Overview, Design and Sample Description
In contrast to many other countries (e.g., the Netherlands; Boomsma et al., Reference Boomsma, De Geus, Vink, Stubbe, Distel, Hottenga and Willemsen2006), no twin registry is available for Germany. Previous efforts to collect twin data have not used probability-based sampling designs or have only focused on specific regions (Busjahn, Reference Busjahn2013; Hahn et al., Reference Hahn, Gottschling and Spinath2013; Kandler et al., Reference Kandler, Riemann, Spinath, Bleidorn, Thiel and Angleitner2013). The German Twin Family Panel, ‘TwinLife’, closes this gap by collecting longitudinal data on, in the first wave, 4097 families with monozygotic or same-sex dizygotic twin children (Diewald et al., Reference Diewald, Riemann, Spinath, Gottschling, Hahn, Kornadt and Weigel2019). As of 2019, two face-to-face, at-home interviews and two telephone interviews have been conducted. The planned observation period comprises 10 years (between 2014 and 2023). TwinLife is the first twin (family) panel in Germany implementing a population register-based sampling design, which allows for reliable comparisons with twin data from other countries. Additionally, TwinLife covers all parts of the country and includes the whole range of the educational, occupational and income structure (Lang & Kottwitz, Reference Lang and Kottwitz2017). Capturing the lower and upper bounds of these social structural characteristics is especially important for TwinLife because these extremes are particularly relevant for the analysis of differential genetic and environmental influences on traits. As the data collection was performed only in German, TwinLife is restricted to families with good proficiency of the German language.
The target population of TwinLife consists of four age cohorts with twins aged 5 (cohort 1), 11 (cohort 2), 17 (cohort 3) and 23–24 (cohort 4) at the time of the first survey (2014/2015). Taken together, the cohorts cover the major developmental transition phases of childhood, adolescence and young adulthood over the course of the study (Hahn et al., Reference Hahn, Gottschling, Bleidorn, Kandler, Spengler, Kornadt and Spinath2016). For example, the youngest twins (cohort 1) were interviewed for the first time prior to school entry. In the course of the planned study duration, they will experience all transitions in the educational system until the end of secondary schooling. The oldest twins (cohort 4) are observed for the first time prior to or shortly after leaving the parental home and pursuing tertiary education or establishing themselves in the labor market. For them, the study covers the typical life phase for family formation and early career employment.
The TwinLife study combines this cohort-sequential design with an extended twin family design (ETFD). As part of the ETFD, the biological and, if applicable, the social parents (i.e., partners of mothers or fathers) as well as the sibling who is closest in age to the twins (and at least 5 years old) are surveyed in addition to the twins themselves. Moreover, the partners of adult twins — if available — are included in the sample, too. Compared to the classical twin design, the ETFD enables a better assessment of family influences on the children’s development, as well as more precise estimates of genetic transmission (Keller et al., Reference Keller, Medland and Duncan2010). Further, the ETFD design entails collecting data from multiple informants per family. To shorten the time interviewers spent in a household, a combination of different survey modes was employed in the face-to-face interviews: computer-assisted personal interviews, computer-assisted self-interviews and paper and pencil interviews (Brix et al., Reference Brix, Pupeter, Rysina, Steinacker, Schneekloth, Baier, Gottschling and Spinath2017).
The target sample size for the first home interview was 1000 twin families in each of the four cohorts sampled from the official registries of residents of 500 communities with more than 5000 inhabitants all over Germany. The communities were themselves sampled out of an official registry of communities, listing approximately 11,900 communities. In this context, a purposeful oversampling of larger communities with more than 50,000 residents was necessary to achieve the desired sample size. In each sampled community, registration offices were contacted and potential twin families were identified based on registration information by locating persons of the same sex with the same or similar birth dates registered at the same address (Lang & Kottwitz, Reference Lang and Kottwitz2017). For the oldest cohort (cohort 4), in which twin children potentially already moved out of their parents homes, registries of residents dating several years back were used to identify potential twin families. For more details on the register-based sampling design, see Lang and Kottwitz (Reference Lang and Kottwitz2017).
