Abstract
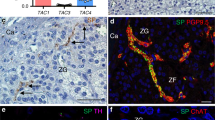
Vasopressin was among the first mammalian hormonal peptides to be identified and to have its structure determined1. Its only undisputed physiological role is as a circulating neurohypophyseal antidiuretic hormone. Other notable effects of vasopressin on peripheral tissues include contraction of vascular smooth muscle, leading to elevation of blood pressure, and activation of glycogenolysis in liver. It has long been clear that vascular smooth muscle and hepatocytes are relatively insensitive to the low concentrations of vasopressin normally present in the circulation, and the physiological significance of their responses has therefore been in doubt. We now report that a new bioactive and immunoreactive vasopressin-like peptide (VLP) is widely distributed in the sympathetic nervous system of mammals, both in the principal noradrenergic neurones of ganglia and in nerve fibres innervating peripheral tissues. In addition to other peptides described in the mammalian sympathetic nervous system2, VLP must be considered as a possible mediator of the non-adrenergic responses to sympathetic activation. Moreover, many of the effects previously attributed to circulating vasopressin may be neurally evoked.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du Vigneaud, V. et al. J. Am. chem. Soc. 25, 4879–4880 (1953).
Lundberg, J. M. et al. Proc. nain. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 1303–1307 (1982).
Schultzberg, M., Hokfelt, T. & Lundberg, J. in Regulatory Peptides of Gut and Brain (ed. Gregory, R.) 309–313 (Churchill Livingstone, London, 1982).
Kessler, J. A., Adler, J. A. Bohn, M. C. & Black, I. B. Science 214, 335–336 (1981).
Valtin, H., Schroeder, A., Benirschke, K. & Sokol, H. W. Nature 196, 1109–1110 (1962).
Creba, J. A. et al. Biochem. J. 212, 733–749 (1983).
Berridge, M. J., Downes, C. P. & Hanley, M. R. Biochem. J. 206, 587–595 (1982).
Kirk, C. J. Cell Calcium 3, 399–411 (1982).
Michell, R. H. et al. in Inositol and Phosphoinositides (eds Bleasdale, J. E., Eichberg, J. & Hauser, G.) (Humana, New York, in the press).
Lundberg, J. M. & Hokfelt, T. Trends Neurosci. 6, 325–333 (1983).
Rosenfeld, M. G. et al. Nature 304, 129–136 (1983).
Fisher, L. A. et al. Nature 305, 534–536 (1983).
Jard, S. in Cellular Receptors for Hormones and Neurotransmitters (eds Schulster, D. & Levitski, A.) 253–266 (Wiley, Chichester, 1980).
McGrath, J. C. J. Physiol., Lond. 283, 23–39 (1978).
Gamse, R., Wax, A., Zigmond, R. E. & Leeman, S. E. Neuroscience 6, 437–441 (1981).
Schultzberg, M. Neuroscience 8, 363–374 (1983).
Lightman, S. L. & Forsling, M. Clin. Endocr. 12, 39–46 (1980).
Tramu, G., Pillez, A. & Leonardelli, J. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 26, 322–324 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanley, M., Benton, H., Lightman, S. et al. A vasopressin-like peptide in the mammalian sympathetic nervous system. Nature 309, 258–261 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/309258a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/309258a0
This article is cited by
-
Emerging drugs to target lower urinary tract symptomatology (LUTS)/benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): focus on the prostate
World Journal of Urology (2020)
-
Dysregulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System and the Vasopressinergic System Interactions in Cardiovascular Disorders
Current Hypertension Reports (2018)
-
Systemic and cavernous plasma levels of vasopressin in healthy males during different functional conditions of the penis
Urological Research (2003)
-
Oxytocin-producing and vasopressin-producing eosinophils in the mouse spleen: immunohistochemical, immuno-electron-microscopic and in situ hybridization studies
Cell and Tissue Research (1995)
-
Stepping up the pressure
Nature (1992)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.