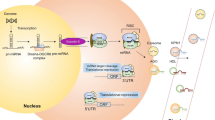
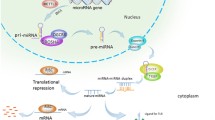
Abstract
microRNAs (miRNAs) are evolutionarily conserved small noncoding RNAs, also known as micromanagers of gene expression. Polymorphisms in the miRNA pathway (miR-polymorphisms) are emerging as powerful tools to study the biology of a disease and have the potential to be used in disease prognosis and diagnosis. Advancements in the miRNA field also indicate a clear involvement of deregulated miRNA gene signatures in cancers, and several polymorphisms in pre-miRNA, miRNA binding sites or targets have been found to be associated with various cancers. The miRNA polymorphisms have also been reported to influence tumor aggressiveness as well as survival of cancer patients. miRNAs have a revolutionary impact on cancer research over recent years. They emerge as important players in tumorigenesis, leading to a paradigm shift in oncology. The extensive and comprehensive use of miRNA microarrays has enabled the identification of a number of miRNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer. Many miRNAs have been identified to act as oncogenes, tumor suppressors, or even modulators of cancer stem cells and metastasis. Some studies not only reported the identified miRNA biomarkers, but also deciphered their target genes and the underlying mechanisms. The rapid discovery of many miRNA targets and their relevant pathways has contributed to the development of miRNA-based therapeutics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 2005;37:495–500.
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E. Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 2005;120:21–24.
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol 2009;11:228–234.
Zeng Y. Principles of micro-RNA production and maturation. Oncogene 2006;25:6156–6162.
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008;455:64–71.
Zhao Y, Srivastava D. A developmental view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci 2007;32:189–197.
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U, Segal E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat Genet 2007;39:1278–1284.
Chen K, Song F, Calin GA, Wei Q, Hao X, Zhang W. Polymorphisms in microRNA targets: a gold mine for molecular epidemiology. Carcinogenesis 2008;29:1306–1311.
Borel C, Antonarakis SE. Functional genetic variation of human miRNAs and phenotypic consequences. Mamm Genome 2008;19:503–509.
Mishra PJ, Humeniuk R, Longo-Sorbello GS, Banerjee D, Bertino JR. A miR-24 microRNA binding-site polymorphism in dihydrofolate reductase gene leads to methotrexate resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:13513–13518.
Tan Z, Randall G, Fan J, Camoretti-Mercado B, Brockman-Schneider R, Pan L, et al. Allele-specific targeting of microRNAs to HLA-G and risk of asthma. Am J Hum Genet 2007;81:829–834.
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors, Dev Biol 2007;302:1–12.
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res 2008;18:350–359.
Duan R, Pak C, Jin P. Single nucleotide polymorphism associated with mature miR-125a alters the processing of pri-miRNA. Hum Mol Genet 2007;16:1124–1131.
Landi D, Gemignani F, Barale R, Landi S. A catalog of polymorphisms falling in microRNA-binding regions of cancer genes. DNA Cell Biol 2008;27:35–43.
Raveche ES, Salerno E, Scaglione BJ, Manohar V, Abbasi F, Lin YC, et al. Abnormal microRNA-16 locus with synteny to human 13q14 linked to CLL in NZB mice. Blood 2007;109:5079–5086.
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Felli N, Dumitru CD, et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:11755–11760.
Hu Z, Chen J, Tian T, Zhou X, Gu H, Xu L, et al. Genetic variants of miRNA sequences and non-small cell lung cancer survival. J Clin Invest 2008;118:2600–2608.
Hu Z, Liang J, Wang Z, Tian T, Zhou X, Chen J, et al. Common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs were associated with increased risk of breast cancer in Chinese women. Hum Mutat 2009;30:79–84.
Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K, Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR, de la Chapelle A. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:7269–7274.
Warthmann N, Das S, Lanz C, Weigel D. Comparative analysis of the MIR319a microRNA locus in Arabidopsis and related Brassicaceae. Mol Biol Evol 2008;25:892–902.
Didiano D, Hobert O. Perfect seed pairing is not a generally reliable predictor for miRNA-target interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2006;13:849–851.
Saunders MA, Liang H, Li WH. Human polymorphism at microRNAs and microRNA target sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:3300–3305.
Evans SC, Kourtidis A, Markham TS, Miller J, Conklin DS, Torres AS. MicroRNA Target Detection and Analysis for Genes Related to Breast Cancer Using MDLcompress. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol 2007;43670.
Gottwein E, Cai X, Cullen BR. A novel assay for viral microRNA function identifies a single nucleotide polymorphism that affects Drosha processing. J Virol 2006;80:5321–5326.
Zhang R, Su B. MicroRNA regulation and the variability of human cortical gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 2008;36:4621–4628.
Zhao Y, Samal E, Srivastava D. Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature 2005;436:214–220.