TwinLife includes only same-sex dizygotic twin children, that is, opposite-sex dizygotic twins were not sampled. Focusing on same-sex dizygotic twin children reduced the target sample size of the study and the number of necessary sampling points (communities). In addition, it simplified the identification process of potential twin families. However, in consequence, TwinLife cannot be used to study the effects of within-twin-pair gender differences on phenotypes.
The twin children and their families are interviewed biyearly through face-to-face interviews at the twin families’ homes. In the years between the face-to-face interviews, the families are surveyed by telephone. In the first telephone interview, all respondents aged 10 and above who participated in the first home interview and were living with one of the twins, including the twins themselves, were surveyed. Siblings and partners not living with one of the twins were not interviewed. For the twin children in the youngest cohort (cohort 1), and for siblings below the age of 10, data were collected based on parental reports. Following the selection rules of the first face-to-face interview, in the second home interview all persons aged 5 and above were again surveyed, including the twins of the first birth cohort.
Table 1 shows the sample sizes and participation rates in the first two home interviews and the first telephone interview of TwinLife by cohort, twins’ zygosity and gender. Additionally, Figure 1 displays the participation rates by cohort. All sample sizes and participation rates reported in Table 1 and Figure 1 are calculated based on at least one family member participating in the respective survey. Sample sizes and participation rates calculated based on at least one twin in the family participating in the first face-to-face survey are similar to those reported here due to the definition of the target population for TwinLife (see above).
Table 1. Families in the first two home and the first telephone interviews of TwinLifea
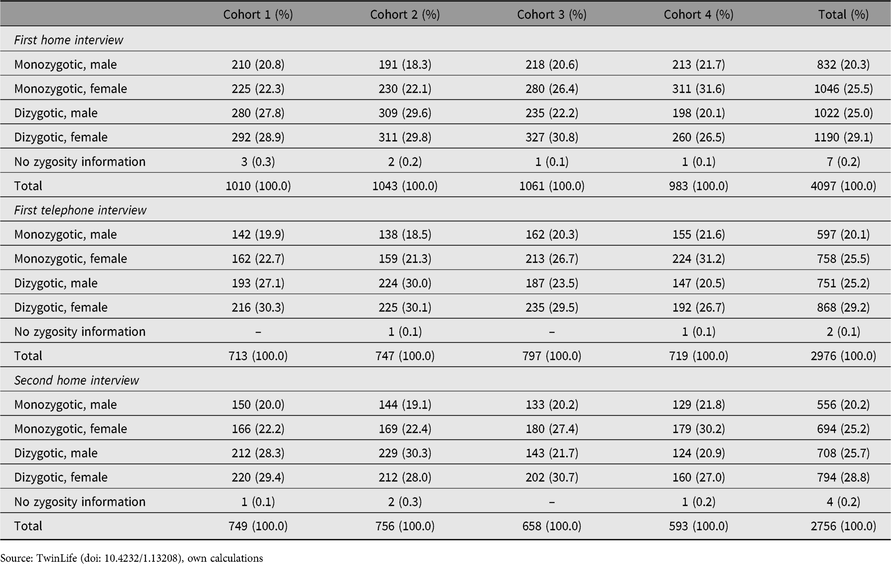
Note: a Reported sample sizes and participation rates are defined by at least one family member participating in the respective survey.
