Abstract
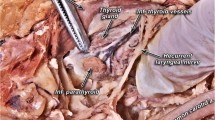
Surgical management of parathyroid gland disease may sometimes be difficult, due mainly to the surgeon’s failure to successfully detect parathyroids in unusual locations. The records of 942 cadavers (574 men and 368 women) who underwent autopsy in the Department of Forensic Medicine in Athens during the period 1988–2009 were reviewed. In total, 3,796 parathyroid glands were resected and histologically verified. Parathyroid glands varied in number. In 47 cases (5 %), one supernumerary (fifth) parathyroid was found, while in 19 cases (2 %) three parathyroid glands found. Superior glands were larger than inferior ones. However, there was no significant difference between the genders with respect to gland size. In 324 (8.5 %) out of 3,796, the glands were detected in an ectopic location: 7 (0.2 %) in the thyroid parenchyma, 79 (2 %) in different sites in the neck and 238 (6.3 %) in the mediastinum, 152 (4.1 %) of which were found in the upper and 86 (2.2 %) in the lower mediastinum. Significant anatomical variations of normal parathyroid glands may exist regarding number and location—knowledge that is essential for their successful identification and surgical management.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerström G, Malmaeus J, Bergström R (1984) Surgical anatomy of human parathyroid glands. Surgery 95:14–21
Alveryd A (1968) Parathyroid glands in thyroid surgery. I. Anatomy of parathyroid glands. II. Postoperative hypoparathyroidism—identification and autotransplantation of parathyroid glands. Acta Chir Scand 389:1–120
Anagnostis P, Karagiannis A, Tziomalos K, Athyros VG, Kita M, Mikhailidis DP (2010) Endocrine hypertension: diagnosis and management of a complex clinical entity. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 8:646–660
Cathelineau G, Siegrist JL (1977) Intrathyroidal parathyroidal adenoma associated to a cold thyroidal nodule (author’s translation). Nouv Presse Med 6:3089–3091
Cope O (1941) Surgery of hyperparathyroidism: the occurrence of parathyroids in the anterior mediastinum and the division of the operation into two stages. Ann Surg 114:706–733
Cope O (1966) The study of hyperparathyroidism at the Massachusetts General Hospital. N Engl J Med 274:1174–1182
Dauphine RT, Riggs BL, Scholz DA (1975) Back pain and vertebral crush fractures: an unemphasized mode of presentation for primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann Intern Med 83:365–367
Feliciano DV (1992) Parathyroid pathology in an intrathyroidal position. Am J Surg 164:496–500
Friedman EW, Schwartz AE, Spiro RH (1973) Changing patterns in hyperparathyroidism. Surg Gynecol Obstet 137:941–944
Gomes EM, Nunes RC, Lacativa PG, Almeida MH, Franco FM, Leal CT, Patrício Filho PJ, Farias ML, Gonçalves MD (2007) Ectopic and extranumerary parathyroid glands location in patients with hyperparathyroidism secondary to end stage renal disease. Acta Cir Bras 22:105–109
Herbst JW, Neff WR, Freeman JB (1976) Hyperparathyroidism: ectopic parathyroid glands. Am J Surg 131:380–381
Hojaij F, Vanderlei F, Plopper C, Rodrigues CJ, Jácomo A, Cernea C, Oliveira L, Marchi L, Brandão L (2011) Parathyroid gland anatomical distribution and relation to anthropometric and demographic parameters: a cadaveric study. Anat Sci Int 86:204–212
Hunt PS, Poole M, Reeve TS (1968) A reappraisal of the surgical anatomy of the thyroid and parathyroid glands. Br J Surg 55:63–66
Ludwing J (ed) (1979) Autopsy protocols, death certificates and interviews. In: Current methods of autopsy practice. Saunders, Orlando, pp 190–197
Mandl F (1947) Hyperparathyroidism: a review of historical developments and the present state of knowledge on the subject. Surgery 21:394–440
Mendoza V, Ramírez C, Espinoza AE, González GA, Peña JF, Ramírez ME, Hernández I, Mercado M (2010) Characteristics of ectopic parathyroid glands in 145 cases of primary hyperparathyroidism. Endocr Pract 16:977–981
Mohebati A, Shaha AR (2012) Anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands and neurovascular relations. Clin Anat 25:19–31
Nanka O, Libánsky P, Sedý J, Pozniak J, Adámek S (2006) Surgical–anatomical study as a part of operative treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism. Rozhl Chir 85:618–623
Palmer JA, Sutton FR (1978) Importance of a fifth parathyroid gland in the surgical treatment of hyperparathyroidism. Can J Surg 21:350–351
Preisman RA, Mehnert JH (1971) A plethora of primary hyperparathyroidism. Arch Surg 103:12–13
Quiros RM, Alioto J, Wilhelm SM, Ali A, Prinz RA (2004) An algorithm to maximize use of minimally invasive parathyroidectomy. Arch Surg 139:501–506
Russell CF, Edis AJ (1982) Surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism: experience with 500 consecutive cases and evaluation of the role of surgery in the asymptomatic patient. Br J Surg 69:244–247
Sandstrom I (1880) Om en ny Kortl has menniskan och atskilliga daggdjur. Upsala lakarforening Forh 15:441
Summers GW (1996) Parathyroid update: a review of 220 cases. Ear Nose Throat J 75:434–439
Thompson NW, Eckhauser FE, Harness JK (1982) The anatomy of primary hyperparathyroidism. Surgery 92:814–821
Vail AD, Coller FC (1967) The parathyroid glands: clinicopathologic correlation of parathyroid disease as found in 200 unselected autopsies. Mol Med 64:234–238
Vellar ID, Shaw J, Brosnan G (1973) Glandula in glandula: the intrathyroid parathyroid. Aust N Z J Surg 42:257–259
Wang C (1976) The anatomic basis of parathyroid surgery. Ann Surg 183:271–275
Wang CA, Mahaffey JE, Axelrod L, Perlman JA (1979) Hyperfunctioning supernumerary parathyroid glands. Surg Gynecol Obstet 148:711–714
Zerizer I, Parsaï A, Win Z, Al-Nahhas A (2011) Anatomical and functional localization of ectopic parathyroid adenomas: 6-year institutional experience. Nucl Med Commun 32:496–502
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lappas, D., Noussios, G., Anagnostis, P. et al. Location, number and morphology of parathyroid glands: results from a large anatomical series. Anat Sci Int 87, 160–164 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-012-0142-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-012-0142-1