Abstract
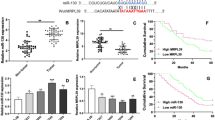
miR152 is involved in diverse biological functions and development of disease. This study investigates the role of mir-152 in cell proliferation and colony formation of liver cancer stem cells. We show that exogenous overexpression of mir-152 suppresses cell proliferation and colony formation in CD133+ hep3B cells. We also show that KIT is a direct target of miR-152 and miR-152 downregulates protein expression of KIT by directly binding to 3′ untranslated region of KIT. Downregulation of KIT by specific siRNAs inhibits proliferation and colony formation of CD133+ hep3B cells, which is similar to inhibitory effects of miR-152. Moreover, exogenous expression of KIT compromises inhibitory effects of miR-152 on cell proliferation and colony formation. Our findings suggest that mir-152 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation of CD133+ hep3B cells by targeting KIT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altekruse SF, Henley SJ, Cucinelli JE, McGlynn KA. Changing hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and liver cancer mortality rates in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(4):542–53. doi:10.1038/ajg.2014.11.
Fan JH, Wang JB, Jiang Y, Xiang W, Liang H, Wei WQ, et al. Attributable causes of liver cancer mortality and incidence in China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(12):7251–6.
Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW. Liver cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2009. Chin J Cancer. 2013;32(4):162–9. doi:10.5732/cjc.013.10027.
Matsuda T, Saika K. Trends in liver cancer mortality rates in Japan, USA, UK, France and Korea based on the WHO mortality database. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012;42(4):360–1. doi:10.1093/jjco/hys048.
Coviello E, Caputi G, Martinelli D, Germinario CA, Prato R. Mortality trends for primary liver cancer in Puglia. Italy Eur J Cancer Prev. 2010;19(6):417–23. doi:10.1097/CEJ.0b013e32833ad36e.
Chiba T, Kamiya A, Yokosuka O, Iwama A. Cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress and perspective. Cancer Lett. 2009;286(2):145–53. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.027.
Sukowati CH, Rosso N, Croce LS, Tiribelli C. Hepatic cancer stem cells and drug resistance: relevance in targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2010;2(3):114–26. doi:10.4254/wjh.v2.i3.114.
Sukowati CH, Tiribelli C. The biological implication of cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: a possible target for future therapy. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;7(8):749–57. doi:10.1586/17474124.2013.846826.
Lee TK, Cheung VC, Ng IO. Liver tumor-initiating cells as a therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2013;338(1):101–9. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.05.001.
Saito T, Chiba T, Yuki K, Zen Y, Oshima M, Koide S, et al. Metformin, a diabetes drug, eliminates tumor-initiating hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e70010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070010.
He XX, Chang Y, Meng FY, Wang MY, Xie QH, Tang F, et al. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 2012;31(28):3357–69. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.500.
Xia H, Ooi LL, Hui KM. MicroRNA-216a/217-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition targets PTEN and SMAD7 to promote drug resistance and recurrence of liver cancer. Hepatology. 2013;58(2):629–41. doi:10.1002/hep.26369.
Gao XN, Lin J, Li YH, Gao L, Wang XR, Wang W, et al. MicroRNA-193a represses c-kit expression and functions as a methylation-silenced tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene. 2011;30(31):3416–28. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.62.
Geng L, Chaudhuri A, Talmon G, Wisecarver JL, Are C, Brattain M, et al. MicroRNA-192 suppresses liver metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene. 2013. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.478.
Ma S, Tang KH, Chan YP, Lee TK, Kwan PS, Castilho A, et al. miR-130b promotes CD133(+) liver tumor-initiating cell growth and self-renewal via tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(6):694–707. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.11.010.
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li L, et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6816. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006816.
Yu F, Deng H, Yao H, Liu Q, Su F, Song E. Mir-30 reduction maintains self-renewal and inhibits apoptosis in breast tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene. 2010;29(29):4194–204. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.167.
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y, Sun S. Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Hepatology. 2010;52(1):60–70. doi:10.1002/hep.23660.
Tsuruta T, Kozaki K, Uesugi A, Furuta M, Hirasawa A, Imoto I, et al. miR-152 is a tumor suppressor microRNA that is silenced by DNA hypermethylation in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71(20):6450–62. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0364.
Wang YS, Chou WW, Chen KC, Cheng HY, Lin RT, Juo SH. MicroRNA-152 mediates DNMT1-regulated DNA methylation in the estrogen receptor alpha gene. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30635. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030635.
Zheng X, Chopp M, Lu Y, Buller B, Jiang F. MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis via NRP-2 and MMP-3. Cancer Lett. 2013;329(2):146–54. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.026.
