Abstract
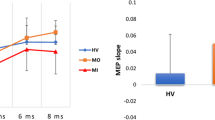
Migraine patients are characterized by increased amplitudes of slow cortical potentials (SCPs), representing pronounced excitability of cortical networks. The present study investigated the efficiency of biofeedback training of SCPs in young migraineurs. Ten children suffering from migraine without aura participated in 10 feedback sessions. They were compared with 10 healthy children for regulation abilities of cortical negativity and with 10 migraineurs from the waiting list for clinical efficacy. During the first two sessions, the migraine children were characterised by lacking ability to control cortical negativity, especially during transfer trials, compared with healthy controls. However, there was no difference following 10 sessions of training. Feedback training was accompanied by significant reduction of cortical excitability. This was probably responsible for the clinical efficacy of the training; a significant reduction of days with migraine and other headache parameters was observed. It is suggested that normalization of the threshold regulation of cortical excitability during feedback training may result in clinical improvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL/4–18, YSR, and TRF profiles. Burlington, VT, University of Vermont.
Afra, J., Marcia, A., Gerard, P., Maertens de Noordhout, A., & Schoenen, J. (1998). Interictal cortical excitability in migraine: A study using transcranial magnetic stimulation of motor and visual cortices. Annals of Neurology, 44, 209-215.
Afra, J., Proietti Cecchini, A., De Pasqua, V., Albert, A., & Schoenen, J. (1998). Visual evoked potentials during long periods of pattern-reversal stimulation in migraine. Brain, 121, 233-241.
Aurora, S. K., Ahmad, B. K., Welch, K. M., Bhardhwaj, P., & Ramadan, N. M. (1998). Transkranial magnetic stimulation confirms hyperexcitability of occipital cortex in migraine. Neurology, 50, 1111-1114.
Barkley, G. L., Tepley, N., Simkins, R., Moran, J., & Welch, K. M. A. (1990). Neuromagnetic fields in migraine: Preliminary findings. Cephalalgia, 10, 171-176.
Besken, E., Pothmann, R., & Sartory, G. (1993). Contingent negative variation in childhood migraine. Cephalalgia, 13, 42-43.
Birbaumer, N., Elbert, T., Canavan, A., & Rockstroh, B. (1990). Slow potentials of the cerebral cortex and behavior. Physiological Review, 70, 1-41.
Birbaumer, N., Roberts, L. E., Lutzenberger, W., Rockstroh, B., & Elbert, T. (1992). Area-specific self-regulation of slow cortical potentials on the sagittal midline and its effects on behavior. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 84, 354-361.
Böcker, K. B. E., Timsit-Berthier, M., Schoenen, J., & Brunia, C. H. M. (1990). Contingent negative variation in migraine. Headache, 30, 604-609.
Brody, S., Rau, H., Köhler, F., Schupp, H., Lutzenberger, W., & Birbaumer, N. (1994). Slow cortical potential biofeedback and the startle reflex. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 19, 1-11.
Buggle, F., & Baumgärtel, F. (1972). Hamburger Neurotizismus-und Extraversionsskala für Kinder und Jugendliche. Göttingen: Hogrefe Verlag.
Del Bene, E. (1982). Multiple aspects of headache risk in children. In M. D. Critchley, A. P. Friedman, S. Gorini, & F. Sicuteri (Eds.), Advances in neurology (pp. 187-198). New York: Raven Press.
Diener, C. H., Scholz, E., Dichgans, J., & Gerber, W. D. (1989). Central effects of drugs used in migraine prophylaxis evaluated by visual evoked potentials. Annals of Neurology, 25, 125-130.
Elbert, T. (1993). Slow cortical potentials reflect the regulation of cortical excitability. In W. C. McCallum & H. Curry (Eds.), Slow potentials in the human brain (pp. 235-252). New York: Plenum Press.
Elbert, T., & Rockstroh, B. (1987). Threshold regulation—A key to the understanding the combined dynamics of EEG and event-related potentials. Journal of Psychophysiology, 4, 317-333.
Elbert, T., Rockstroh, B., Lutzenberger, W., & Birbaumer, N. (1980). Biofeedback of slow cortical potentials. I. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 48, 293-301.
Evers, S., Bauer, B., Grotemeyer, K., Kurlemann, G., & Husstedt, I. W. (1998). Event-related potentials (P300) in primary headache in childhood and adolescence. Journal of Child Neurology, 13, 322-326.
Evers, S., Bauer, B., Suhr, B., Husstedt, I. W., & Grotemeyer, K. H. (1997). Cognitive processing in primary headache: A study on event-related potentials. Neurology, 48, 108-113.
Evers, S., Quibelday, F., Grotemeyer, K-H., Suhr, B., & Husstedt, I-W. (1999). Dynamic changes of cognitive habituation and serotonin metabolism during the migraine interval, Cephalalgia, 19, 485-491.
