Abstract
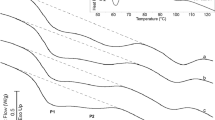
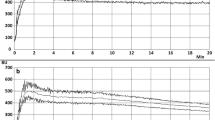
The effect of the partial substitution (0, 10, 15, and 20%) of wheat flour with resistant starch (RS) on dough rheology and structure, and on the quality and staling rate of bread was evaluated. The results from farinograph, extensograph, alveograph, oscillatory rheological tests, and from confocal laser scanning microscopy, indicated that the substitution up to 15% of flour with RS slightly affected the dough structure, weakening it through dilution of gluten protein. Bread made with 15% of RS had specific volume, crumb moisture, and firmness values similar to those of the control bread (without RS), indicating very good quality. During storage, the RS breads had higher crumb moisture, lower firmness, and a lower retrogradation rate than the control bread. The lower retrogradation rate, in conjunction with the higher crumb moisture and high water-retention capacity of RS, was responsible for lower crumb firmness in bread containing up to 15% RS. Using wheat flour of high quality helped to minimize the deleterious effect of RS on the dough and provided high-fiber bread with high quality and low staling.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2000) Approved methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed. St. Paul
Albano KM, Franco CML, Telis VRN (2014) Rheological behavior of Peruvian carrot starch gels as affected by temperature and concentration. Food Hydrocoll 40:30–43
Almeida EL, Chang YK, Steel CJ (2013) Dietary fibre sources in bread: influence on technological quality. LWT Food Sci Technol 50:445–453
Altuna L, Romano RCO, Pileggi RG, Ribotta PD, Tadini C (2016) Torque measurement in real time during mixing and kneading of bread dough with high content of resistant maize starch and enzymes. Int J Food Eng 12:719–728
Armero E, Collar C (1998) Crumb firming kinetics of wheat breads with antistaling additives. J Cereal Sci 28:165–174
Cauvain SP, Young LS (1999) Technology of breadmaking. Aspen Publishers, Gaithersburg
Curti H, Carini E, Tribuzio G, Vittadini E (2014) Bread staling: effect of gluten on physico-chemical properties and molecular mobility. LWT Food Sci Technol 59:418–425
El-Dash AA (1978) Standardized mixing and fermentation procedure for experimental baking test. Cereal Chem 55:336–446
Englyst HN, Kingman SM, Cummings JH (1992) Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur J Clin Nutr 46:33–50
Fu L, Tian JC, Sun C, Li C (2008) RVA and farinograph properties study on blends of resistant starch and wheat flour. Agric Sci China 7:812–822
Gómez AV, Buchner D, Tadini CC, Añón MC, Puppo MC (2013) Emulsifiers: effects on quality of fibre-enriched wheat bread. Food Bioprocess Technol 6:1228–1239
Goñi I, Garcia-Diz L, Mañas E, Saura-Calixto F (1996) Analysis of resistant starch: a method for foods and food products. Food Chem 56:445–449
Gray JA, BeMiller JN (2003) Bread staling: molecular basis and control. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2:1–21
Higgins JA (2014) Resistant starch and energy balance: impact on weight loss and maintenance. Crit Rev Food Sci 54:1158–1166
Khatkar BS, Schofield JD (2002) Dynamic rheology of wheat flour dough. I. Non linear viscoelastic behaviour. J Sci Food Agric 82:827–829
Nara S, Komiya T (1983) Studies on the relationship between water-saturated state and crystallinity by the diffraction method for moistened potato starch. Starch/Staerke 35:407–410
Oliveira DS, Telis-Romero J, Da-Silva R, Franco CML (2014) Effect of a Thermoascus aurantiacus thermostable enzyme cocktail on wheat bread quality. Food Chem 143:139–146
Ozturk S, Koksel H, Ng PKW (2009) Farinograh properties and bread quality of flours supplemented with resistant starch. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60:449–457
Peighambardoust SH, Van Der Goot AJ, Van Vliet T, Hamer RJ, Boom RM (2006) Microstructure formation and rheological behaviour of dough under simple shear flow. J Cereal Sci 43:183–197
Primo-Martín C, Van Nieuwenhuijzen NH, Hamer RJ, Van Vliet T (2007) Crystallinity changes in wheat starch during the bread-making process: starch crystallinity in the bread crust. J Cereal Sci 45:219–226
Ronda F, Quilez J, Pando V, Ross YH (2014) Fermentation time and fiber effects on recrystallization of starch components and staling of bread from frozen part baked bread. J Food Eng 131:116–123
Rosell CM, Santos E (2010) Impact of fibers on physical characteristics of fresh and staled bake of bread. J Food Eng 98:273–281
Rosell CM, Santos E, Collar C (2010) Physical characterization of fiber enriched bread doughs by dual mixing and temperature constraint using the Mixolab. Eur Food Res Technol 231:535–544
Ruan R, Almaer S, Huang VT, Perkins P, Chen P, Fulcher RG (1996) Relationship between firming and water mobility in starch-based food systems during storage. Cereal Chem 73:328–332
Salvador A, Sanz T, Fiszman SM (2006) Dynamic rheological characteristics of wheat flour–water doughs. Effect of adding NaCl, sucrose and yeast. Food Hydrocoll 20:780–786
Sanz-Penella JM, Wronkowska M, Soral-Smietana M, Collar C, Haros M (2010) Impact of the addition of resistant starch from modified pea starch on dough and bread performace. Eur Food Res Technol 231:499–508
Shah AR, Shah RK, Madamwar D (2006) Improvement of the quality of whole wheat bread by supplementation of xilanase from Aspergillus foetidus. Biores Technol 97:2047–2053
Sharma A, Yadav BS, Ritika BS (2008) Resistant starch: physiological roles and food applications. Food Rev Int 24:193–234
Sharma S, Singh N, Katyal M (2016) Effect of gelatinized-retrograded and extruded starches on characteristics of cookies, muffins and noodles. J Food Sci Technol 53:2482–2491
Tian YQ, Li Y, Jin ZY, Xu XM, Wang JP, Jiao AQ, Yu B, Talb T (2009) β-cyclodextrin: a new approach in bread staling. Thermoch Acta 489:22–26
USDA (2015) U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture, 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th ed. Retrieved Aug. 18, 2017, from: http://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/
Van de Velde F, Weinbreck F, Edelman MW, Van Der Linden E, Tromp RH (2003) Visualization of biopolymers mixtures using confocal scanning laser microscopy (CSLM) and covalent labelling techniques. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 31:159–168
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the São Paulo Research Foundation—FAPESP—(Grants Nos. 2013/17725-8 and 2009/53990-2) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—CNPQ (Grant No. 306320/2012-6) in Brazil for financial support. The authors also thank Dr Patricia S. L. Vilamaior for technical support on confocal microscopy analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barros, J.H.T., Telis, V.R.N., Taboga, S. et al. Resistant starch: effect on rheology, quality, and staling rate of white wheat bread. J Food Sci Technol 55, 4578–4588 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3393-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3393-6