Zhu C, Li J, Ding Q, Cheng G, Zhou H, Tao L, et al. miR-152 controls migration and invasive potential by targeting TGFalpha in prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate. 2013;73(10):1082–9. doi:10.1002/pros.22656.
Yin S, Li J, Hu C, Chen X, Yao M, Yan M, et al. CD133 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells possess high capacity for tumorigenicity. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(7):1444–50. doi:10.1002/ijc.22476.
Ma S, Chan KW, Hu L, Lee TK, Wo JY, Ng IO, et al. Identification and characterization of tumorigenic liver cancer stem/progenitor cells. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(7):2542–56. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.025.
Suetsugu A, Nagaki M, Aoki H, Motohashi T, Kunisada T, Moriwaki H. Characterization of CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells as cancer stem/progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(4):820–4. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.128.
Piao LS, Hur W, Kim TK, Hong SW, Kim SW, Choi JE, et al. CD133+ liver cancer stem cells modulate radioresistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2012;315(2):129–37. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.012.
Ji D, Chen Z, Li M, Zhan T, Yao Y, Zhang Z, et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor suppressor WIF-1. Mol Cancer. 2014;13(1):86. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-86.
Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S, Ding J, et al. MicroRNA-125b suppressed human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting oncogene LIN28B2. Hepatology. 2010;52(5):1731–40. doi:10.1002/hep.23904.
Liu X, Zhan Z, Xu L, Ma F, Li D, Guo Z, et al. MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIalpha. J Immunol. 2010;185(12):7244–51. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1001573.
Muto S, Katsuki M, Horie S. Decreased c-kit function inhibits enhanced skin carcinogenesis in c-Ha-ras protooncogene transgenic mice. Cancer Sci. 2007;98(10):1549–56. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00577.x.
Yasuda A, Sawai H, Takahashi H, Ochi N, Matsuo Y, Funahashi H, et al. The stem cell factor/c-kit receptor pathway enhances proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:46. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-5-46.
Gavert N, Shvab A, Sheffer M, Ben-Shmuel A, Haase G, Bakos E, et al. c-Kit is suppressed in human colon cancer tissue and contributes to L1-mediated metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013;73(18):5754–63. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0576.
Wiesner C, Nabha SM, Dos Santos EB, Yamamoto H, Meng H, Melchior SW, et al. C-kit and its ligand stem cell factor: potential contribution to prostate cancer bone metastasis. Neoplasia. 2008;10(9):996–1003.
Chau WK, Ip CK, Mak AS, Lai HC, Wong AS. c-Kit mediates chemoresistance and tumor-initiating capacity of ovarian cancer cells through activation of Wnt/beta-catenin-ATP-binding cassette G2 signaling. Oncogene. 2013;32(22):2767–81. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.290.
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Kaller M, Hermeking H. Repression of c-Kit by p53 is mediated by miR-34 and is associated with reduced chemoresistance, migration and stemness. Oncotarget. 2013;4(9):1399–415.
Fan R, Zhong J, Zheng S, Wang Z, Xu Y, Li S, et al. MicroRNA-218 inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell and invasion by targeting KIT. Tumour Biol. 2013. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1551-z.
Gao XN, Lin J, Gao L, Li YH, Wang LL, Yu L. MicroRNA-193b regulates c-Kit proto-oncogene and represses cell proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2011;35(9):1226–32. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2011.06.010.
Gits CM, van Kuijk PF, Jonkers MB, Boersma AW, van Ijcken WF, Wozniak A, et al. MiR-17-92 and miR-221/222 cluster members target KIT and ETV1 in human gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(6):1625–35. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.483.
Kim WK, Park M, Kim YK, Tae YK, Yang HK, Lee JM, et al. MicroRNA-494 downregulates KIT and inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell proliferation. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(24):7584–94. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0166.
Koelz M, Lense J, Wrba F, Scheffler M, Dienes HP, Odenthal M. Down-regulation of miR-221 and miR-222 correlates with pronounced Kit expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int J Oncol. 2011;38(2):503–11. doi:10.3892/ijo.2010.857.
Li P, Ma L, Zhang Y, Ji F, Jin F. MicroRNA-137 down-regulates KIT and inhibits small cell lung cancer cell proliferation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68(1):7–12. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2013.12.002.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by grants from the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province (2008B030301028) and the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Guangdong Medical College (STI F201107).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Haili Huang, Min Hu, and Peng Li contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Hu, M., Li, P. et al. Mir-152 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells by targeting KIT. Tumor Biol. 36, 921–928 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2719-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2719-x