Ferrari, M. D. (1998). Migraine. Lancet, 351, 1043-1051.
Ferrari, M. D., Odink, J., & Bos, K. D. (1990). Neuro-excitatory plasma aminoacids are elevated in migraine. Neurology, 40, 1582-1586.
Ferrari, M., & Saxena, P. R. (1993). On serotonin and migraine: A clinical and pharmacological review. Cephalalgia, 13, 151-165.
Gerber, W. D., & Schoenen, J. (1998). Biobehavioral correlates in migraine: The role of hypersensitivity and information-processing dysfunction. Cephalalgia, 18,Suppl. 21, 5-11.
Goadsby, P. J. (1997). Bench to bedside: What have we learnt recently about headache? Current Opinions in Neurology, 10, 215-220.
Hermann, C., Kim, M., & Blanchard, E. B. (1995). Behavioral and prophylactic pharmacological intervention studies of paediatric migraine: An exploratory meta-analysis. Pain, 60, 239-255.
Kotchoubey, B., Schneider, D., Schleichert, H., Stehl, U., Uhlmann, C., Blankenhorn, V., Froscher, W., & Birbaumer, N. (1996). Self-regulation of slow cortical potentials in epilepsy: A retrial with analysis of influencing factors. Epilepsy Research, 25, 269-276.
Kratzmeier, H., & Horn, R. (1979). Paven Standard Progressive Matrices (German Edition). Berlin: Beltztest.
Kropp, P., & Gerber, D. (1993). Is increased amplitude of contingent negative variation in migraine due to cortical hyperactivity or to reduced habituation? Cephalalgia, 13, 37-41.
Kropp, P., & Gerber, W. D. (1995). Contingent negative variation during migraine attack and interval: Evidence for normalisation of slow cortical potentials during the attack. Cephalalgia, 15, 123-128.
Kropp, P., & Gerber, W. D. (1998). Prediction of migraine attacks using a slow cortical potential, the contingent negative variation. Neuroscience Letters, 257, 73-76.
Lodi, R., Montagna, P., Soriani, S., Iotti, S., Arnaldi, C., Cortelli, P., Pierangeli, G., Patuelli, A., Zaniol, P., & Barbiroli, B. (1997). Deficit of brain and sceletal muscle bioenergetics and low brain magnesium in juvenile migraine: An in vivo 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Paediatric Research, 42, 866-871.
Lutzenberger, W., Elbert, T., Rockstroh, B., & Birbaumer, N. (1982). Biofeedback produced slow brain potentials and task performance. Biological Psychology, 14, 99-111.
Lutzenberger, W., Haag, G., Birbaumer, N., & Stegagno, L. (1980). Biofeedback langsamer kortikaler Potentiale (LKP): Der Zusammenhang von LKP und Reaktionslatenz bei Patienten mit psychosomatischen Störungen. Medizinische Psychologie, 6, 140-151.
Lutzenberger, W., Roberts, L. E., & Birbaumer, N. (1993). Memory performance and area-specific self-regulation of slow cortical potentials: Dual-task interference. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 15, 217-226.
Maertens de Noordhout, A., Timsit-Berthier, M., Timsit, M., & Schoenen, J. (1987). Contingent negative variation in headache. Annals of Neurology, 19, 78-80.
Maertens de Noordhout, A., Timsit-Berthier, M., Timsit, M., & Schoenen, J. (1988). Effects of beta blockade on contingent negative variation in migraine. Annals of Neurology, 21, 111-112.
Maytal, J., Young, M., Shechter, A., & Lipton, R. B. (1997). Pediatric migraine and the International Headache Society criteria. Neurology, 48, 602-607.
Rockstroh, B. (1987). Operant control of slow brain potentials. In J. N. Hengtgen, D. Hellhammer, & G. Huppmann (Eds.), Advanced Methods in Psychobiology (pp. 179-190). C. J. Hogrefe, Inc.
Rockstroh, B., Elbert, T., Birbaumer, N., & Lutzenberger, W. (1990). Biofeedback-produced hemispheric asymmetry of slow cortical potentials and its behavioral effects. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 9, 151-165.
Rockstroh, B., Elbert, T., Birbaumer, N., Wolf, P., Düchting-Röth, A., Reker, M., Daum, I., Lutzenberger, W., & Dichgans, J. (1993). Cortical self-regulation in patients with epilepsies. Epilepsy Research, 14, 63-72.
Rockstroh, B., Elbert, T., Lutzenberger, W., & Birbaumer, N. (1980). Slow cortical potentials and response speed. In H. H. Kornhuber & L. Deecke (Eds.), Motivation, motor and sensory processes of the brain: Electrical potentials, behavior and clinical use (pp. 431-434). North-Holland: Elsevier.
Rockstroh, B., Elbert, T., Lutzenberger, W., & Birbaumer, B. (1982). The effect of slow cortical potentials on response speed. Psychophysiology, 19, 211-217.
