Abstract
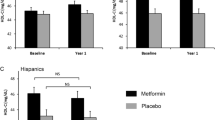
Metformin reduces total cholesterol level, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level, blood glucose level and increases high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level associated with cardiovascular disease. We evaluated effect of metformin on lipid profile in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes aged 64 yeras or older. We retrospectively examined 307 outpatients treated with metformin in a hospital setting with a follow-up period of 4.7 years. Metformin was not associated with the improvement in total cholesterol level (adjusted mean difference; 30.6 mg/dl, 95% CI: 24.9 to 36.4) and HDL-C level (adjusted mean difference; 2.6 mg/dl, 95% CI: 0.09 to 4.64) but may be associated with improvement in triglyceride level (adjusted mean difference; 41.5 mg/dl, 95% CI: 24.7 to 58.3). In comparison to the placebo groups (Kooy et al., 2009), there was a 1.5-fold decrease in triglyceride level and a 2-fold decrease in HDL-C level in our study. The frequency of Scr level that increased above the defined level [Scr ≥ 1.5 mg/dl for male, ≥1.4 mg/dl for female] was 6.7% [mean difference of elevated Scr: −0.9 mg/dl, 95% CI: −0.41 to −1.44, p < 0.002]. To confirm the efficacy of metformin use on triglyceride level and HDL-C level associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease in patient with diabetes, further placebo-controlled investigations are required.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, C. J., Metformin: effect on micro and macrovascular complications in type2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther., 22, 215–224 (2008).
Beckman, J. A., Creager, M. A., and Libby, P., Diabetes and atherosclerosis, epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA, 287, 2570–2581 (2002).
Bristol-myers squibb company: Glucophage and Glucophage XR prescribing information.available: http://packageinserts.bms.com/pi/pi_glucophage.pdf.accessed July 03 (2009).
Coresh, J., Wei, G. L., McQuillan, G., Brancati, F. L., Levey, A. S., Jones, C., and Klag, M. J., Prevalence of high blood pressure and elevated serum creatinine level in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med., 161, 1207–1216 (2001).
Corti, M. C., Guralnik, J. M., Salive, M. E., Harris, T., Field, T. S., Wallace, R. B., Berkman, L. F., Seeman, T. E., Glynn, R. J., Hennekens, C. H., and Havik, R. J., High density lipoprotein cholesterol predicts coronary heart disease mortality in older persons. JAMA, 274, 539–544 (1995).
Culleton, B. F., Larson, M. G., Evans, J. C., Wilson, P. W., Barrett, B. J., Parfrey, P. S., and Levy, D., Prevalence and correlates of elevated serum creatine levels. Arch. Intern. Med., 159, 1785–1790 (1999).
DeFronzo, R. A., Goodman, A. M., and multicenter metformin study group, Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med., 333, 541–549 (1995).
Di Angelantonio, E., Sarwar, N., Kaptoge, S., Ray, K. K., Thompson, A., Wood, A. M., Lewington, S., Sattar, N., Packard, C. J., Collins, R., Thompson, S. G., and Danesh, J., Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. JAMA, 302, 1993–2000 (2009).
Hemmingsen, B., Lund, S. S., Wetterslev, J., and Vaag, A., Oral hypoglycemic agent, insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol., 161, 1–9 (2009).
Hunt, S. A., Abraham, W. T., Chin, M. H., Feldman, A. M., Francis, G. S., Ganiats, T. G., Hessup, M., Konstam, M. A., Mancini, D. M., Michl, K., Oates, J. A., Rahko, P. S., Silver, M. A., Stvensen, L. W., and Yancy, C. W., ACC/AHA 2005 guideline update for the diagnosis and management of chronic heart failure in the adult. A report of the ACC/AHA task force on practice guideline (trunk), Betheseda (MD). American College of Cardiology foundation (ACCF), August 82p, [694 references] (2005).
Kooy, A., de Jager, J., Lehert, P., Bets, D., Wulffelé, M. G., Donker, A. J., and Stehouwer, C. D., Long term effect of metformin on metabolism and microvascullar and macrovascular disease. Arch. Intern. Med., 169, 616–625 (2009).
