Abstract
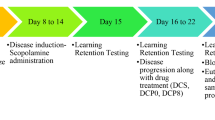
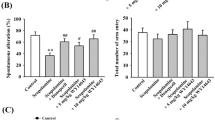
In the present study, we identified the effects of inhaled Pimpinella peregrina essential oil (1 and 3 %, for 21 continuous days) on scopolamine-induced memory impairment, anxiety, and depression in laboratory rats. Y-maze and radial arm-maze tests were used for assessing memory processes. Also, the anxiety and depressive responses were studied by means of the elevated plus-maze and forced swimming tests. The scopolamine alone-treated rats exhibited the following: decrease of the spontaneous alternation percentage in Y-maze test, increase of the number of working and reference memory errors in radial arm-maze test, along with decrease of the exploratory activity, the percentage of the time spent and the number of entries in the open arm within elevated plus-maze test and decrease of swimming time and increase of immobility time within forced swimming test. Inhalation of the P. peregrina essential oil significantly improved memory formation and exhibited anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects in scopolamine-treated rats. Our results suggest that the P. peregrina essential oil inhalation ameliorates scopolamine-induced memory impairment, anxiety, and depression. Moreover, studies on the P. peregrina essential oil may open a new therapeutic window for the prevention of neurological abnormalities closely related to Alzheimer’s disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eckert GP, Lipka U, Muller WE (2013) Omega-3 fatty acids in neurodegenerative diseases: focus on mitochondria. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 88(1):105–114. doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2012.05.006
Ma T, Tan M-S, Yu J-T, Tan L (2014) Resveratrol as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:13. doi:10.1155/2014/350516
Otto R, Penzis R, Gaube F, Winckler T, Appenroth D, Fleck C, Tränkle C, Lehmann J et al (2014) Beta and gamma carboline derivatives as potential anti-Alzheimer agents: a comparison. Eur J Med Chem 87:63–70. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.09.048
Whiteley CG (2014) Arginine metabolising enzymes as targets against Alzheimers’ disease. Neurochem Int 67:23–31. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2014.01.013
Berent S, Giordani B, Foster N, Minoshima S, Lajiness-Oneill R, Koeppe R, Kuhl DE (1999) Neuropsychological function and cerebral glucose utilization in isolated memory impairment and Alzheimers disease. J Psychiatr Res 33(1):7–16. doi:10.1016/S0022-3956(98)90048-6
Hernández F, Avila J (2008) The role of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in the early stages of Alzheimers’ disease. FEBS Lett 582(28):3848–3854. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.10.026
Behl P, Edwards J, Kiss A, Lanctot K, Streiner D, Black S, Stuss D (2014) Treatment effects in multiple cognitive domains in Alzheimer’s disease: a two-year cohort study. Alzheimers Res Ther 6(4):48
Li X-L, Hu N, Tan M-S, Yu J-T, Tan L (2014) Behavioral and psychological symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Res Int;2014:Article ID 927804:9. doi:10.1155/2014/927804
Popović M, Giménez de Béjar V, Popović N, Caballero-Bleda M (2015) Time course of scopolamine effect on memory consolidation and forgetting in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 118:49–54. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2014.11.006
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A (2010) The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: a review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(8):1307–1350. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.04.001
Gülçın İ, Oktay M, Kıreçcı E, Küfrevıoǧlu Öİ (2003) Screening of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) seed extracts. Food Chem 83(3):371–382. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00098-0
Tabanca N, Demirci B, Kirimer N, Baser KHC, Bedir E, Khan IA, Wedge DE (2005) Gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of essential oils from Pimpinella aurea, Pimpinella corymbosa, Pimpinella peregrina and Pimpinella puberula gathered from Eastern and Southern Turkey. J Chromatogr A 1097(1–2):192–198. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.10.047
Ertan Anli R, Bayram M (2010) Traditional aniseed-flavoured spirit drinks. Food Rev Int 26:246–269
Tepe B, Akpulat HA, Sokmen M, Daferera D, Yumrutas O, Aydin E, Polissiou M, Sokmen A (2006) Screening of the antioxidative and antimicrobial properties of the essential oils of Pimpinella anisetum and Pimpinella flabellifolia from Turkey. Food Chem 97(4):719–724. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.045
Adams RP (2007) Identification of essential oil by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy, 4th edn. Allured Publishing Corporation, Carol Stream
Gradinariu V, Cioanca O, Hritcu L, Trifan A, Gille E, Hancianu M (2015) Comparative efficacy of Ocimum sanctum L. and Ocimum basilicum L. essential oils against amyloid beta (1–42)-induced anxiety and depression in laboratory rats. Phytochem Rev 14:567–575. doi:10.1007/s11101-014-9389-6
Hritcu L, Noumedem J, Cioanca O, Hancianu M, Kuete V, Mihasan M (2014) Methanolic extract of Piper nigrum fruits improves memory impairment by decreasing brain oxidative stress in amyloid beta(1–42) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34(3):437–449. doi:10.1007/s10571-014-0028-y
Hayashi Y, Sogabe S, Hattori Y, Tanaka J (2012) Anxiolytic and hypnotic effects in mice of roasted coffee bean volatile compounds. Neurosci Lett 531(2):166–169. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.10.044
