Abstract
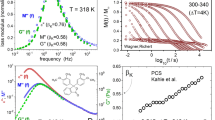
WE have found that ovalbumin dissolved in water decreases the proton spin–lattice relaxation time T1 and proton spin–spin relaxation time T2 and we show that this effect is due to an increase of correlation time of part of the water molecules. The correlation time τ can be defined as the mean time of persistence of the angular position of a water molecule and is simply related1 to the Debye dielectric relaxation time τd, τ=τd/3. According to the theory of nuclear magnetic relaxation by Solomon2, T1 and T2 are functions of τ. In some cases τ can be expressed as a function of the macroscopic viscosity of the liquid1, but in the case of protein solutions such an explanation is not possible as was shown by Hennel et al.3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloembergen, N., Purcell, E. M., and Pound, R. V., Phys. Rev., 73, 679 (1948).
Solomon, I., Phys. Rev., 99, 559 (1955).
Hennel, J. W., Hrynkiewicz, A. Z., Krynicki, K., Waluga, T., and Zapalski, G., Arch. Sci. (Geneva), 11, 243 (1958).
Carr, H. Y., and Purcell, E. M., Phys. Rev., 94, 630 (1954).
Meiboom, S., and Gill, D., Rev. Sci. Instr., 29, 688 (1958).
Buchanan, T. J., Haggis, G. H., Hasted, J. B., and Robinson, B. G., Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 213, 379 (1952).
Sheraga, H. A., Protein Structure, 195 (Academic Press, New York, 1961).
Zimmerman, J. R., and Brittin, W. E., J. Phys. Chem., 61, 1328 (1957).
Landolt-Börnstein, Zahlenwerte und Funktionen, 6 Aufl., 1, Teil 2, 333 (Springer, Berlin, 1955).
Edsall, J. T., in The Proteins, edit. by Neurath, H., and Bailey, K., 1, 702 (Academic Press, New York, 1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
K.-DASZKIEWICZ, O., HENNEL, J., LUBAS, B. et al. Proton Magnetic Relaxation and Protein Hydration. Nature 200, 1006–1007 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/2001006a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2001006a0
This article is cited by
-
Assessing Antigen-Adjuvant Complex Stability Against Physical Stresses By wNMR
Pharmaceutical Research (2023)
-
Investigating Morphology of Food Systems and Water-biopolymer Interactions in Food Using 1H NMR Relaxometry
Food Biophysics (2022)
-
Investigation of Temperature Dependence of Protein Solutions by NMR Spectroscopy
Journal of Solution Chemistry (2021)
-
Increasing signal intensity within the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1W magnetic resonance images in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: correlation with cumulative dose of a macrocyclic gadolinium-based contrast agent, gadobutrol
European Radiology (2016)
-
Gadolinium deposition within the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus after repeated administrations of gadolinium-based contrast agents—current status
Neuroradiology (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.