Abstract
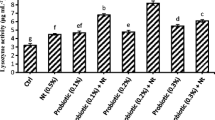
An 8-week study was conducted to evaluate three different diets supplemented with bovine lactoferrin (LF) at 0 (control), 800, and 1200 mg LF kg−1 diet on somatic growth, hemato-immunological parameters, antioxidant status, and digestive enzyme activities in silvery-black porgy (Sparidentex hasta) juveniles. Fish fed the 800 mg LF kg−1 diet had higher growth performance and feed utilization parameters than the other groups. Hematological and liver antioxidant parameters were not affected by dietary LF supplementation. Fish fed the 800 mg LF kg−1 diet had higher plasma lysozyme activity values than the other groups. Total protease activity was higher in fish fed LF-supplemented diets than the control group. Results indicated that diet supplemented with 800 mg kg−1 for 8 weeks enhanced somatic growth performance, lysozyme activity, and proteolytic digestive enzyme activities in S. hasta, as well as improving feed efficiency parameters like the protein efficiency and feed conversion ratios.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romero J, Feijoó CG, Navarrete P (2012) Antibiotics in aquaculture—use, abuse and alternatives. In: Carvalho ED, David GS, Silva RJ (eds) Health and environment in aquaculture. InTechOpen Sience, Rijeka, pp 159–198
Wang W, Sun J, Liu C, Xue Z (2017) Application of immunostimulants in aquaculture: current knowledge and future perspectives. Aquac Res 48:1–23
Vallejos-Vidal E, Reyes-LópezF TM, MacKenzie S (2016) The response of fish to immunostimulant diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol 56:34–69
Gonzalez-Chavez SA, Arevalo-Gallegos S, Rascon-Cruz Q (2009) Lactoferrin: structure, function and applications. Inter J Antimicrob Agents 33(4):1–8
Sandomirsky BP, Galchenko SE, Galchenko KS (2003) Antioxidative properties of lactoferrin from bovine colostrum before and after lyophilization. CryoLetters 24:275–280
Giansanti F, Panella G, Leboffe L, Antonini G (2016) Lactoferrin from milk: nutraceutical and pharmacological properties. Pharmaceuticals 9:61
Yokoyama S, Koshio S, Takakura N, Oshida K, Ishikawa M, Gallardo Cigarroa FJ, Catacutan MR, Teshima S (2006) Effect of dietary bovine lactoferrin on growth response, tolerance to air exposure and low salinity stress conditions in orange spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 255:507–513
Kakuta I (1996) Effect of orally administrated bovine lactoferrin on growth and blood properties of goldfish. Suisanzoshoku 44:419–426
Kumari J, Swain T, Sahoo PK (2003) Dietary bovine lactoferrin induces changes in immunity level and disease resistance in Asian catfish Clarias batrachus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 94:1–9
Kamilya D, Ghosh D, Bandyopadhyay S, Mala BC, Maiti TK (2006) In vitro effects of bovine lactoferrin, mushroom glucan and Abrus agglutinin on Indian major carp, catla (Catla catla) head kidney leukocytes. Aquaculture 253:130–139
Rahimnejad S, Agh N, Kalbassi MR, Khosravi S (2012) Effect of dietary bovine lactoferrin on growth, haematology and non-specific immune response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac Res 43:1451–1459
Moradian AM, Dorafshan S, Paykan Heyrati F, Ebrahimi E (2017) Effects of dietary bovine lactoferrin on growth, haemato-biochemical parameters, immune functions and tolerance to air exposure stress in the African cichlid Sciaenochromis fryeri. Aquac Nut 00:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12570
Yokoyama S, Koshio S, Takakura N, Oshida K, Ishikawa M, Gallardo Cigarroa FJ, Teshima S-I (2005) Dietary bovine lactoferrin enhances tolerance to high temperature stress in Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 249:367–373
Kakuta I (1996) Protective effect of orally administrated bovine lactoferrin against experimental infection of goldfish Carassius auratus with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Suisanzoshoku 44:427–432
Kakuta I, Ogata T, Igarashi K, Sunada T, Nakamura H, Shibui T (1998) Effect of orally administrated bovine lactoferrin on the survival rate of juvenile ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis, held under deteriorating environmental conditions. Suisanzoshoku 46:93–96
Lygren B, Sveier H, Hjeltnes B, Waagbø R (1999) Examination of the immunomodulatory properties and the effect on disease resistance of dietary bovine lactoferrin and vitamin C fed to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) for a short-term period. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:95–107
Welker TL, Lim C, Yildirim-Aksoy M, Klesius PH (2007) Growth, immune function, and disease and stress resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed graded levels of bovine lactoferrin. Aquaculture 262:156–162
Basurco B, Lovatelli A, Garcıa B (2011) Current status of Sparidae aquaculture. In: Pavlidis M, Mylonas C (eds) Sparidae: biology and aquaculture of gilthead sea bream and other species. Wiley-Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 1–50
Mozanzadeh MT, Marammazi JG, Yaghoubi M, Agh N, Pagheh E, Gisbert E (2017) Macronutrient requirements of silvery-black porgy (Sparidentex hasta): a comparison with other farmed sparid species. Aust Fish 2:5
Morshedi V, Agh N, Marammazi J, Noori F, Mohammadian T (2015) Effects of dietary lactoferrin on growth performance, feed utilization, hematological and non-specific immune responses in sobaity (Sparidentex hasta) fingerling. J Anim Environ (In Persian) 2:189–198
Morshedi V, Agh N, Marammazi J, Noori F, Mohammadian T (2016) Effects of different levels of dietary lactoferrin on digestive enzymes, body composition and intestine bacterial flora of sobaity (Sparidentex hasta) fingerling. Vet J (In Persian) 113:65–74
Blaxhall PC, Daisley KW (1973) Routine hematological methods for use fish with blood. J Fish Biol 5:771–781
