Abstract
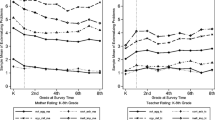
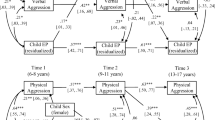
This study examined the infancy- and toddler-age precursors of children's later externalizing problem behavior. Risk constructs included suboptimal patterns of observed caregiver-child interaction and the caregiver's perception of child difficultness and resistance to control. In addition, a novel dimension of caregiver-child relationship quality, the caregiver's perception of her toddler's unresponsiveness to her, was examined as a possible precursor of children's externalizing behavior. Externalizing problem outcomes were assessed throughout the school-age period and again at age 17, using multiple informants. As toddlers, children at risk for later externalizing behavior were perceived as difficult and resistant to control, and relationships with their caregivers were relatively low in warmth and affective enjoyment. Finally, the caregiver's perception of her toddler as emotionally unresponsive to her was a consistent predictor of later externalizing behavior, suggesting that negative maternal cognitions associated with child conduct problems may begin in toddlerhood. These predictive patterns were similar for boys and girls, and with minor exceptions, generalized across different subdimensions of externalizing problem behavior. Our findings underscore the importance of the infancy and toddler periods to children's long-term behavioral adjustment, and indicate the desirability of further research into the nature of caregivers' early perceptions of child unresponsiveness.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. (1983). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and Revised Child Behavior Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1986). Manual for the Teacher's Report Form and Teacher Version of the Child Behavior Profile. Burlington, VT: Author.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Youth Self-Report and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT. University ofVermont, Dept. of Psychiatry.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Bates, J. E. (1987). Temperament in infancy. In J. D. Osofsky (Ed.), Handbook of infant development (2nd ed). New York: Wiley.
Bates, J. E., & Bayles, K. (1984). Objective and subjective components in mothers' perceptions of their children from 6 months to 3 years. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 30, 111-130.
Bates, J. E., & Bayles, K. (1988). The role of attachment in the development of behavior problems. In J. Belsky & T. Nezworski (Eds.), Clinical implications of attachment (pp. 253-299). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Bates, J. E., Bayles, K., Bennet, D. S., Ridge, B., & Brown, M. (1991). Origins of externalizing behavior problems at eight years of age. In D. J. Pepler & K. H. Rubin (Eds.), The development and treatment of childhood aggression (pp. 93-120). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Bates, J. E., Freeland, C. B., & Lounsbury, M. L. (1979). Measurement of infant difficultness. Child Development, 50, 794-803.
Bates, J. E., Maslin, C. A., & Frankel, K. A. (1985). Attachment security, mother-child interaction, and temperament as predictors of behavior problem ratings at age three years. In I. Bretherton & E. Waters (Eds.), Growing points in attachment theory and research (pp. 167-193). Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 50(1-2, Serial No. 209).
Bates, J. E., Olson, S. L., Pettit, G. S., & Bayles, K. (1982). Dimensions of individuality in the mother-infant relationship at six months of age. Child Development, 53, 445-461.
Bates, J. E., Pettit, G. S., Dodge, K. A., & Ridge, B. (1998). The interaction of temperamental resistance to control and restrictive parenting in the development of externalizing behavior. Developmental Psychology, 34, 51-67.
Bell, R. Q. (1968). A reinterpretation of the direction of effects in studies of socialization. Psychological Review, 75, 81-95.
Bickett, L. R., Milich, R., & Brown, R. T. (1996). Attributional styles of aggressive boys and their mothers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24, 457-472.
Campbell, S. B. (1990). Behavior problems in preschool children: Clinical and developmental issues. New York: Guilford Press.
Campbell, S. B., Pierce, E. W., March, C. L., Ewing, L. J., & Szumowski, E. K. (1994). Hard-to-manage preschool boys: Symptomatic behavior across contexts and time. Child Development, 65, 836-851.
Caspi, A., & Silva, P. (1995). Temperamental qualities at age 3 predict personality traits in young adilthood. Child Development, 66, 486-498.
Deater-Deckard, Dodge, Bates, & Pettit. (1998). Multiple risk factors in the development of externalizing behavior problems: Group and individual differences. Development and Psychopathology, 10, 469-493.
Dix, T., & Lochman, J. E. (1990). Social cognition and negative reactions to children: A comparison of mothers of aggressive and non-aggressive boys. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 9, 418-438.
Greenberg, M. T., Speltz, M., & DeKylen, M. (1993). The role of attachment in the early development of disruptive behavior problems. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 191-213.
Henry, B., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., & Silva, P. A. (1996). Temperamental and familial predictors of violent and nonviolent criminal convictions. Age 3 to age 18. Developmental Psychology, 32, 614-623.
Hinshaw, S. P. (1987). On the distinction between attentional deficits/hyperactivity and conduct problems/aggression in child psychopathology. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 443-463.