Source: TwinLife (doi: 10.4232/1.13208), own calculations
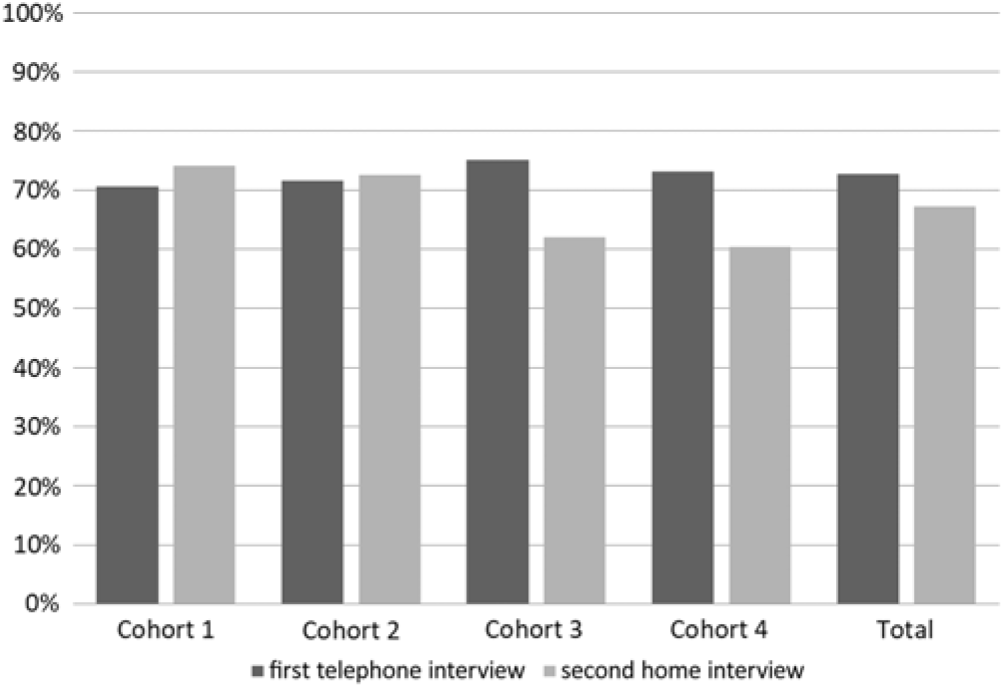
Fig. 1. Participation rates of families in the first two home and the first telephone interviews of TwinLife.
Approximately 45% of the twin pairs in cohorts 1–3 and 53% of the twin pairs in cohort 4 are monozygotic, indicating that the probability-based sampling design worked well to counteract the typically strong overrepresentation of monozygotic twin pairs (Lykken et al., Reference Lykken, McGue and Tellegen1987). Approximately 98% of the families declared their willingness to participate further in the panel after the first home interview. The panel participation rates of these families in the first telephone survey were above 70% in each cohort, with approximately 5% permanent refusals (i.e., panel dropouts). Further, in the first telephone survey, no twins were interviewed in the youngest cohort (cohort 1, see above) and participation rates for the other cohorts calculated based on at least one participating twin per family were about 65%. With respect to the first home interview, the panel participation rates in the second home interview were again above 70% in the two younger birth cohorts and slightly above 60% in the two older cohorts. Also, participation rates calculated based on at least one participating twin per family were around 70% in the younger and around 60% in the two older cohorts. The lower participation rates in the older cohorts are mostly due to twins moving out of the parental home, making it more difficult to contact them and to schedule interviews.
Given the ETFD and these sample selection rules for the first telephone survey, the sample contains information on 16,954 persons for the first home interview, 8721 persons for the first telephone interview and 10,956 persons for the second home interview. The lower number of persons per family surveyed in the telephone interview is mostly related to not interviewing the twins in cohort 1 (see above).
Data on the first home and telephone interviews are already available free of charge as a scientific use-file at the GESIS data archive via the Data Catalogue (for the current release see: https://doi.org/10.4232/1.13208).
Sample Representativeness
The TwinLife data are a probability sample based on registries of residents. To assess the representativeness of the TwinLife sample with respect to the social stratification in Germany, Lang and Kottwitz (Reference Lang and Kottwitz2017) compared the distributions of parental education and occupational status as well as household income in TwinLife with those of a proxy-twin sample based on the German Microcensus (Destatis, 2014). The German Microcensus is a representative household register sample. Proxy-twin pairs were identified as persons with the same year of birth living in the same household. The analysis showed an approximately 15 percentage points higher share of tertiary-educated households, a slightly higher median household income and mean occupational status, as well as an approximately 10 percentage points lower share of households with no German citizenship in TwinLife. These results indicated that participation in TwinLife was, to some degree, selective, especially regarding parental education. The lower share of households with no German citizenship in TwinLife can account for about a quarter of the differences in household education, income and occupation between TwinLife and the Microcensus. Most importantly, the analysis confirmed the sample’s full coverage of the core socioeconomic indicators including the lower and upper bounds.
