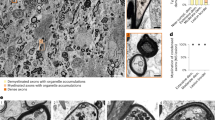
Abstract
Myelination provides extrinsic trophic signals that influence normal maturation and long-term survival of axons. The extent of axonal involvement in diseases affecting myelin or myelin forming cells has traditionally been underestimated. There are, however, many examples of axon damage as a consequence of dysmyelinating or demyelinating disorders. More than a century ago, Charcot described the pathology of multiple sclerosis (MS) in terms of demyelination and relative sparing of axons. Recent reports demonstrate a strong correlation between inflammatory demyelination in MS lesions and axonal transection, indicating axonal loss at disease onset. Disruption of axons is also observed in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus disease, two animal models of inflammatory demyelinating CNS disease. A number of dysmyelinating mouse mutants with axonal pathology have provided insights regarding cellular and molecular mechanisms of axon degeneration. For example, the myelin-associated glycoprotein and proteolipid protein have been shown to be essential for mediating myelin-derived trophic signals to axons. Patients with the inherited peripheral neuropathy Charcot-Marie Tooth disease type 1 develop symptomatic progressive axonal loss due to abnormal Schwann cell expression of peripheral myelin protein 22. The data summarized in this review indicate that axonal damage is an integral part of myelin disease, and that loss of axons contributes to the irreversible functional impairment observed in affected individuals. Early neuroprotection should be considered as an additional therapeutic option for these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguayo, A., Attiwell, M., Trecarten, J., Perkins, S. & Bray, G. (1977) Abnormal myelination in transplanted Trembler mouse Schwann cells. Na ture 265, 73–75.
Anderson, T. J., Schneider, A., Barrie, J. A., Klugmann, M., Mcculloch, M. C., Kirkham, D., Kyriakides, E., Nave, K.-A. & Griffiths, I. R. (1998) Late-onset neurodegeneration in mice with increased dosage of the proteolipid protein gene. Journal of Comparative Neurology 394, 506–519.
Anzini, P., Neuberg, D. D.-H., Schachner, M., Nelles, E., Willecke, K., Zielasek, J., Toyka, K. V., Suter, U. & Martini, R. (1997) Structural abnormalities and deficient maintenance of peripheral nerve myelin in mice lacking the gap junction protein connexin 32. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 4545–4551.
Arnold, D. L., Reiss, G. T., Matthews, P. M., Francis, G. S., Collins, D. L., Wolfson, C. & Antel, J. P. (1994) Use of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy for monitoring disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology 36, 76–82.
Arquint, M., Roder, J., Chia, L.-S., Down, J., Wilkinson, O., Bayley, H., Braun, P. & Dunn, R. (1987) Molecular cloning and primary structure of myelin-associated glycoproteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 600–604.
Barnes, D., Munro, P. M. G., Youl, B. D., Prineas, J. W. & Mcdonald, W. I. (1991) The longstandingMS lesion. Brain 114, 1271–1280.
Bell, J. I. & Lathrop, G. M. (1996) Multiple loci for multiple sclerosis. Nature Genetics 13, 377–378.
Bergoffen, J., Scherer, S. S., Wang, S., Oronzi scott, M., Bone, L. J., Paul, D. L., Chen, K., Lensch, M. W., Chance, P. F. & Fischbeck, K. H. (1993) Connexin mutations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Science 262, 2039–2042.
Bjartmar, C., Rudick, R., MÖrk, S. & Trapp, B. D. (1999) Axonal transection in multiple sclerosis [abstract]. Journal of Neurochemistry 72, S40.
Bradley, W. G. (1987) Recent viewsonamyotrophic lateral sclerosis with emphasis on electrophysiological studies. Muscle Nerve 10, 490–502.
Brown, A., Mcfarlin, D. E. & Raine, C. S. (1982) Chronologic neuropathology of relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Laboratory Investigation 46, 171–185.
BÖ, L., MÖrk, S., Kong, P. A., Nyland, H., Pardo, C. A. & Trapp, B. D. (1994) Detection of MHC class II-antigens on macrophages and microglia, but not on astrocytes and endothelia in active multiple sclerosis lesions. Journal of Neuroimmunology 51, 135–146.
