Abstract
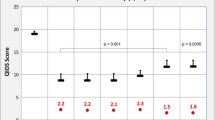
The study compared patients' satisfaction with psychiatric inpatient treatment between an open and a closed ward. During a six-month period, all voluntarily participating patients on two wards of a psychiatric University hospital were investigated anonymously at admission and/or before discharge. A self-rating questionnaire (SATQ-98) was used to assess satisfaction with several domains of psychiatric inpatient treatment. In total, 135 questionnaires were received (retrieval rate 49%). The general level of satisfaction with treatment was high. General satisfaction, satisfaction with medication, ward equipment, visiting opportunities, and regulations for going out were significantly lower at discharge on the closed ward. Dissatisfaction with medication was related to low actual mood, and to low satisfaction with the frequency of psychotherapeutic interventions, visiting opportunities, and with the treating doctor. The results thus far strongly support the need for patients' satisfaction with treatment to be taken into account in order to improve psychiatric inpatient services, particularly on closed wards.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Priebe S, Kaiser W, Huxley PJ, et al: Do different subjective evaluation criteria reflect distinct constructs? Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 186:385-392, 1998.
Gruyters T, Priebe S: Die Bewertung psychiatrischer Behandlung durch den Patienten-Eine Studie zu Erfassungsmethodik und zeitlichen Stabilität. Fortschritte Neurologie und Psychiatrie 60:140-145, 1992.
Leimkühler AM, Müller U: Patient satisfaction-artefact or social reality? Nervenarzt 67:765-773, 1996.
Leimkühler AM: Die Qualität klinischer Versorgung im Urteil der Patienten. In: Gaebel W ed., Qualitätssicherung im psychiatrischen Krankenhaus. Berlin, Springer, 1995.
Kunze H, Priebe S: Assessing the quality of psychiatric hospital care: A German approach. Psychiatric Services 49:794-796, 1998.
Greenwood N, Key A, Burns T, et al: Satisfaction with inpatient psychiatric services. Relationship to patient and treatment factors. British Journal of Psychiatry 174:159-163, 1999.
Ruggeri M: Patients' and relatives' satisfaction with psychiatric services: The state of art of its measurement. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 29:212-227, 1994.
Gruyters T, Priebe S: Die Bewertung psychiatrischer Behandlung durch den Patienten-Resultate und Probleme der systematischenErforschung. Psychiatrische Praxis 21:88-95, 1994.
Priebe S, Gruyters T: Patients' assessment of treatment predicting outcome. Schizophrenia Bulletin 21:87-94, 1995.
Priebe S, Gruyters T, Heinze M, et al: Subjektive Evaluationskriterien in der psychiatrischen Versorgung-Erhebungsmethoden für Forschung und Praxis. Psychiatrische Praxis 22:140-144, 1995.
Holcomb WR, Parker JC, Leong GB, et al: Customer satisfaction and self-reported treatment outcomes among psychiatric inpatients. Psychiatric Services 49:929-934, 1998.
Vuori H: Patient satisfaction-does it matter? Quality Assurance in Health Care 3:183-189, 1991.
Kalman TP: An overview of patient satisfaction with psychiatric treatment. Hospital and Community Psychiatry 34:48-54, 1983.
Buchanan A: A two year prospective study of treatment compliance in patients with schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine 22:787-797, 1992.
Buchanan A: Compliance with treatment in schizophreniaq. Maudsley Monographs 37. East Sussex, Taylor &; Francis, 1996.
Kemp R, David A: Psychological predictors of insight and compliance in psychotic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 169:444-450, 1996.
Benkert O, Graf-Morgenstern M, Hillert A, et al: Public opinion on psychotropic drugs: An analysis of the factors influencing acceptance or rejection. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 185:151-158, 1997.
Demyttenaere K: Compliance during treatment with antidepressants. Journal of Affective Disorders 43:27-39, 1997.
Schou M: The combat of noncompliance during prophylactic lithium treatment. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 95:361-363, 1997.
Keck PE, McElroy SL, Strakowski SM, et al: Compliance with maintenance treatment in bipolar disorder. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 33:87-91, 1997.
