgins N et al (2013) A post hoc comparison of the effects of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate and osmotic-release oral system methylphenidate on symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. CNS drugs 27(9):743–751. doi:10.1007/s40263-013-0086-6
Spencer T, Heiligenstein JH, Biederman J, Faries DE, Kratochvil CJ, Conners CK, Potter WZ (2002) Results from 2 proof-of-concept, placebo-controlled studies of atomoxetine in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. The Journal of clinical psychiatry 63(12):1140–1147
Stein MA, Sikirica V, Weiss MD, Robertson B, Lyne A, Newcorn JH (2015) Does guanfacine extended release impact functional impairment in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? Results from a randomized controlled trial. CNS drugs 29(11):953–962. doi:10.1007/s40263-015-0291-6
Sumner CR, Schuh KJ, Sutton VK, Lipetz R, Kelsey DK (2006) Placebo-controlled study of the effects of atomoxetine on bladder control in children with nocturnal enuresis. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 16(6):699–711. doi:10.1089/cap.2006.16.699
Svanborg P, Thernlund G, Gustafsson PA, Hägglöf B, Poole L, Kadesjö B (2009) Efficacy and safety of atomoxetine as add-on to psychoeducation in the treatment of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in stimulant-naïve Swedish children and adolescents. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 4:240–249. doi:10.1007/s00787-008-0725-5
Svanborg P, Thernlund G, Gustafsson PA, Hägglöf B, Schacht A, Kadesjö B (2009) Atomoxetine improves patient and family coping in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in Swedish children and adolescents. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 12:725–735. doi:10.1007/s00787-009-0031-x
Takahashi M, Takita Y, Yamazaki K, Hayashi T, Ichikawa H, Kambayashi Y, Koeda T, Oki J et al (2009) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of atomoxetine in Japanese children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 19(4):341–350. doi:10.1089/cap.2008.0154
Thurstone C, Riggs PD, Salomonsen-Sautel S, Mikulich-Gilbertson SK (2010) Randomized, controlled trial of atomoxetine for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adolescents with substance use disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(6):573–582. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2010.02.013
Wang Y, Zheng Y, Du Y, Song D, Shin YJ, Cho S, Kim B, Ahn D et al (2007) Atomoxetine versus methylphenidate in paediatric outpatients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind comparison trial. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 41(3):222–230
Wehmeier PM, Schacht A, Wolff C, Otto WR, Dittmann RW, Banaschewski T (2011) Neuropsychological outcomes across the day in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder treated with atomoxetine: results from a placebo-controlled study using a computer-based continuous performance test combined with an infra-red motion-tracking device. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 21(5):433–444. doi:10.1089/cap.2010.0142
Weiss M, Tannock R, Kratochvil C, Dunn D, Velez-Borras J, Thomason C, Tamura R, Kelsey D et al (2005) A randomized, placebo-controlled study of once-daily atomoxetine in the school setting in children with ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 44(7):647–655. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000163280.47221.c9
Wigal SB, Nordbrock E, Adjei AL, Childress A, Kupper RJ, Greenhill L (2015) Efficacy of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release capsules (Aptensio XR) in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a phase III, randomized. Double-Blind Study CNS drugs. doi:10.1007/s40263-015-0241-3
Wilens TE, Bukstein O, Brams M, Cutler AJ, Childress A, Rugino T, Lyne A, Grannis K et al (2012) A controlled trial of extended-release guanfacine and psychostimulants for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51(1):74–85 . doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.10.012e72
Wilens TE, McBurnett K, Bukstein O, McGough J, Greenhill L, Lerner M, Stein MA, Conners CK et al (2006) Multisite controlled study of OROS methylphenidate in the treatment of adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 160(1):82–90
Wilens TE, Robertson B, Sikirica V, Harper L, Young JL, Bloomfield R, Lyne A, Rynkowski G et al (2015) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of guanfacine extended release in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 54(11):916–925 . doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2015.08.016e912
King S, Griffin S, Hodges Z, Weatherly H, Asseburg C, Richardson G, Golder S, Taylor E et al. (2006) A systematic review and economic model of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methylphenidate, dexamfetamine and atomoxetine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England) 10 (23):iii-iv, xiii-146
Pliszka SR, Crismon ML, Hughes CW, Corners CK, Emslie GJ, Jensen PS, McCracken JT, Swanson JM et al (2006) The Texas Children’s medication algorithm project: revision of the algorithm for pharmacotherapy of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 45(6):642–657
Alper K, Schwartz KA, Kolts RL, Khan A (2007) Seizure incidence in psychopharmacological clinical trials: an analysis of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) summary basis of approval reports. Biol Psychiatry 62(4):345–354
Shoptaw SJ, Kao U, Heinzerling K, Ling W (2009) Treatment for amphetamine withdrawal. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 2
Acknowledgments
We thank our hospital for its great effort and all the colleagues of department for their mutual cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ying Li and Jie Gao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Gao, J., He, S. et al. An Evaluation on the Efficacy and Safety of Treatments for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents: a Comparison of Multiple Treatments. Mol Neurobiol 54, 6655–6669 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0179-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0179-6