Catterall, W. A. (1984) The molecular basis of neuronal excitability. Science 223, 653–661.
Charcot, M. (1868) Histologie de le sclerose en plaques. Gazette Hopitaux 141, 554–558.
Colello, R. J. & Pott, U. (1997) Signals that initiate myelination in the developing mammalian nervous system. Molecular Neurobiology 15, 83–100.
Collins, B. E., Yang, L. J.-S., Mukhopadhyay, G., Filbin, M. T., Kiso, M., Hasegawa, A. & Schnaar, R. L. (1997) Sialic acid specificity of myelinassociated glycoprotein binding. Journal of Biological Chemistry 272, 1248–1255.
Davie, C. A., Hawkins, C. P., Barker, G. J., Brennan, A., Tofts, P. S., Miller, D. H. & McDonald, W. I. (1994) Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in acute multiple sclerois lesions. Brain 117, 49–58.
Davie, C. A., Barker, G. J., Webb, S., Tofts, P. S., Thompson, A. J., Harding, A. E., Mcdonald, W. I. & Miller, D. H. (1995) Persistent functional deficit in multiple sclerosis and autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia is associated with axon loss. Brain 118, 1583–1592.
De Stefano, N., Matthews, P. M., Antel, J. P., Preul, M., Francis, G. & Arnold, D. L. (1995) Chemical pathology of acute demyelinating lesions and its correlation with disability. Annals of Neurology 38, 901–909.
De Stefano, N., Matthews, P. M., Fu, L., Narayanan, S., Stanley, J., Francis, G. S., Antel, J. P. & Arnold, D. L. (1998) Axonal damage correlates with disability in patients with relapsingremitting multiple sclerosis. Results of a longitudinal magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Brain 121, 1469–1477.
De waegh, S. M. & Brady, S. T. (1990) Slow axonal transport in Trembler mouse: Altered cytoskeletal dynamics in a myelin deficient mouse model. Journal of Neuroscience 10, 1855–1865.
De waegh, S. M. & Brady, S. T. (1991) Local control of axonal properties by Schwann cells: Neurofilaments and axonal transport in homologous and heterologous nerve grafts. Journal of Neuroscience Reserch 30, 201–212.
De waegh, S. M., Lee, V. M.-Y. & Brady, S. T. (1992) Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal caliber, and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells. Cell 68, 451–463.
Dugandzija-novakovic, S., Koszowski, A. G., Levinson, S. R. & Shrager, P. (1995) Clustering of Na+ channels and node of Ranvier formation in remyelinating axons. Journal of Neuroscience 15, 492–503.
Duncan, I. D., Hammang, J. P. & Trapp, B. D. (1988) Abnormal compact myelin in the myelin-deficient rat: Absence of proteolipid protein correlates with a defect in the intraperiod line. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 6287–6291.
Drescher, K. M., Pease, L. R. & Rodriques, M. (1997) Antiviral immune responses modulate the nature of central nervous system (CNS) disease in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. Immunological Reviews 159, 177–193.
Dyck, P. J., Karnes, J. L. & Lambert, E. H. (1989) Longitudinal study of neuropathic deficits and nerve conduction abnormalities in hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 1. Neurology 39, 1302–1308.
Dyck, P. J., Chance, P., Lebo. R. & Carney, J. A. (1993) Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies. In Peripheral neuropathy, 3rd ed. (edited by Dyck, P. J., Thomas, P. K., Griffin, J. W., Low, P. A. & Poduslo, J. F.), pp. 1094–1136. Philadelphia: WB Saunders.
Ebers, G. C. & Dyment, D. A. (1998) Genetics of multiple sclerosis. Seminars in Neurology 18, 295–299.
Ferguson, B., Matyszak, M. K., Esiri, M. M. & Perry, V. H. (1997) Axonal damage in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 120, 393–399.