Rockstroh, B., Elbert, T., Lutzenberger, W., & Birbaumer, N. (1990). Biofeedback: Evaluation and therapy in children with attentional dysfunction. In A. Rothenberger (Ed.), Brain and Behaviour in Child Psychiatry (pp. 345-357). Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Roberts, L. E., Birbaumer, N., Rockstroh, B., Lutzenberger, W., & Elbert, T. (1989). Self-report during feedback regulation of slow cortical potentials. Psychophysiology, 26, 392-403.
Sartory, G., Besken, E., & Pothmann, R. (1997). Contingent negative variation in childhood migraine. Journal of Psychophysiology, 11, 138-146.
Schneider, F., Elbert, T., Heimann, H., Welker, A., Stetter, F., Mattes, R., Birbaumer, N., & Mann, K. (1993). Self-regulation of slow cortical potentials in psychiatric patients: Alcohol dependency. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 18, 23-32.
Schneider, F., Rockstroh, B., Heimann, H., Lutzenberger, W., Mattes, R., Elbert, T., Birbaumer, N., & Bartels, M. (1992). Self-regulation of slow cortical potentials in psychiatric patients: Schizophrenia. Biofeed-back and Self-Regulation, 17, 292-312.
Schoenen, J. (1996). Abnormal cortical information processing between migraine attacks. In M. Sandler, M. Ferrari, & S. Harnett (Eds.), Migraine: Pharmacology and genetics (pp. 233-253). London: Altman.
Schoenen, J. (1998). The pathophysiology of migraine: A review based on the literature and on personal contributions. Functional Neurology, 1, 7-16.
Siniatchkin, M., Gerber, W. D., Kropp, P., & Vein, A. (1999). How the brain anticipates an attack—A study of neurophysiological periodicity in migraine. Functional Neurology, 14, 69-77.
Siniatchkin, M., Gerber, W. D., & Vein, A. (1998). Clinical efficacy and central mechanisms of cyclandelate in migraine: A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Functional Neurology, 13, 47-56.
Siniatchkin, M., Kropp, P., Gerber, W. D., & Vein, A. (1998). Contingent negative variation in patients with chronic daily headache. Cephalalgia, 18, 565-569.
Speckmann, E. J., Caspers, H., & Elger, C. E. (1984). Neuronal mechanisms underlying the generation of field potentials. In T. Elbert, B. Rockstroh, W. Lutzenberger, & N. Birbaumer (Eds.), Self-regulation of the brain and behavior (pp. 9-25). Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., & Lushene, R. E. (1970). Test manual for the State-Trait-Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Stiensmeier-Polster, J., Schürmann, M., & Duda, K. (1989). Depressionsinventar für Kinder und Jugendliche (DIKJ). Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Trimmel, M. (1987). Contingent negative variation (CNV) influenced by preceding slow potential shifts (pSPSs). Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 66, 71-74.
Van der Kamp, W., van den Brink, A., Ferrari, M. D., & van Dijk, J. G. (1996). Interictal cortical hyperexcitability in migraine patients demonstrated with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 139, 106-110.
Wang, W., & Schoenen, J. (1998). Interictal potentiation of passive “oddball” auditory event-related potentials in migraine. Cephalalgia, 18, 261-265.
Wang, W., Timsit-Berthier, M., & Schoenen, J. (1996). Intensity dependence of auditory evoked potentials is pronounced in migraine: An indication of cortical potentiation and low serotonergic neurotransmission. Neurology, 46, 1404-1409.
Welch, K. M. A. (1998). Current opinions in headache pathogenesis: Introduction and synthesis. Current Opinions in Neurology, 11, 193-197.
Welch, K. M. A., Cao, Y., Aurora, S., Wigins, G., & Vikingstad, E. M. (1998). MRI of the occipital cortex, red nucleus, and substantia nigra during visual aura of migraine. Neurology, 51, 1465-1469.
Welch, K. M. A., & Lewis, D. (1997). Migraine and epilepsy. Neurologicy Clinics, 15, 107-114.
Welch, K. M. A., & Ramadan, N. M. (1995). Mitochondria, magnesium and migraine. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 134, 9-14.
Weiller, C., May, A., Limmroth, V., Jupner, M., Kaube, V., Schayck, R. V., Coenen, H. H., & Diener, H. C. (1995). Brain stem activation in spontaneous human migraine attacks. Nature Medicine, 1, 658-660.
Woods, R. P., Iacoboni, M., & Mazziotta, J. C. (1994). Bilateral spreading cerebral hypoperfusion during spontaneous migraine attack. New England Journal of Medicine, 331, 1689-1692.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siniatchkin, M., Hierundar, A., Kropp, P. et al. Self-regulation of Slow Cortical Potentials in Children with Migraine: An Exploratory Study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 25, 13–32 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009581321624
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009581321624