Abstract
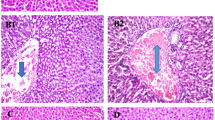
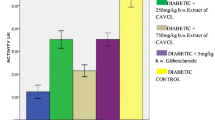
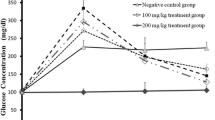
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common endocrine diseases. In UAE many traditional plants such as the Citrullus colocynthis (Handal) are used as antidiabetic remedies. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of the aqueous extract of the seed of C. colocynthis on the biochemical parameters of normal and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes mellitus was induced by a single intraperitoneal (60 mg/kg body wt1) injection of STZ. Normal and diabetic rats were fed with the plant extract daily by oral intubation for 2 weeks. Blood sample were collected at the beginning and end of the experiment for the measurement of biochemical parameters. The plasma level of alanine aminotranferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) increased significantly after the onset of diabetes. Oral administration of the plant extract reduced the plasma level of AST and LDH significantly. However, the plant extract failed to reduce the increased blood level of GGT and ALP in diabetic rats. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) increased significantly after the onset of diabetes. No significant difference was observed in the blood creatinine, K+, Na+, Ca2+ and P levels of normal and diabetic rats. The plant extract did not have any effect on BUN level, however, it caused an increase in the level of K+, Na+ in diabetic rats. In conclusion, oral administration of the aqueous extract of the C. colocynthis can ameliorate some of the toxic effects of streptozotocin. (Mol Cell Biochem 261: 143–149, 2004)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeghate E: Diabetes mellitus—multifactorial in aetiology and global in prevalence. Arch Physiol Biochem 109: 197–199, 2001
Wester AR: The flora of the United Arab Emirates an introduction. UAE University Publication, 1989
Abdel-Hassan IA, Abdel-Barry JA, Mohammeda ST: The hypogly-caemic and antihyperglycaemic effect of Citrullus colocynthis fruit aqueous extract in normal and alloxan diabetic rabbits. J Ethnopharmacol 71: 325–330, 2000
Kirtikar KR, Basu M: Indian medicinal plants. Vols I–IV, 2nd ed. Bishen Singh, Mahendra Pal Singh, Dehra Dun, India, 1984
Baquar SR, Tasnif M: Medicinal plants of Southern West Pakistan, Periodical Export Book Agency, Delhi, 1984
Subramoniam A, Pushpangadn P, Rajasekharan S, Evans AD, Latha GP, Valsaraj R: Effects of Artemisia pallens wall on blood glucose levels in normal and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 50: 13–17, 1996
Adeghate E: Effect of subcutaneous pancreatic tissue transplants on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. I. Morphological studies on normal, diabetic and transplanted pancreatic tissues. Tissue Cell 31: 66–72, 1999
Baily CJ, Flatte PR: Antidiabetic drugs, new developments. Indian Biotechnol 6: 139–142, 1986
Abdel-Barry JA, Abdel-Hassan IA, Al-Hakiien MH: Hypoglycaemic and antihyperglycaemic effects of Trigonella foenum-graecum leaf in normal and alloxan induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 58: 149–155, 1997
Palm F, Cederberg J, Hansell P, Liss P, Carlsson PO: Reactive oxygen species cause diabetes-induced decrease in renal oxygen tension. Diabetologia 46: 1153–1160, 2003
Ohata M, Toda G: Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (gamma-GT)]. Rinsho Byori 116: 62–71, 2001
Braulich H, Marx F, Fleck C, Stein G: Kidney function in rats after 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6 NX); effort of treatment with vitamin E. Exp Toxicol Pathol 49: 135–139, 1997
Hwang DF, Lai YS, Chiang MT: Toxic effects of grass carp, snake and chicken bile juices in rats. Toxicol Lett 85: 85–92, 1997
Travols GS, Morris RW, Elwell MR, Duke A, Rosenblum S, Thompson MB: Frequency and relationship of clinical chemistry and liver and kidney histopathology findings in 13-weeks toxicity studies in rats. Toxicology 107: 17–19, 1996
Greenspan FS, Strewler GJ: Basic and clinical endocrinology. 5th ed. Appleton and Lange, 1996, pp 595–610
Singh J, Adeghate E, Salido GM, Pariente JA, Yago MD, Juma LO: Interaction of islet hormones with cholecystokinin octapeptide-evoked secretory responses in the isolated pancreas of normal and diabetic rats. Exp Physiol 84: 299–318, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ghaithi, F., El-Ridi, M.R., Adeghate, E. et al. Biochemical effects of Citrullus colocynthis in normal and diabetic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 261, 143–149 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000028749.63101.cc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000028749.63101.cc