Friedman, B., Scherer, S. S., Rudge, J. S., Helgren, M., Morrisey, D., Mcclain, J., Wang, D., Wiegand, S. J., Furth, M. E., Lindsay, R. M. & Ip, N. Y. (1992) Regulation of ciliary neurotrophic factor expression in myelin-related Schwann cells in vivo. Neuron 9, 295–305.
Fu, L., Matthews, P. M., De stefano, N., Worsley, K. J., Narayanan, S., Francis, G. S., Antel, J. P., Wolfson, C. & Arnold, D. L. (1998) Imaging axonal damage of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Brain 121, 103–113.
Giese, K. P., Martini, R., Lemke, G., Soriano, P. & Schachner, M. (1992) Mouse P0 gene disruption leads to hypomyelination, abnormal expression of recognition molecules, and degeneration of myelin and axons. Cell 71, 565–576.
Greenfield, J. G. & King, L. S. (1936) Observations on the histopathology of the cerebral lesions in disseminated sclerosis. Brain 59, 445–458.
Griffiths, I. R., Schneider, A., Anderson, J. & Nave, K.-A. (1995) Transgenic and natural mouse models of proteolipid protein (PLP) related dysmyelination and demyelination. Brain Pathology 5, 275–281.
Griffiths, I., Klugmann, M., Anderson, T., Yool, D., Thomson, C., Schwab, M. H., Schneider, A., Zimmermann, F., McCulloch, M., Nadon, N. & Nave, K.-A. (1998) Axonal swellings and degeneration in mice lacking the major proteolipid of myelin. Science 280, 1610–1613.
Hafer-macko, C., Hsieh, S.-T., Li, C. Y., Ho, T. W., Sheikh, K., Cornblath, D. R., Mckhann, G. M., Asbury, A. K. & Griffin, J. W. (1996) Acute motor axonal neuropathy: An antibody-mediated attack on axolemma. Annals of Neurology 40, 635–644.
Hanemann, C. O. & MÖller, H. W. (1998) Pathogenesis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth IA (CMTIA) neuropathy. Trends in Neuroscience 21, 282–286.
Hayasaka, K., Himoro, M., Sato, W., Takada, G., Uyemura, K., Shimizu, N., Bird, T. D., Coneally, P. M. & Chance, P. F. (1993) Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1B is associated with mutations of the myelin P0 gene. Nature Genetics 5, 31–34.
Helynck., G., Luu, B., Nussbaum, J. L., Picken, D., Skalidis, G., Trifilieff, E., Van dorsselaer, A., Seta, P., Sandeaux, R., Gavach, C., Heitz, F., Simon, D. & Spach, G. (1983) Brain proteolipids. Isolation, purification and effect on ionic permeability of membranes. European Journal of Biochemistry 133, 689–695.
Hildebrand, C., Remahl, S., Persson, H. & Bjartmar, C. (1993) Myelinated nerve fibres in the CNS. Progress in Neurobiology 43, 85–141.
Ho, T. W., Mckhann, G. M. & Griffin, J. W. (1998) Human autoimmune neuropathies. Annual Review of Neuroscience 21, 187–226.
Hodes, M. E., Pratt, V. M. & Dlouhy, S. R. (1993) Genetics of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Developmental Neuroscience 15, 383–394.
Hohlfeld, R. (1997) Biotechnological agents for the immunotherapy of multiple sclerosis. Principles, problems and perspectives [invited review]. BRAIN 120, 865–916.
Inoue, K., Osaka, H., Imaizumi, K., Nezu, A., Takanashi, J., Arii, J., Murayama, K., Ono, J., Kikawa, Y., Mito, T., Shaffer, L. G. & Lupski, J. R. (1999) Proteolipid protein gene duplications causing Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: Molecular mechanism and phenotypic manifestations. Annals of Neurology 45, 624–632.
Kaplan, M. R., Meyer-franke, A., Lambert, S., Bennett, V., Duncan, I. D., Levison, S. R. & Barres, B. A. (1997) Induction of sodium channel clustering by oligodendrocytes. Nature 386, 724–728.
Kidd, D., Thorpe, J. W., Thompson, A. J., Kendall, B. E., Moseley, I. F., Macmanus, D. G., Mcdonald, W. I. & Miller, D. H. (1993) Spinal cord MRI using multi-array coils and fast spin echo. II. Findings in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 43, 2632–2637.