Hinshaw, S. P., Lahey, B. B., & Hart, E. (1993). Issues of taxonomy and comorbidity in the development of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 31-49.
Institute of Medicine. (1989). Research on children and adolescents with mental, behavioral, and developmental disorders.Washington, DC: National Academic Press.
Kazdin, A. E. (1987). Conduct disorder in childhood and adolescence. Newberry Park, CA: Sage.
Keenan, K., & Shaw, D. (1997). Developmental and social influences on young girls' early problem behaviors. Psychological Bulletin, 121, 95-113.
Lahey, B. B., Loeber, R., Quay, H. C., Frick, P. J., & Grimm, P. (1992). Oppositional defiant and conduct disorders: Issues to be resolved for DSM-IV. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 31, 539-546.
Lee, C. L., & Bates, J. E. (1985). Mother-child interaction at age two years and perceived difficult temperament. Child Development, 56, 1314-1325.
Loeber, R. (1990). Development and risk factors of juvenile antisocial behavior and delinquency. Clinical Psychology Review, 10, 1-41.
Loeber, R., Wung, P., Keenan, K., Giroux, B., Stouthamer-Loeber, M., Van Kammen, W. B., & Maughan, B. (1993). Developmental pathways in disruptive child behavior. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 103-133.
Loney, J. (1987). Hyperactivity and aggression in the diagnosis of attention deficit disorder. In B. B. Lahey & A. E. Kazdin (Eds.), Advances in clinical child psychology (Vol. 10, pp. 99-135). New York: Plenum Press.
Lyons-Ruth, K. (1996). Attachment relationships among children with aggressive behavior problems: The role of disorganized early attachment problems. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64, 64-73.
Lytton, H. (1990). Child and parent effects in boys' conduct disorder: A reinterpretation. Developmental Psychology, 26, 683-697.
McFayden-Ketchum, S. A., Bates, J., Dodge, K. A., & Pettit, G. S. (1996). Patterns of change in early childhood aggressive-disruptive behavior: Gender differences in predictions from early coercive and affectionate mother-child interactions. Child Development, 67, 2417-2433.
Moffitt, T. (1990). Juvenile delinquency and attention deficit disorder: Boys' developmental trajectories from age 3 to age 15. Child Development, 61, 893-910.
Olson, S. L., Bates, J. E., & Bayles, K. (1982). Maternal perceptions of infant behavior: A longitudinal, construct validation study. Infant Behavior and Development, 5, 397-410.
Olson, S. L., Bates, J. E., & Bayles, K. (1984). Mother-infant interaction and the development of individual differences in childen's cognitive competence. Developmental Psychology, 20, 166-179.
Olson, S. L., Bates, J. E., & Bayles, K. (1989). Predicting long-term developmental outcomes from maternal perceptions of infant and toddler behavior. Infant Behavior and Development, 12, 77-92.
Patterson, G. R., DeBarsyshe, B. D., & Ramsey, E. (1989). A developmental perspective on antisocial behavior. American Psychologist, 44, 329-335.
Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (1989). Family interaction patterns and children's behavior problems from infancy to age 4 years. Developmental Psychology, 24, 413-420.
Pettit, G. S., Bates, J. E., & Dodge, K. A. (1997). Supportive parenting, ecological context, and children's adjustment: A seven-year longitudinal study. Child Development, 68, 908-923.
Robins, L. (1991). Conduct disorder. Journal of Child Psychiatry and Psychology, 32, 193-212.
Rothbart, M. K., & Bates, J. E. (1998). Temperament. In W. Damon and N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology (5th Ed., Vol. 3, pp. 105-176). New York: Wiley.
Rothbaum, F., & Weisz, J. R. (1994). Parental caregiving and child externalizing behavior in nonclinical samples: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 116, 55-74.
Sameroff, A. J. (1995). General systems theories and developmental psychopathology. In D. Cicchetti and D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of development and psychopathology. New York: Wiley.
Sanson, A., Smart, D., Prior, M., & Oberklaid, F. (1993). Precursors of hyperactivity and aggression. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 32, 1207-1216.
Shaw, D. S., & Bell, R. Q. (1993). Developmental theories of parental contributors to antisocial behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 21, 493-518.
Shaw, D. S., Owens, E. B., Vondra, J. I., Keenan, K., & Winslow, E. (1996). Early risk factors and pathways in the development of disruptive behavior problems. Development & Psychopathology, 8, 679-699.
Shaw, D. S., Winslow, E. B., Owens, E. B., Vondra, J. I., Cohn, J. F., & Bell, R. Q. (1998). The development of early externalizing problems among children from low-income families:Atransformational perspective. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26, 95-107.
Wilkinson, L. (1989). SYSTAT: The system for statistics. Evanston, IL: SYSTAT, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, S.L., Bates, J.E., Sandy, J.M. et al. Early Developmental Precursors of Externalizing Behavior in Middle Childhood and Adolescence. J Abnorm Child Psychol 28, 119–133 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005166629744
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005166629744