Andani HRR, Tukmechi A, Meshkini S, Sheikhzadeh N (2012) Antagonistic activity of two potential probiotic bacteria from fish intestines and investigation of their effects on growth performance and immune response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Appl Ichthyol 28:728–734
Ellis AE (1990) Serum antiproteases in fish and lysozyme assays. In: Stolen JS, Fletcher TC, Anderson DP, Roberson BS, Van Muiswinkel WB (eds) Techniques in fish immunology. SOS Publications, Fair Haven, pp 95–103
Siwicki AK, Anderson DP, Rumsey GL (1994) Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against furunculosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 41:125–139
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during oxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arc Biochem Biophys 186:189–195
Koroluk MM, Ivanova L, Mayorova I, Tokorev W (1988) Method of determination of catalase activity. Lab Tech 1:16–19
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAPA assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76
Solovyev MM, Gisbert E (2016) Influence of time, storage temperature and freeze/thaw cycles on the activity of digestive enzymes from gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1383–1394
Chong ASC, Hashim R, Lee CY, Ali BA (2002) Partial characterization and activities of proteases form the digestive tract of discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciata). Aquaculture 203:321–333
Garcia-Carreno FL, Haard NF (1993) Characterization of proteinase classes in langostilla (Pleuroncodes planipes) and crayfish (Pacifastacus astacus) extracts. J Food Biochem 17:97–113
Iijima N, Tanaka S, Ota Y (1998) Purification and characterization of bile salt activated lipase from the hepatopancreas of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Physiol Biochem 18:59–69
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Lonnerdal B (2009) Nutritional roles of lactoferrin. Curr Opin Clinic Nutr Metabol Care 12:293–297
Eslamloo K, Falahatkar B, Yokoyama S (2012) Effects of dietary bovine lactoferrin on growth, physiological performance, iron metabolism and non-specific immune responses of Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baeri. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:976–985
Esteban MA, Rodriguez A, Cuesta A, Meseguer J (2005) Effects of lactoferrin on non-specific immune responses of gilthead seabream Sparus aurata. Fish Shellfish Immunol 18:109–124
Falahatkar B, Eslamloo K, Yokoyama S (2014) Suppression of stress responses in Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baeri, juveniles by the dietary administration of bovine lactoferrin. J World Aquac Soc 45:699–708
Welker TL, Lim C, Yildirim-Aksoy M, Klesius PH (2010) Dietary bovine lactoferrin increases resistance of juvenile channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, to enteric septicemia. J World Aquac Soc 41:28–39
Kawakami H, Hiratsuka M, Dosako S (1988) Effects of iron-saturated lactoferrin on iron absorption. Agric Biol Chem 52:903–908
Cooper CA, Nelson KM, Maga EA, Murray JD (2013) Consumption of transgenic cows’ milk containing human lactoferrin results in beneficial changes in the gastrointestinal tract and systemic health of young pigs. Transgenic Res 22:571–578
Ren T, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Micheal FR, Uyan O, Tung HT (2007) Influence of dietary vitamin C and bovine lactoferrin on blood chemistry and non- specific immune responses of Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Aquaculture 267:31–37
Sakai M, Kobayashi M, Yoahida T (1995) Activation of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, phagocytic cells by administration of bovine lactoferrin. Comp Biochem Physiol 110B:755–759
Kakuta I, Kurokura H, Nakamura H, Yamauchi K (1996) Enhancement of the nonspecific defense activity of the skin mucus of red seabream by oral administration of bovine lactoferrin. Suisan Zoshoku 44:197–202
Samuelsen Ø, Haukland HH, Ulvatne H, Vorland LH (2004) Anti-complement effects of lactoferrin-derived peptides. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 41:141–148
Henry MA, Alexis MN (2009) Effects of in vitro lactoferricin and lactoferrin on the head kidney cells of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) Vet Immunol Immunopathol 130:236–242
Cecchini S, Caputo AR (2009) Serum disposition of bovine lactoferrin after oral and anal administration and its proteolytic cleavage by gastric transit in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss W.) Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:65–71
Kumari J, Sahoo PK (2006) Dietary levamisole modulates the immune response and disease resistance of Asian catfish Clarias batrachus (Linnaeus). Aquac Res 37:500–509
Li Q, Hu W, Zhao J, Wang J, Dai Y, Zhao Y, Meng Q, Li N (2014) Supplementation transgenic cow’s milk containing recombinant human lactoferrin enhances systematic and intestinal immune responses in piglets. Mol Biol Rep 41:2119–2128
Nguyen DN, Li Y, Sangild PT, Bering SB, Chatterton DEW (2014) Effects of bovine lactoferrin on the immature porcine intestine. Brit J Nutr 111:321–331
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the director (Mr. Mojtaba Zabayeh Najafabadi) and staff of the Mariculture Research Station, Sarbandar, Iran for providing the necessary facilities for conducting this project.
Funding
This study was funded by Iran National Science Foundation (grant number 92011610).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagheh, E., Marammazi, J.G., Agh, N. et al. Growth Performance, Hemato-Immunological Responses, and Digestive Enzyme Activities in Silvery-Black Porgy (Sparidentex hasta) Fed Dietary Bovine Lactoferrin. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 10, 399–407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9340-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9340-4