Kirkpatrick, L. L. & Brady, S. T. (1994) Modulation of the axonal microtubule cytoskeleton by myelinating Schwann cells. Journal of Neuroscience 14, 7440–7450.
Kitagawa, K., Sinoway, M. P., Yang, C., Gould, R. M. & Colman, D. R. (1993) A proteolipid protein gene family: expression in sharks and rays and possible evolution from an ancestral gene encoding a poreforming polypeptide. Neuron 11, 433–448.
Koo, E. H., Sisodia, S. S., Archer, D. R., Martin, L. J., Weidemann, A., Beyreuther, K., Fischer, P., Masters, C. L. & Price, D. L. (1990) Precursor of amyloid protein in Alzheimer disease undergoes fast anterograde axonal transport. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 87, 1561–1565.
Lai, C., Brow, M. A., Nave, K.-A., Noronha, A. B., Quarles, R. H., Bloom, F. E., Milner, R. J. & Sutcliffe, J. G. (1987) Two forms of 1B236/myelinassociated glycoprotein (MAG), a cell adhesion molecule for postnatal neural development, are produced by alternative splicing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 4337–4341.
Li, C., Tropak, M. B., Gerial, R., Clapoff, S., Abramow-newerly, W., Trapp, B., Peterson, A. & Roder, J. (1994) Myelination in the absence of myelin-associated glycoprotein. Nature 369, 747–750.
Li, M., Shibata, A., Li, C., Braun, P. E., McKerracher, L., Roder, J., Kater, S. B. & David, S. (1996) Myelin-associated glycoprotein inhibits neurite/axon growth and causes growth cone collapse. Journal of Neuroscience Research 46, 404–414.
Linington, C. (1998) Experimental animal models. In Immunotherapy in Neuroimmunologic Diseases, (edited by Zhang, J., Hafler, D., Hohlfeld, R. & Miller, A.), pp. 11–28. London: Martin Dunitz.
Lloyd, K. G. (1977) CNS compensation to dopamine neuron loss in Parkinson's disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 90, 255–266.
Losseff, N. A., Webb, S. L., O'riordan, J. I., Page, R., Wang, L., Barker, G. J., Tofts, P. S., McDonald, W. I., Miller, D. H. & Thompson, A. J. (1996a) Spinal cord atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. A new reproducible and sensitive MRI method with potential to monitor disease progression. Brain 119, 701–708.
Losseff, N. A., Wang, L., Lai, H. M., Yoo, D. S., Gawne-cain, M. L., Mcdonald, W. I., Miller, D. H. & Thompson, A. J. (1996b) Progressive cerebral atrophy in multiple sclerosis. A serial MRI study. Brain 119, 2009–2019.
Losseff, N. A. & Miller, D. H. (1998) Measures of brain and spinal cord atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 64, S102–S105.
Low, P. A. & Mcleod, J. G. (1975) Hereditary demyelination neuropathy in the Trembler mouse. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 26, 565–574.
Lublin, F. D. & Reingold, S. C. (1996) Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. Neurology 46, 907–911.
Matthews, P. M., Pioro, E., Narayanan, S., De Stefano, N., Fu, L., Francis, G., Antel, J., Wolfson, C. & Arnold, D. L. (1996) Assessment of lesion pathology in multiple sclerosis using quantitative MRI morphometry and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Brain 119, 715–722.
Matthews, P. M., De stefano, N., Narayanan, S., Francis, G. S., Wolinsky, J. S., Antel, J. P. & Arnold, D. L. (1998) Putting magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in context: Axonal damage and disability in multiple sclerosis. Seminars in Neurology 18, 327–336.
Mcfarland, H. F., Frank, J. A., Albert, P. S., Smith, M. E., Martin, R., Harris, J. O., Patronas, N., Maloni, H. & Mcfarlin, D. E. (1992) Using gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging lesions to monitor disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology 32, 758–766.