Rodgers RJ, Dalvi A (1997) Anxiety, defence and the elevated plus-maze. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21(6):801–810. doi:10.1016/S0149-7634(96)00058-9
Cryan JF, Markou A, Lucki I (2002) Assessing antidepressant activity in rodents: recent developments and future needs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:238–245
Campos M, Fernandes E, Ferreira J, Santos AS, Calixto J (2005) Antidepressant-like effects of Trichilia catigua (Catuaba) extract: evidence for dopaminergic-mediated mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 182(1):45–53. doi:10.1007/s00213-005-0052-1
Chen W, Cheng X, Chen J, Yi X, Nie D, Sun X, Qin J, Tian M et al (2014) Lycium barbarum polysaccharides prevent memory and neurogenesis impairments in scopolamine-treated rats. PLoS ONE 9(2):e88076. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088076
Yoo DY, Kim W, Yoo K-Y, Lee CH, Choi JH, Kang I-J, Yoon YS, Kim D-W et al (2011) Effects of Nelumbo nucifera rhizome extract on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in a scopolamine-induced amnesia animal model. Phytother Res 25(6):809–815. doi:10.1002/ptr.3337
Kotani S, Yamauchi T, Teramoto T, Ogura H (2008) Donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Chem Biol Interact 175(1–3):227–230. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.04.004
Park SJ, Jung JM, Lee HE, Lee YW, Kim DH, Kim JM, Hong JG, Lee CH et al (2012) The memory ameliorating effects of INM-176, an ethanolic extract of Angelica gigas, against scopolamine- or Aβ1–42-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 143:611–620. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.019
Coelho VR, Gianesini J, Von Borowski R, Mazzardo-Martins L, Martins DF, Picada JN, Santos ARS, Brum LFS et al (2011) (−)-Linalool, a naturally occurring monoterpene compound, impairs memory acquisition in the object recognition task, inhibitory avoidance test and habituation to a novel environment in rats. Phytomedicine 18(10):896–901. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2011.02.010
Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LRM, Bonini JS, Rossatto JI, Medina JH, Izquierdo I (2004) Hippocampal glutamate receptors in fear memory consolidation. Neurotox Res 6:205–212
Lima MNM, Laranja DC, Bromberg E, Roesler R, Schröder N (2005) Pre- or posttraining administration of the NMDA receptor blocker MK-801 impairs object recognition memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 156:139–143
Cioanca O, Hritcu L, Mihasan M, Trifan A, Hancianu M (2014) Inhalation of coriander volatile oil increased anxiolytic–antidepressant-like behaviors and decreased oxidative status in beta-amyloid (1–42) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Physiol Behav 131:68–74. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.04.021
Sahak MKA, Mohamed AM, Hashim NH, Hasan Adli DS (2013) Nigella sativa oil enhances the spatial working memory performance of rats on a radial arm maze. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med;2013:Article ID 180598:5. doi:10.1155/2013/180598
Blainski A, Piccolo VK, Mello JCP, de Oliveira RMW (2010) Dual effects of crude extracts obtained from Petiveria alliacea L. (Phytolaccaceae) on experimental anxiety in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 128(2):541–544. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2010.01.012
Adebesin IF, Akindele AJ, Adeyemi OO (2015) Evaluation of neuropharmacological effects of aqueous leaf extract of Albizia glaberrima (Leguminosae) in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 160:101–108. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.11.040
Riss J, Cloyd J, Gates J, Collins S (2008) Benzodiazepines in epilepsy: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Acta Neurol Scand 118(2):69–86. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2008.01004.x
Emamghoreishi M, Khasaki M, Aazam MF (2005) Coriandrum sativum: evaluation of its anxiolytic effect in the elevated plus-maze. J Ethnopharmacol 96(3):365–370. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2004.06.022
Kessler A, Sahin-Nadeem H, Lummis SCR, Weigel I, Pischetsrieder M, Buettner A, Villmann C (2014) GABAA receptor modulation by terpenoids from Sideritis extracts. Mol Nutr Food Res 58(4):851–862. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201300420
Porsolt R, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229:327–336
Caspani O, Reitz M-C, Ceci A, Kremer A, Treede R-D (2014) Tramadol reduces anxiety-related and depression-associated behaviors presumably induced by pain in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:290–296. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2014.06.018
Acknowledgments
Emel Aydin was supported by LLP Erasmus (2013/2014), Alexandru Ioan Cuza University, Iasi, Romania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Rats were treated in accordance with the guidelines of the animal bioethics of the Act on Animal Experimentation and Animal Health and Welfare from Romania and all procedures were in compliance with Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. This study was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iasi (Permit Number: 2192) and also, efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and to reduce the number of animals used.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin, E., Hritcu, L., Dogan, G. et al. The Effects of Inhaled Pimpinella peregrina Essential Oil on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment, Anxiety, and Depression in Laboratory Rats. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6557–6567 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9693-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9693-9