Perreault M, Rogers WL, Leichner P, et al: Patients' requests and satisfaction with services in an outpatient psychiatric setting. Psychiatric Services 47:287-292, 1996.
Van Putten T, May PR: Subjective response as a predictor of outcome in pharmacotherapy: The consumer has a point. Archives of General Psychiatry 35:477-480, 1978.
Van Putten T, May PR, Marder SR: Response to antipsychotic medication: The doctor's and the consumer's view. American Journal of Psychiatry 141:16-19, 1984.
Naber D: A selfrating to measure subjective effects of neuroleptic drugs, relationships to objective psychopathology, quality of life, compliance and other clinical variables. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 10(suppl 3):133-138, 1995.
Gerber GJ, Prince PN: Measuring client satisfaction with assertive community treatment. Psychiatric Services 50:546-550, 1999.
Kalali AH, Potkin SG: Patient's satisfaction with and acceptability of “Seroquel”. European Neuropsychopharmacology 6(suppl 3), 249, 1996.
Pickett SA, Lyons JS, Polonus T, et al: Factors predicting patients' satisfaction with managed mental health care. Psychiatric Services 46:722-723, 1995.
Rosenheck R, Wilson NJ, Meterko M: Influence of patient and hospital factors on consumer satisfaction with inpatient mental health treatment. Psychiatric Services 48:1553-1561, 1997.
Spießl H, Cording C, Klein HE: Quality control by patient interviews. Zeitschrift für arztliche Fortbildung und Qualitätssicherung ZaeFQ 91:761-765, 1997.
Linder-Pelz SU: Toward a theory of patient satisfaction. Social Sciences in Medicine 16:577-582, 1982.
Linden M: Negative vs. positive Therapieerwartungen und Compliance vs. NonCompliance. Psychiatrische Praxis 14:132-136, 1987.
Atkinson MJ, Caldwell L: The differential effects of mood on patients' ratings of life quality and satisfaction with their care. Journal of Affective Disorders 44:169-175, 1997.
Sitzia J, Wood N: Patient satisfaction: A review of issues and concepts. Social Sciences in Medicine 45:1829-1843, 1997.
Weinstein R: Patient attitudes toward mental hospitalization. A review of quantitative research. Journal of Health and Social Behavior 20:237-258, 1979.
Koivumaa-Honkanen HT, Viinamäki H, Honkanen R, et al: Correlates of life satisfaction among psychiatric patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 94:372-378, 1996.
Lehman AF: The wellbeing of chronic mentally ill patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 40:369-373, 1973.
Sullivan G, Wells KB, Leake B: Clinical factors associated with better quality of life in a seriously mentally ill population. Hospital and Community Psychiatry 43:794-798, 1992.
Spießl H, Spießl A, Cording C: Die “ideale” stationär-psychiatrische Behandlung aus Sicht der Patienten. Psychiatrische Praxis 26:3-8, 1999.
Henderson C, Phelan M, Loftus L, et al: Comparison of patient satisfaction with communitybased vs. hospital psychiatric services. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 99:188-195, 1999.
Vartiainen H, Vuorio O, Halonen P, et al: The patients' opinions about curative factors in involuntary treatment. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 91:163-166, 1995.
Fähndrich E, Smolka M: Die psychiatrische Abteilung im Urteil der Patienten. Eine Nutzerbefragung als Teil der Qualit ätssicherung in der Psychiatrie. Psychiatrische Praxis 25:72-75, 1998.
Bröker M, Röhricht F, Priebe S: Initial assessment of hospital treatment by patients with paranoid schizophrenia: A predictor of outcome. Psychiatry Research 58:77-81, 1995.
Priebe S, Bröker M: Prediction of hospitalizations by schizophrenia patients' assessment of treatment: An expanded study. Journal of Psychiatric Research 33:113-119, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, M.J., Schlösser, R., Kapp-Steen, G. et al. Patients' Satisfaction with Psychiatric Treatment: Comparison Between an Open and a Closed Ward. Psychiatr Q 73, 93–107 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015099526445
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015099526445