Mckerracher, L., David, S., Jackson, D. L., Kottis, V., Dunn, R. J. & Braun, P. E. (1994) Identification of myelin-associated glycoprotein as a major myelin-derived inhibitor of neurite growth. Neuron 13, 805–811.
Mews, I., Bergmann, M., Bunkowski, S., Gullotta, F. & BrÑck, W. (1998) Oligodendrocyte and axon pathology in clinically silent multiple sclerosis lesions. Multiple Sclerosis 4, 55–62.
Montag, D., Giese, K. P., Bartsch, U., Martini, R., Lang, Y., BlÑthmann, H., Karthigasan, J., Kirschner, D. A., Wintergerst, E. S., Nave, K.-A., Zielasek, J., Toyka, K. V., Lipp, H.-P. & Schachner, M. (1994) Mice deficient for the myelinassociated glycoprotein show subtle abnormalities in myelin. Neuron 13, 229–246.
Mukhopadhyay, G., Doherty, P., Walsh, F. S., Crocker, P. R. & Filbin, M. T. (1994) A novel role for myelin-associated glycoprotein as an inhibitor of axonal regeneration. Neuron 13, 757–767.
Narayanan, S., Fu, L., Pioro, E., De stefano, N., Collins, D. L., Francis, G. S., Antel, J. P., Matthews, P. M. & Arnold, D. L. (1997) Imaging of axonal damage in multiple sclerosis: spatial distribution of magnetic resonance imaging lesions. Annals of Neurology 41, 385–391.
Njenga, M. K., Murray, P. D., Mcgavern, D., Lin, X., Drescher, K. M. & Rodriguez, M. (1999) Absence of spontaneous central nervous system remyelination in class II-deficient mice infected with Theiler's virus. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 58, 78–91.
Notterpek, L. M. & Rome, L. H. (1994) Functional evidence for the role of axolemma in CNS myelination. Neuron 13, 473–485.
Oppenheimer, D. R. (1978) The cervical cord in multiple sclerosis. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 4, 151–162.
Owens, T. & Sriram, S. (1995) The immunology of multiple sclerosis and its animal model, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neurologic Clinics 13, 51–73.
Perkins, S., Aguayo, A. & Bray, G. (1981) Behaviour of Schwann cells from Trembler mouse unmyelinated fibers transplanted into myelinated nerves. Experimental Neurology 71, 515–526.
Prineas, J. W. & Mcdonald, W. I. (1997) Demyelinating diseases. In Greenfield's Neuropathology, 6th ed. (edited by Graham, D. I. & Lantos, P. L.), pp. 813–881. International Society of Neuropathology.
Powell, H. C. & Myers, R. R. (1996) The axon in Guillain-Barr, syndrome: Immune target or innocent bystander? Annals of Neurology 39, 4–5.
Putnam, T. J. (1936) Studies in multiple sclerosis. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 35, 1289–1308.
Raine, C. S. (1984) Biology of disease. Analysis of autoimmune demyelination: its impact upon multiple sclerosis. Laboratory Investigation 50, 608–635.
Raine, C. S. & Cross, A. H. (1989) Axonal dystrophy as a consequence of long-term demyelination. Laboratory Investigation 60, 714–725.
Ritchie, J. M. (1984) Physiological basis of conduction in myelinated nerve fibers. In Myelin (edited by Morell, P.), pp. 117–146. New York: Plenum Press.
Rivera-quinones, C., Mcgavern, D., Schmelzer, J. D., Hunter, S. F., Low, P. A. & Rodriguez, M. (1998) Absence of neurological deficits following extensive demyelination in a class I-deficient murine model of multiple sclerosis. Nature Medicine 4, 187–193.
Rodriguez, M., Olezak, E. & Leibowitz, J. (1987) Theiler'smurine encephalomyelitis:Amodel of demyelination and persistence of virus. Critical Reviews in Immunology 7, 325–365.
Rosenbluth, J. (1988) Role of glial cells in the differentiation and function of myelinated axons. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 6, 3–24.
Rudick, R., Cohen, J. A., Weinstock-guttman, B., Kinkel, R. P. & Ransohoff, R. M. (1997) Management of Multiple Sclerosis. New England Journal of Medicine 337, 1604–1611.