Zygosity Questionnaire/Determination
Genotyping zygosity may offer an almost perfect method to determine zygosity, but it comes with certain disadvantages, such as higher costs and a greater burden for participants. In TwinLife, the zygosity of the twins was, therefore, assessed using physical similarity questionnaires (see Goldsmith, Reference Goldsmith1991; Oniszczenko et al., Reference Oniszczenko, Angleitner, Strelau and Angert1993). In cohorts 1 and 2, the questions were answered by the twins’ parents. In cohorts 3 and 4, the questions were answered by the twins themselves. To assess the accuracy of the classification, zygosity estimation based on the questionnaire was validated by genotyping a subsample of twins (n = 328). The results indicate a high validity of questionnaire-based zygosity determination with correct classifications for 97% of parental reports and 96% of self-reports (see Lenau et al., Reference Lenau, Hahn, Peters, Gottschling, Thiel and Spinath2017).
Overview of the Measurements
To comprehensively study unequal life chances, the TwinLife study includes a wide range of constructs, some of which have rarely been addressed in previous longitudinal studies (for an overview, see Table 2). The constructs cover six domains of social inequality (see Figure 2): (1) skill formation and education, (2) career and labor market attainment, (3) political and social integration and participation, (4) subjective perception of quality of life, (5) physical and psychological health and (6) deviant behavior and behavioral problems. A detailed overview of all available constructs is provided online at the TwinLife page of the GESIS Data Catalogue (https://doi.org/10.4232/1.13208). Moreover, the constructs cover important information about different life course transitions, ranging from school to labor market entry, and other important life course events, such as mating and starting a family. To make use of the panel design and to compare results with those from other large-scale panel studies, TwinLife often uses the same constructs and measurements that are used in other representative family or household samples that are not twin-based, such as the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP; Goebel et al., Reference Goebel, Grabka, Liebig, Kroh, Richter, Schröder and Schupp2018) and the German Family Panel (Pairfam; Brüderl et al., Reference Brüderl, Drobnič, Hank, Huinink, Nauck, Neyer and Wilhelm2018; Huinink et al., Reference Huinink, Brüderl, Nauck, Walper, Castiglioni and Feldhaus2011).
Table 2. Summary of measures collected for the German Twin Family panel (TwinLife)
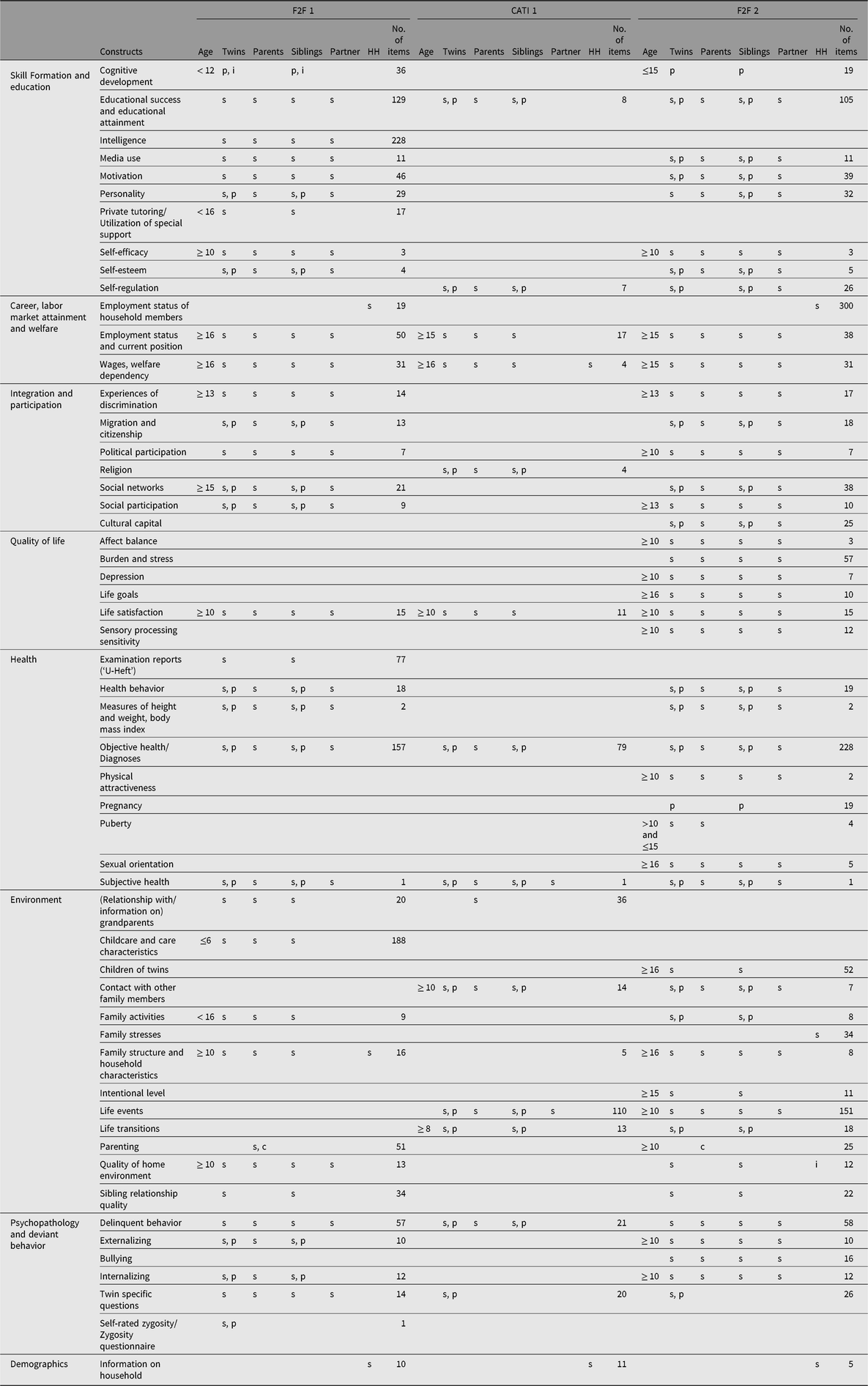
Note: s = self-report, p = parental report, c = children report, i = interviewer rating.
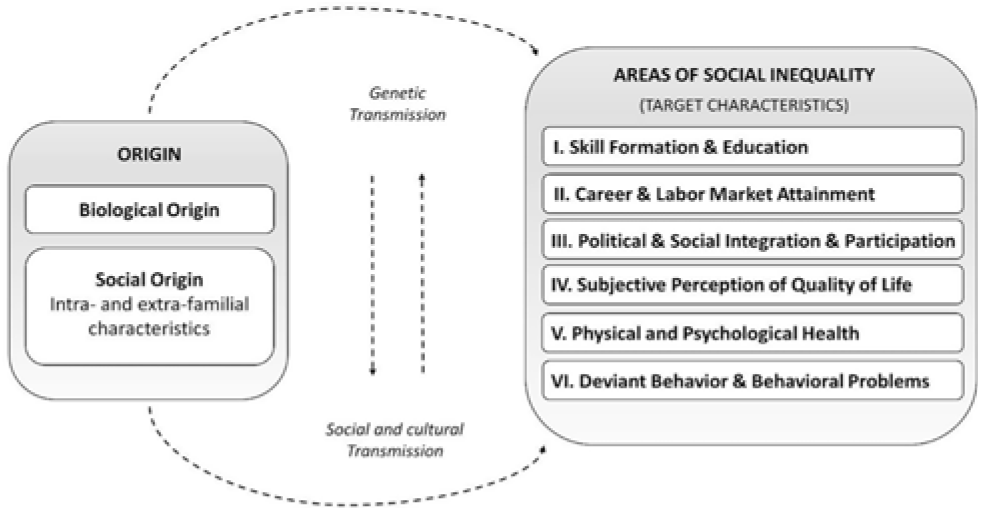
Fig. 2. Basic concept and six domains of social inequality.
