Abstract
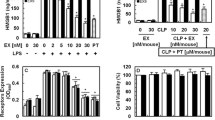
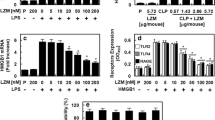
Endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) plays an important role in the protein C anticoagulation pathway and in the cytoprotective pathway. Previously, EPCR can be shed from the cell surface, which is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme (TACE). Soluble EPCR levels are increased in patients with systemic inflammatory diseases. Recently, we reported that a new active compound, emodin-6-O-β-d-glucoside (EG) from Reynoutria japonica, has anti-inflammatory activities. However, little is known of the effects of EG on EPCR shedding. Here, we investigated this issue by monitoring the effects of EG on the phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) or the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-mediated EPCR shedding and its underlying mechanisms. Data showed that EG potently inhibited the PMA and CLP-induced EPCR shedding by suppressing TACE expression. Given these results, EG could be used as a candidate therapeutic for the treatment of vascular inflammatory diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, B.B., H. Ichikawa, P. Garodia, P. Weerasinghe, G. Sethi, I.D. Bhatt, M.K. Pandey, S. Shishodia, and M.G. Nair. 2006. From traditional ayurvedic medicine to modern medicine: Identification of therapeutic targets for suppression of inflammation and cancer. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets 10: 87–118.
Bae, J.S. 2012. Role of high mobility group box 1 in inflammatory disease: Focus on sepsis. Archives of Pharmacal Research 35: 1511–1523.
Bae, J.S., and A.R. Rezaie. 2011. Activated protein C inhibits high mobility group box 1 signaling in endothelial cells. Blood 118: 3952–3959.
Bae, J.S., L. Yang, and A.R. Rezaie. 2007. Receptors of the protein C activation and activated protein C signaling pathways are colocalized in lipid rafts of endothelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104: 2867–2872.
Buras, J.A., B. Holzmann, and M. Sitkovsky. 2005. Animal models of sepsis: Setting the stage. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 4: 854–865.
Esmon, C.T. 2006. The endothelial protein C receptor. Current Opinion in Hematology 13: 382–385.
Fukudome, K., and C.T. Esmon. 1994. Identification, cloning, and regulation of a novel endothelial cell protein C/activated protein C receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry 269: 26486–26491.
Fukudome, K., S. Kurosawa, D.J. Stearns-Kurosawa, X. He, A.R. Rezaie, and C.T. Esmon. 1996. The endothelial cell protein C receptor. Cell surface expression and direct ligand binding by the soluble receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271: 17491–17498.
Guitton, C., N. Gerard, V. Sebille, C. Bretonniere, O. Zambon, D. Villers, and B. Charreau. 2011. Early rise in circulating endothelial protein C receptor correlates with poor outcome in severe sepsis. Intensive Care Medicine 37: 950–956.
Han, H., B. Du, X. Pan, J. Liu, Q. Zhao, X. Lian, M. Qian, and M. Liu. 2010. CADPE inhibits PMA-stimulated gastric carcinoma cell invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by FAK/MEK/ERK-mediated AP-1 activation. Molecular Cancer Research 8: 1477–1488.
Kim, D.C., W. Lee, and J.S. Bae. 2011. Vascular anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin on HMGB1-mediated responses in vitro. Inflammation Research 60: 1161–1168.
Kim, T.H., S.K. Ku, I.C. Lee, and J.S. Bae. 2012. Anti-inflammatory functions of purpurogallin in LPS-activated human endothelial cells. BMB Reports 45: 200–205.
Kimura, Y., H. Okuda, and M. Kubo. 1995. Effects of stilbenes isolated from medicinal plants on arachidonate metabolism and degranulation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 45: 131–139.
Kurosawa, S., D.J. Stearns-Kurosawa, C.W. Carson, A. D’Angelo, P. Della Valle, and C.T. Esmon. 1998. Plasma levels of endothelial cell protein C receptor are elevated in patients with sepsis and systemic lupus erythematosus: Lack of correlation with thrombomodulin suggests involvement of different pathological processes. Blood 91: 725–727.
Kurosawa, S., D.J. Stearns-Kurosawa, N. Hidari, and C.T. Esmon. 1997. Identification of functional endothelial protein C receptor in human plasma. Journal of Clinical Investigation 100: 411–418.