Sahenk, Z. & Chen, L. (1998) Abnormalities in the axonal cytoskeleton induced by a Connexin32 mutation in nerve xenografts. Journal of Neuroscience Research 51, 174–184.
Sahenk, Z., Chen, L. & Mendell, J. R. (1999) Effects of PMP22 duplication and deletions on the axonal cytoskeleton. Annals of Neurology 45, 16–24.
Salzer, J. L., Holmes, W. P. & Colman, D. R. (1987) The amino acid sequences of the myelin-associated glycoproteins: homology to the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Journal of Cell Biology 104, 957–965.
Sanchez, I., Hassinger, L., Paskevich, P. A., Shine, H. D. & Nixon, R. A. (1996) Oligodendroglia regulate the regional expansion of axon caliber and local accumulation of neurofilaments during development independently of myelin formation. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 5095–5105.
Scherer, S. (1999) Axonal pathology in demyelinating diseases. Annals of Neurology 45, 6–7.
Scherer, S. S., Xu, Y. T., Nelles, E., Fischbeck, K. & Bone, L. J. (1998) Connexin32-null mice develop demyelinating peripheral neuropathy. Glia 24, 8–20.
Seitelberger, F. (1995) Neuropathology and genetics of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain Pathology 5, 267–273.
Sheikh, K. A., Sun, J., Kawai, H., Crawford, T. O., Proia, R. L., Griffin, J. W. & Schnaar, R. L. (1999) Mice lacking complex gangliosides develop Wallerian degeneration and myelination defects. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 96, 7532–7537.
Sternberger, N. H., Quarles, R. H., Itoyama, Y. & Webster, H. D. (1979) Myelin-associated glycoprotein demonstrated immunocytochemically in myelin and myelin forming cells of developing rats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 76, 1510–1514.
Tasaki, I. (1982) Physiology and Electrochemistry of Nerve Fibers. New York: Academic.
Trapp, B. D., Andrews, S. B., Cootauco, C. & Quarles, R. H. (1989) The myelin-associated glycoprotein is enriched in multivesicular bodies and periaxonal membranes of actively myelinating oligodendrocytes. Journal of Cell Biology 109, 2417–2426.
Trapp, B. D., Peterson, J., Ransohoff, R. M., Rudick, R., MÖrk, S. & BÖ, L. (1998) Axonal transection in the lesions of multiple sclerosis. New England Journal of Medicine 338, 278–285.
Trapp, B. D., Ransohoff, R. M., Fisher, E. & Rudick, R. (1999) Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis: relationship to neurological disability. The Neuroscientist 5, 48–57.
Voyvodic, J. T. (1989) Target size regulates calibre and myelination of sympathetic axons. Nature 342, 430–433.
Waxman, S. G. (1998) Demyelinating diseasesÑnew pathological insights, new therapeutic targets. New England Journal of Medicine 338, 223–225.
Windenbank, A. J., Wood, P., Bunge, R. P. & Dyck, P. J. (1985) Myelination determines the caliber of dorsal root ganglion neurons in culture. Journal of Neuroscience 5, 1563–1569.
Yang, L. J.-S., Zeller, C. B., Shaper, N. L., Kiso, M., Hasegawa, A., Shapiro, R. E. & Schnaar, R. L. (1996) Gangliosides are neuronal ligands for myelin-associated glycoprotein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 93, 814–818.
Yin, X., Crawford, T. O., Griffin, J. W., Tu, P., Lee, V. M.-Y., Li, C., Roder, J. & Trapp, B. D. (1998) Myelin-associated glycoprotein is a myelin signal that modulates the caliber of myelinated axons. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 1953–1963.
Yu, M., Nishiyama, A., Trapp, B. D., Tuohy, V. (1996) Interferon-β inhibits progression of relapsingremitting experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Neuroimmunology 64, 91–100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bjartmar, C., Yin, X. & Trapp, B.D. Axonal pathology in myelin disorders. J Neurocytol 28, 383–395 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007010205037
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007010205037