Jing Q, Huang S, Guth S, Zarubin T, Motoyama A, Chen J, et al. Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA instability. Cell 2005;120:623–634.
Hon LS, Zhang Z. The roles of binding site arrangement and combinatorial targeting in microRNA repression of gene expression. Genome Biol 2007;8:R166.
Lehmann U, Hasemeier B, Christgen M, Muller M, Romermann D, Langer F, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of microRNA gene hsa-mir-9-1 in human breast cancer. J Pathol 2008;214:17–24.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–15529.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 2005;65:7065–7070.
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res 2005;33:1290–1297.
Ruan K, Fang X, Ouyang G. MicroRNAs: Novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Letters 2009;285:116–126.
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302:1–12.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene, Nature 2005;435:828–833.
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y, et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network, Nature 2007;447:1130–1134.
Croce CM. Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J Med 2008;358:502–511.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nature Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–866.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lungcancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006;9:189–198.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006;103:2257–2261.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000;100:57–70.
Ye Y, Wang KK, Gu J, Yang H, Lin J, Ajani JA, et al. Genetic Variations in MicroRNA-Related Genes Are Novel Susceptibility Loci for Esophageal Cancer Risk. Cancer Prev Res 2008;1:460–469.
Brendle A, Lei H, Brandt A, Johansson R, Enquist K, Henriksson R, et al. Polymorphisms in predicted microRNA-binding sites in integrin genes and breast cancer: ITGB4 as prognostic marker. Carcinogenesis 2008;29:1394–1399.
Manolio TA, Brooks LD, Collins FS. A HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease. J Clin Invest 2008;118:1590–1605.
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP. Disrupting the Pairing Between let-7 and Hmga2 Enhances Oncogenic Transformation. Science 2007; 315:1576–1579.
Yang H, Dinney CP, Ye Y, Zhu Y, Grossman HB, Wu X. Evaluation of genetic variants in microRNA-related genes and risk of bladder cancer. Cancer Res 2008;68:2530–2537.
Cowland JB, Hother C, Gronbaek K. MicroRNAs and cancer. APMIS 2007;115:1090–1106.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, varez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005;435:834–838.
Lawrie H. microRNA expression in lymphoid malignancies: new hope for diagnosis and therapy? J Cell Mol Med 2008;12(5A):1432–1444.
Chen CZ. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1768–1771.
Drakaki A, Iliopoulos D. MicroRNA Gene Networks in Oncogenesis. Current Genomics 2009;10:35–41.
Sethupathy P, Collins FS. MicroRNA target site polymorphisms and human disease. Trends Genet 2008;24:489–497.
Glinsky GV. An SNP-guided microRNA map of fifteen common human disorders identifies a consensus disease phenocode aiming at principal components of the nuclear import pathway. Cell Cycle 2008;7:2570–2583.
Marcucci G, Maharry K, Radmacher MD, Mrozek K, Vukosavljevic T, Paschka P, et al. Prognostic significance of, and gene and microRNA expression signatures associated with, CEBPA mutations in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia with high-risk molecular features: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:5078–5087.
Shi X-B, Tepper CG, deVere White RW. microRNAs and prostate cancer. J Cell Mol Med 2008;12(5A):1456–1465.
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M, Ittmann M. Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:1788–1793.
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK, Vessella RL, Tammela TL, Visakorpi T. MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2007;67:6130.
Lynam-Lennon N, Maher SG, Reynolds JV. The roles of microRNA in cancer and apoptosis. Biol Rev 2009;84:55–71.
Weidhaas JB, Babar I, Nallur SM, Trang P, Roush S, Boehm M, et al. MicroRNAs as potential agents to alter resistance to cytotoxic anticancer therapy. Cancer Res 2007;67:11111–11116.
Weidhaas JB, Eisenmann DM, Holub JM, Nallur SV. A conserved RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway regulates DNA damage-induced cell death postirradiation in Radelegans. Cancer Res 2006;66:10434–10438.
Josson S, Sung SY, Lao K, Chung LW, Johnstone PA. Radiation modulation of MicroRNA in prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 2008;68:1599–1606.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs — microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nature Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–269.
Wiemer EAC. The role of microRNAs in cancer: No small matter. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:1529–1544.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449:682–688.
Zhang B, Farwell MA. microRNAs: a new emerging class of players for disease diagnostics and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med 2008;12(1):3–21.
Ivan M, Harris AL, Martelli F, Kulshreshtha R. Hypoxia response and microRNAs: no longer two separate worlds. J Cell Mol Med 2008;12:1426–1431.
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Garzon R, Alder H, Agosto-Perez FJ, et al. A microRNA signature of hypoxia, Mol Cell Biol 2007;27:1859–1867.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, G.P., Mittal, R.D. MicroRNAs: Potential biomarkers in cancer. Indian J Clin Biochem 25, 4–14 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0008-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0008-z