Lee, W., S.K. Ku, T.H. Kim, and J.S. Bae. 2013. Emodin-6-O-beta-d-glucoside inhibits HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. Food and Chemical Toxicology 52: 97–104.
Leng, Y., T.L. Steiler, and J.R. Zierath. 2004. Effects of insulin, contraction, and phorbol esters on mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in skeletal muscle from lean and ob/ob mice. Diabetes 53: 1436–1444.
Liaw, P.C., P.F. Neuenschwander, M.D. Smirnov, and C.T. Esmon. 2000. Mechanisms by which soluble endothelial cell protein C receptor modulates protein C and activated protein C function. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275: 5447–5452.
Lopez-Sagaseta, J., R. Montes, C. Puy, N. Diez, K. Fukudome, and J. Hermida. 2007. Binding of factor VIIa to the endothelial cell protein C receptor reduces its coagulant activity. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 5: 1817–1824.
Menschikowski, M., A. Hagelgans, G. Eisenhofer, and G. Siegert. 2009. Regulation of endothelial protein C receptor shedding by cytokines is mediated through differential activation of MAP kinase signaling pathways. Experimental Cell Research 315: 2673–2682.
Mosnier, L.O., B.V. Zlokovic, and J.H. Griffin. 2007. The cytoprotective protein C pathway. Blood 109: 3161–3172.
Qu, D., Y. Wang, N.L. Esmon, and C.T. Esmon. 2007. Regulated endothelial protein C receptor shedding is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme/ADAM17. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 5: 395–402.
Qu, D., Y. Wang, Y. Song, N.L. Esmon, and C.T. Esmon. 2006. The Ser219–>Gly dimorphism of the endothelial protein C receptor contributes to the higher soluble protein levels observed in individuals with the A3 haplotype. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 4: 229–235.
Regan, L.M., D.J. Stearns-Kurosawa, S. Kurosawa, J. Mollica, K. Fukudome, and C.T. Esmon. 1996. The endothelial cell protein C receptor. Inhibition of activated protein C anticoagulant function without modulation of reaction with proteinase inhibitors. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271: 17499–17503.
Saposnik, B., E. Peynaud-Debayle, A. Stepanian, G. Baron, M. Simansour, L. Mandelbrot, D. de Prost, and S. Gandrille. 2012. Elevated soluble endothelial cell protein C receptor (sEPCR) levels in women with preeclampsia: A marker of endothelial activation/damage? Thrombosis Research 129: 152–157.
Saposnik, B., J.L. Reny, P. Gaussem, J. Emmerich, M. Aiach, and S. Gandrille. 2004. A haplotype of the EPCR gene is associated with increased plasma levels of sEPCR and is a candidate risk factor for thrombosis. Blood 103: 1311–1318.
Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J., S. Kurosawa, J.S. Mollica, G.L. Ferrell, and C.T. Esmon. 1996. The endothelial cell protein C receptor augments protein C activation by the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93: 10212–10216.
Wang, H., H. Liao, M. Ochani, M. Justiniani, X. Lin, L. Yang, Y. Al-Abed, C. Metz, E.J. Miller, K.J. Tracey, and L. Ulloa. 2004. Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in experimental sepsis. Nature Medicine 10: 1216–1221.
Xu, J., D. Qu, N.L. Esmon, and C.T. Esmon. 2000. Metalloproteolytic release of endothelial cell protein C receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275: 6038–6044.
Yang, H., M. Ochani, J. Li, X. Qiang, M. Tanovic, H.E. Harris, S.M. Susarla, L. Ulloa, H. Wang, R. DiRaimo, C.J. Czura, J. Roth, H.S. Warren, M.P. Fink, M.J. Fenton, U. Andersson, and K.J. Tracey. 2004. Reversing established sepsis with antagonists of endogenous high-mobility group box 1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101: 296–301.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea government [MEST] (Grant No. 2012-0009400) and by the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant No. A111305).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wonhwa Lee and Sae-Kwang Ku contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, W., Ku, SK. & Bae, JS. Emodin-6-O-β-d-glucoside down-regulates endothelial protein C receptor shedding. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 1160–1165 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0114-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0114-6