Assessment of Cognitive Ability
TwinLife includes an assessment of cognitive ability and uses the Culture Fair Test to measure nonverbal (fluid) intelligence as a proxy for general cognitive ability (CFT; Weiß, Reference Weiß2006; Weiß & Osterland, Reference Weiß and Osterland2012). Three different subtests (figural reasoning, figural classification and matrices) were administered to children aged 5–9. For participants aged 10 years and older, four subtests were used (reasoning in addition to the aforementioned three). For the younger group, the test was applied in a paper-and-pencil version by a trained interviewer. The older group completed the test using a computer. Confirmatory factor analyses with the three subtests (respectively, four subtests in the older group) yielded a single latent (g) factor of cognitive ability. For more information on this measure, see Gottschling (Reference Gottschling2017).
Children’s Medical Records (Yellow Booklet)
The study also includes data on the children’s medical records collected in booklets (called ‘U-Heft’ in Germany). These booklets document the results of regular medical checkups from birth (U1; immediately after birth) to school age (U9; 60th to 64th month of life). Examinations include information on, for example, height, weight, head circumference, diseases, as well as other irregularities, and serve to monitor the child’s development. All medical records were photographed by the interviewer.
Report Cards
To assess educational success as accurately as possible, photos of the most recent report card of the children were taken. This information was transferred to a more generalized report card scheme. All corresponding variables contain basic (e.g., school type, school year, grade) as well as more detailed information (e.g., grades in specific subjects). If the actual report card was not available, the parents or the children themselves were asked questions about their academic performance (e.g., school type, grades in German and Mathematics and type of school leaving certificate). For more details, see Mattheus et al. (Reference Mattheus, Starr, Kornadt and Riemann2017).
Recent Major Findings
Findings on Cognitive Abilities
Cognitive abilities are a key research interest in the TwinLife project. Gottschling et al. (Reference Gottschling, Hahn, Beam, Spinath, Carroll and Turkheimer2019) examined the Scarr–Rowe interaction hypothesis, which suggests that the heritability of cognitive abilities is higher under more privileged socioeconomic conditions for the three oldest cohorts in TwinLife. Using a modified twin correlation model, the Scarr–Rowe hypothesis was found to adequately describe the pattern of results in middle childhood and adolescence but not in adulthood in our German twin sample.
Baier (Reference Baier2019) investigated whether sibling similarities in cognitive ability varied by parents’ education. Her results showed that siblings are less alike in cognitive ability in highly educated families compared to less educated families.
Findings on Educational Outcomes
As achievement motivation is a prerequisite of educational success, Klassen et al. (Reference Klassen, Eifler, Hufer and Riemann2018) investigated its etiology, showing that nonshared environmental factors played a major role, as did additive and nonadditive genetic variance.
Schulz et al. (Reference Schulz, Schunck, Diewald and Johnson2017) investigated different ‘pathways linking parental socioeconomic position to their children’s cognitive ability and academic track attendance in secondary school’ (p. 2194). They showed that separate dimensions of socioeconomic resources influenced child cognitive ability, while a child’s own cognitive ability, parental cognitive ability and parental socioeconomic resources directly affected the child’s track attendance.
Based on twin fixed-effects models, Gil-Hernández (Reference Gil-Hernández2019) studied whether high socioeconomic status families ‘compensate for low cognitive ability in the transition to secondary education in Germany’ (p. 150). His results did not provide any evidence for highly educated families compensating for low cognitive ability in their twin children.
Concerning the final educational degree attained, Baier and Lang (Reference Baier and Lang2019) found a pattern following the Scarr–Rowe interaction hypothesis for the young adults in the oldest birth cohort of twins. Whereas genetic influences were more important for educational attainment of twins in families with higher educated parents, shared environmental influences mattered more if parental education was low. Moreover, controlling for assortative mating of parents based on their education accounted for a substantial part of the genetic influences on educational attainment.