National kidney foundation (K/DOQI)., K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis., 45, S1–S153 [736 references] (2005).
Nordestgaard, B. G., Benn, M., Schnohr, P., and Tybjaerg-Hansen, A., Non-fasting triglyceride and risk of MI, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. JAMA, 298, 299–308 (2007).
Pradhan, A. D., Everett, B. M., Cook, N. R., Rifai, N., and Ridker, P. M., Effect of initiating insulin and metformin on glycemic control and inflammatory biomarkers among patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA, 302, 1186–1194 (2009).
Psaty, B. M. and Lumley, T., Surrogate end points and FDA approval. JAMA, 299, 1474–1476 (2008).
Roper, N. A., Bilous, R. W., Kelly, W. F., Unwin, N. C., and Connolly, V. M., Cause-specific mortality in a population with diabetes. Diabetes Care, 25, 43–48 (2002).
Ryden, L., Standl, E., Bartnik, M., Betterridge, J., Van den Berghe, G., de Boer, M. J., Cosentino, F., Jonsson, B., Laakso, M., Malmberg, K., Priori, S., Ostergren, J., Tuomilehto, J., and Thrainsdottir, I., Task force on diabetes cardiovascular diseases guideline on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Societ. of Cardiology (ESC), 72p [711 references] (2007).
Selvin, E., Coresh, J., Golden, S. H., Brancati, F. L., Folsom, A. R., and Steffes, M. W., Glycemic control and coronary heart disease risk in persons with and without diabetes. Arch. Intern. Med., 165, 1910–1916 (2005).
Selvin, E., Bolen, S., Yeh, H. C., Wiley, C., Wilson, L. M., Marinopoulos, S. S., Feldman, L., Vassy, J., Wilson, R., Bass, E. B., and Brancati, F. L., Cardiovascular outcomes in trial of oral diabetes medications. Arch. Intern. Med., 168, 2070–2080 (2008).
Simmons, R. K., Sharp, S., Boekholdt, S. M., Sargeant, L. A., Khaw, K. T., Wareham, N. J., and Griffin, S. J., Evaluation of the Framingham risk score in the European prospective investigation of cancer-norfolk cohort. Arch. Intern. Med., 168, 1209–1216 (2008).
Sniderman, A. D., Scantlebury, T., and Cianflone, K., Hypertriglyceridemic hyperapo B: The unappreciated atherogenic dyslipoproteinemia in tye 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med., 135, 447–459 (2001).
Sone, H., Mizuno, S., Fujii, H., Yoshimura, Y., Yamasaki, Y., Ishibashi, S., Katayama, S., Saito, Y., Ito, H., Ohashi, Y., Akanuma, Y., and Yamada, N., Is the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome useful for predicting cardiovascular disease in Asian diabetic patients? Diabetes Care, 28, 1463–1471 (2005).
Stern, M. P., The effect of glycemic control on the incidence of macrovascular complications of type2 diabetes. Arch. Fam. Med., 7, 155–162 (1998).
Summary of revisions for the 2009: clinical practice recommendations. Diabetes Care, 32Suppl, S3–S5 (2009).
Turner, R. C., Millns, H., Neil, H. A., Stratton, I. M., Manley, S. E., Matthews, D. R., and Holman, R. R., Risk factors for coronary artery disease in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: United kingdom prospective diabetes study (UKPDS23). BMJ, 316, 823–828 (1998).
Turner, R. C., Cull, C. A., Frighi, V., and Holman, R. R., Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin inpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). JAMA, 281, 2005–2012 (1999).
Warnick, G. R. and Wood, P. D., National cholesterol education program recommendations for measurement of high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol: executive summary. The national cholesterol education program working group on lipoprotein measurement. Clin. Chem., 41, 1427–1433 (1995).
Weverling-Rijnsburger, A. W., Jonkers, I. J., Exel, E., Gussekloo, J., and Westendorp, R. G., High density vs low density lipoprotein cholesterol as the risk factor for coronary artery disease and stroke in old age. Arch. Intern. Med., 163, 1549–1554 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sin, H.Y., Kim, J.Y. & Jung, K.H. Total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein and triglyceride for cardiovascular disease in elderly patients treated with metformin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 99–107 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0112-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0112-5