Abstract
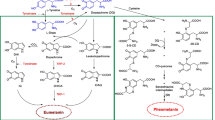
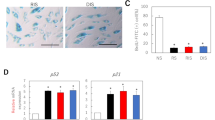
Arbutin has been used as a whitening agent in cosmetic products. Melanin, the major pigment that gives color to skin, may be over-produced with sun exposure or in conditions such as melasma or hyperpigmentary diseases. Tyrosinase is a key enzyme that catalyzes melanin synthesis in melanocytes; therefore, inhibitors of the tyrosinase enzyme could be used for cosmetic skin whitening. A recent study has reported that arbutin decreases melanin biosynthesis through the inhibition of tyrosinase activity. However, this inhibitory mechanism of arbutin was not sufficiently demonstrated in skin tissue models. We found that arbutin both inhibits melanin production in B16 cells induced with α-MSH and decreases tyrosinase activity in a cell-free system. Furthermore, the hyperpigmentation effects of α-MSH were abrogated by the addition of arbutin to brownish guinea pig and human skin tissues. These results suggest that arbutin may be a useful agent for skin whitening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiu, S., Suzuki, Y., Asahara, T., Fujinuma, Y., and Fukuda, M., Inhibitory effect of arbutin on melanogenesis-biochemical study using cultured B16 melanoma cells. Nippon. Hifuka. Gakkai. Zasshi., 101, 609–613 (1991).
Boisnic, S., Branchet-Gumila, M. C., Nocera, T., and Verriere, F., RALGA (Diacneal) decreases melanin content in a human skin model. Dermatology., 210Suppl 1, 35–38 (2005).
Briganti, S., Camera, E., and Picardo, M., Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation. Pigment. Cell. Res., 16, 101–110 (2003).
Grabe, M., Techniques histologiques. Masson, Paris, (1968).
Ha, S. K., Koketsu, M., Lee, K., Choi, S. Y., Park, J. H., Ishihara, H., and Kim, S. Y., Inhibition of tyrosinase activity by N,N-unsubstituted selenourea derivatives. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 28, 838–840 (2005).
Hori, I., Nihei, K., and Kubo, I., Structural criteria for depigmenting mechanism of arbutin. Phytother. Res., 18, 475–479 (2004).
Hosoi, J., Abe, E., Suda, T., and Kuroki, T., Regulation of melanin synthesis of B16 mouse melanoma cells by 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and retinoic acid. Cancer. Res., 45, 1474–1478 (1985).
Jimenez, M., Kameyama, K., Maloy, W. L., Tomita, Y., and Hearing, V. J., Mammalian tyrosinase: biosynthesis, processing, and modulation by melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA., 85, 3830–3834 (1988).
Jung, G. D., Yang, J. Y., Song, E. S., and Par, J. W., Stimulation of melanogenesis by glycyrrhizin in B16 melanoma cells. Exp. Mol. Med., 33, 131–135 (2001).
Kim, D. S., Jeong, Y. M., Park, I. K. et al., A new 2-imino-1,3-thiazoline derivative, KHG22394, inhibits melanin synthesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 30, 180–183 (2007).
Kim, Y. J., No, J. K., Lee, J. H., and Chung, H. Y., 4,4′-Dihydroxybiphenyl as a new potent tyrosinase inhibitor. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 28, 323–327 (2005).
Maeda, K. and Fukuda, M., Arbutin: mechanism of its depigmenting action in human melanocyte culture. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 276, 765–769 (1996).
Nakajima, M., Shinoda, I., Fukuwatari, Y., and Hayasawa, H., Arbutin increases the pigmentation of cultured human melanocytes through mechanisms other than the induction of tyrosinase activity. Pigment. Cell. Res., 11, 12–17 (1998).
Ohguchi, K., Akao, Y., and Nozawa, Y., Involvement of calpain in melanogenesis of mouse B16 melanoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 275, 103–107 (2005).
Schwahn, D. J., Xu, W., Herrin, A. B., Bales, E. S., and Medrano, E. E., Tyrosine levels regulate the melanogenic response to alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in human melanocytes: Implications for pigmentation and proliferation. Pigment. Cell. Res., 14, 32–39 (2001).
Sturm, R. A., Box, N. F., and Ramsay, M., Human pigmentation genetics: the difference is only skin deep. Bioessays., 20, 712–721 (1998).
Sugimoto, K., Nishimura, T., Nomura, K., Sugimoto, K., and Kuriki, T., Syntheses of arbutin-alpha-glycosides and a comparison of their inhibitory effects with those of alpha-arbutin and arbutin on human tyrosinase. Chem. Pharm. Bull (Tokyo)., 51, 798–801 (2003).
Sugimoto, K., Nishimura, T., Nomura, K., Sugimoto, K., and Kuriki, T., Inhibitory effects of alpha-arbutin on melanin synthesis in cultured human melanoma cells and a three-dimensional human skin model. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 27, 510–514 (2004).
Sulaimon, S. S. and Kitchell, B. E., The biology of melanocytes. Vet. Dermatol. 14, 57–65 (2003).
Tammi, R., Jansen, C. T., and Santti, R., Histometric analysis of human skin in organ culture. J. Invest. Dermatol., 73, 138–140 (1979).
Thody, A. J., alpha-MSH and the regulation of melanocyte function. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci., 885, 217–229 (1999).
Tobiishi, M., Haratake, A., Kaminaga, H., Nakahara, M., Komiya, A., Koishikawa, H., Uchiwa, H., Kawa, Y., and Mizoguchi, M., Pigmentation in intrinsically aged skin of A1 guinea pigs. Pigment. Cell. Res. 17, 651–658 (2004).
Tsuji-Naito, K., Hatani, T., Okada, T., and Tehara, T., Modulating effects of a novel skin-lightening agent, alpha-lipoic acid derivative, on melanin production by the formation of DOPA conjugate products. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 15, 1967–1975 (2007).
Usuki, A., Ohashi, A., Sato, H., Ochiai, Y., Ichihashi, M., and Funasaka, Y., The inhibitory effect of glycolic acid and lactic acid on melanin synthesis in melanoma cells. Exp. Dermatol., 12Suppl 2, 43–50 (2003).
Virador, V. M., Kobayashi, N., Matsunaga, J., and Hearing, V. J., A standardized protocol for assessing regulators of pigmentation. Anal. Biochem., 270, 207–219 (1999).
Yamaguchi, Y., Brenner, M., and Hearing, V. J., The regulation of skin pigmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 27557–27561 (2007).
Yoshida, M., Hirotsu, S., Nakahara, M., Uchiwa, H., and Tomita, Y., Histamine is involved in ultraviolet Binduced pigmentation of guinea pig skin. J. Invest. Dermatol., 118, 255–260 (2002).
Zhong, S., Wu, Y., Soo-Mi, A., Zhao, J., Wang, K., Yang, S., Jae-Ho, Y., and Zhu, X., Depigmentation of melanocytes by the treatment of extracts from traditional Chinese herbs: a cell culture assay. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 29, 1947–1951 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, YJ., Lee, E.H., Kang, T.H. et al. Inhibitory effects of arbutin on melanin biosynthesis of α-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced hyperpigmentation in cultured brownish guinea pig skin tissues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 367–373 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1309-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1309-8