Findings on Social and Political Integration
Another current research focus in TwinLife is on social and political integration as an indicator of social inequality. In this vein, Kornadt et al. (Reference Kornadt, Hufer, Kandler and Riemann2018) analyzed the genetic and environmental sources of variance in political interest and evaluated political and social participation using a nuclear twin family design (NTFD), a specific form of the ETFD. Hufer et al. (Reference Hufer, Kornadt, Kandler and Riemann2019) further investigated political orientation. These studies provided evidence that political traits are moderately to strongly heritable and that parental environmental transmission is less prominent than often assumed. Additionally, Weinschenk et al. (Reference Weinschenk, Dawes, Kandler, Bell and Riemann2019) showed a significant genetic overlap of political engagement, openness and cognitive ability.
Findings on Health
Johnson et al. (Reference Johnson, Hahn, Gottschling, Lenau, Spinath and McGue2018) compared influences of parental socioeconomic status on the relative contribution of genetic and environmental factors to body mass index in German and Minnesotan youths. The authors concluded that socioeconomic status moderates genetic influences, especially in females.
Findings on Personality Traits
Using a NTFD, Bleidorn et al. (Reference Bleidorn, Hufer, Kandler, Hopwood and Riemann2018) found moderate heritability and strong influences of nonshared environmental factors on self-esteem, supporting earlier findings based on a classical twin design. Kandler et al. (Reference Kandler, Waaktaar, Mõttus, Riemann and Torgersen2019) demonstrated an increase of genetic variance in Big Five personality traits from late childhood to early adulthood.
Outlook
Molecular Genetic Extension/Saliva Collection
Twin studies/registries traditionally rely on comparing monozygotic with dizygotic twin pairs to measure the contributions of genes and environment to a specific trait. However, there are increasing efforts to genotype twins, because molecular genetic data offer additional possibilities for analyzing how genes and environment and their combinations (gene–environment correlation and interaction) influence a specific trait (Boomsma et al., Reference Boomsma, Busjahn and Peltonen2002), and this information can easily be integrated in standard social science modeling approaches. Respectively, there is a growing number of twin studies/registries that contain molecular genetic data, such as the Twins Early Development Study (Haworth et al., Reference Haworth, Davis and Plomin2013), the UK Adult Twin Registry (Spector & Williams, Reference Spector and Williams2006) or the Swedish Twin Registry (Magnusson et al., Reference Magnusson, Almqvist, Rahman, Ganna, Viktorin, Walum and Larsson2013). In parallel with the face-to-face survey wave 3, which started in 2018, saliva collection kits were given to twins, biological parents and siblings participating in TwinLife. The collection of saliva — in cooperation with the Universitätsklinikum Bonn — is part of the third TwinLife funding period, with a goal of adding molecular genetic data to the longitudinal survey data at a later time point. The planned genetic analyses comprise the construction of polygenic scores for a variety of phenotypes relevant to attainment and mobility as well as the computation of genomewide association studies for specific behavioral traits, which form the basis for subsequent single-nucleotide polymorphism-based heritability, genetic correlation and pathway analyses.
Microm
For particular analyses, the TwinLife sample can be matched with a range of neighborhood-related variables. These include information on spending power, type of building development, type of roads, age structure as well as Sinus-Geo-Milieus (reflecting dominant sociocultural diversity), phases of life, mobility and Microm typologies. The variables were calculated based on data collected by the data research and marketing firm Microm. Prospectively, these data will be accessible by special agreement.
Acknowledgments
The TwinLife Project is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) (grant number 220286500) awarded to Martin Diewald, Rainer Riemann and Frank M. Spinath. The TwinLife study (‘Genetic and social causes of life chances. A genetically informative, longitudinal study of the life course and individual development’) received ethical approval from the German Psychological Association (protocol numbers: RR 11.2009 and RR 09.2013).








