Abstract
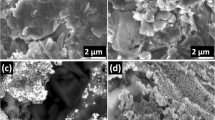
The surfaces of five commercially available titanium implants (Brånemark Nobel Biocare, 3i ICE, 3i OSSEOTITE, ITI-TPS, and ITI-SLA) were compared by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy. All five implant types were screw-shaped and fabricated from commercially pure (cp) titanium, but their surface properties differed both as regards surface morphology and surface chemical composition. The macro- and microstructure of the implant surfaces were investigated by scanning electron microscopy. The surfaces chemical composition was determined using the surface-sensitive analytical techniques of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and time-of-flight secondary ion spectrometry. Surface topographies were found to reflect the type of mechanical/chemical fabrication procedures applied by the manufacturers. The titanium oxide (passive) layer thickness was similar (5–6 nm) and typical for oxide films grown at or near room temperature. A variety of elements and chemical compounds not related to the metal composition were found on some implant types. They ranged from inorganic material such as sodium chloride to specific organic compounds believed to be due to contamination during fabrication or storage. The experimental findings are believed to make a contribution to a better understanding of the interplay between industrial fabrication procedure and physico-chemical implant surface properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Lausmaa, J. Electron Spectr. Rel. Phenom. 81 (1996) 343.
D. C. Smith, R. M. Pillar and G. Murray, Trans. 11th Annu. Meeting Soc. Biomater. 8 (1985) 8.
B. Kasemo and J. Lausmaa, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 22 (1988) 145.
J. J. Collis and G. Embery, Biomaterials 13 (1992) 553.
C. B. Johansson, H. A. Hhansson and T. Albrektsson, ibid. 11 (1990) 277.
S. G. Steinemann, Periodontology 2000, 17 (1998) 7.
K. E. Healy and P. Ducheyne, Biomaterials 13 (1992) 553.
D. M. Brunette, in “Surface characterization of Biomaterials” (Elsevier Science Publisher B.V., Amsterdam, 1998) p. 203.
B. Kasemo and J. Lausmaa, in “The Bone-Biomaterials Interface”, edited by J. E. Davies (University of Toronto Press, Toronto, 1991) p. 19.
D. Buser, R. K. Schenk, S. Steinemann, J. P. Fiorellini, C. H. Fox and H. Stich, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 25 (1991) 889.
M. Wong, J. Eulenberger, R. Schenk and E. Hunziker, ibid. 29 (1995) 1567.
A. Wennerberg, in “On Surface Roughness and Implant Incorporation”. Dissertation, Göteborg University, Göteborg (1996) p. 65.
R. K. Schenk and D. Buser, Periodontology 2000 17 (1998) 22.
R. Solar, S. Pollak and E. Korostoff, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 13 (1979) 217.
J. Woodman, J. Jacobs, J. Galante and R. Urban, J. Orthop. Res. 1 (1984) 421.
M. Wieland, C. Sittig, M. Textor, V. Schenk, S.-W. Ha, B. A. Keller, E. Wintermantel and N. D. Spencer, ECASIA97 (1997) p. 139.
A. Arys, C. Philippard, N. Dourov, Y. He, Q. T. Le and J. J. Pireaux, J. Biomed. Res. 43(3) (1998) 300.
B. D. Ratner, in “Surface Characterisation of Biomaterials”, (Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam, 1988) p. 13.
C. D. Wagner, L. E. Davis, M. V. Zeller, J. A. Taylor, R. M. Raymond and L. H. Gale, Surf. Interf. Anal. 3 (1981) 211.
R. N. S. Sodhi, A. Weninger, J. E. Davies and K. Sreenivas, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 9(3) (1991) 1329.
C. Sittig, M. Wieland, P.-H. Vallotto, M. Textor and N. D. Spencer, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 10 (1998) 35.
C. Sittig, in “PhD thesis ETH Nr. 12657”, ETH Zürich, 1998.
J. F. Molder, W. F. Stickle, P. E. Sobol, K. D. Bomben and J. Chastain, Handbook of X-ray Photoelecyron Spectroscopy, Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Physical Electronics Division, Minnesota (1992).
D. Briggs, A. Brown and J. C. Vickerman, “Handbook of Static Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry” (John Wiley & Sons, Chichester/New York/Brisbane/Toronto/Singapore, 1989) p. 50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massaro, C., Rotolo, P., De Riccardis, F. et al. Comparative investigation of the surface properties of commercial titanium dental implants. Part I: chemical composition. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 13, 535–548 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015170625506
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015170625506