Abstract
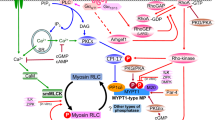
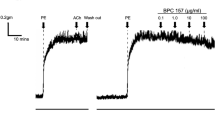
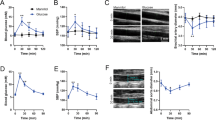
The action of some vascular smooth muscle relaxants depends on the presence of the endothelium1–10. We have recently shown that relaxation may be mediated through the formation of cyclic GMP10. The nitrovasodilators are another class of relaxants which exert ,their effects through the formation of cyclic GMP11–13, although their relaxation is independent of the presence of the endothelium1,2,10. Their relaxant properties seem to depend on free radical formation—specifically, the formation of nitric oxide14,15. The NO-induced smooth muscle relaxation is proposed to occur through activation of guanylate cyclase and the formation of cyclic GMP11–13. Protein phosphorylation is thought to be a common event in the pathway for many biological phenomena16. Moreover, sodium nitroprusside and 8-bromo cyclic GMP induce similar patterns of protein phosphorylation in intact rat thoracic aorta17. Here we report that the patterns of protein phosphorylation induced by the endothelium-dependent vasodilators and nitrovasodilators were identical. Incorporation of 32P into myosin light chain was decreased by both classes of agents. Removal of the endothelium abolished the changes in phosphorylation with the endothelium-dependent vasodilator (acetylcholine), but not those with the nitrovasodilator (sodium nitroprusside). These results suggest that endothelium-dependent vasodilators and nitrovasodilators induce relaxation through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of myosin light chain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furchgott, R. F. & Zawadzki, J. V. Nature 288, 273–276 (1980).
Furchgott, R. F. Trends pharmac. Sci. 2, 173–176 (1981).
Altura, B. M. & Chand, N. Br. J. Pharmac. 74, 10–11 (1981).
Chand, N. & Altura, B. M. Science 213, 1376–1379 (1981).
De Mey, J. G. & Vanhoutte, P. M. J. Physiol., Lond. 316, 347–355 (1981).
Cherry, P. D., Furchgott, R. F., Zawadzki, J. V. & Jothianandan, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 2106–2110 (1982).
De Mey, J. G. & Vanhoutte, P. M. Circulation Res. 51, 439–447 (1982).
De Mey, J. G., Claeys, M. & Vanhoutte, P. M. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 222, 166–173 (1982).
Ku, D. D. Science 218, 576–578 (1982).
Rapoport, R. M. & Murad, F. Circulation Res. 52, 352–357 (1983).
Katsuki, S., Arnold, W., Mittal, C. & Murad, F. J. Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 3, 23–25 (1977).
Katsuki, S. & Murad, F. Molec. Pharmac. 13, 330–341 (1977).
Schultz, K.-D., Schultz, K. & Schultz, G. Nature 256, 750–751 (1977).
Arnold, W. P., Mittal, C. K., Katsuki, S. & Murad, F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 74, 3203–3207 (1977).
Katsuki, S., Arnold, W., Mittal, C. & Murad, F. J. Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 3, 23–25 (1977).
Greengard, P. Science 199, 146–152 (1978).
Rapoport, R. M., Draznin, M. B. & Murad, F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6470–6474 (1982).
Draznin, M. B., Rapoport, R. M., Martinez, G. A. & Murad, F. Clin. Res. 31, 466A (1983).
Furchgott, R. F. & Bhadrakom, S. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 108, 129–143 (1953).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, A. L., Farr, A. L. & Randall, R. J. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Anderson, N. G. & Anderson, N. L. Analyt. Biochem. 85, 331–340 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rapoport, R., Draznin, M. & Murad, F. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat aorta may be mediated through cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Nature 306, 174–176 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/306174a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/306174a0
This article is cited by
-
VEGF-A-induced changes in distal outflow tract structure and function
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2024)
-
Sensitive electrochemical measurement of nitric oxide released from living cells based on dealloyed PtBi alloy nanoparticles
Microchimica Acta (2023)
-
Multidrug-resistant protein inhibitor and phosphodiesterase inhibitor potentiate the vasodilator effect induced by photobiomodulation in isolated aortic rings
Lasers in Medical Science (2022)
-
Effects of light-emitting diode therapy on cardiovascular and salivary nitrite responses in postmenopausal women submitted to a single bout of high-intensity interval training
Lasers in Medical Science (2022)
-
Violet LED induces vasodilation in rat aortic rings by soluble guanylate cyclase–dependent mechanism and increases SOD activity
Lasers in Medical Science (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.