Abstract
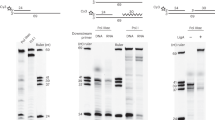
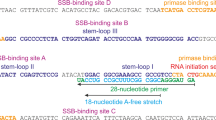
Enzymatic synthesis of DNA from the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication has been reconstituted in vitro with eight purified components. DNA polymerase α-primase complex first initiates DNA synthesis at the replication origin and continues as the lagging strand polymerase. Subsequently, the DNA polymerase δ complex initiates replication on the leading strand template. Some prokaryotic DNA polymerase complexes can replace the eukaryotic polymerase δ complex. A model for polymerase switching during initiation of DNA replication is presented.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, J. J. & Kelly, T. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 6973–6977 (1984).
Li, J. J. & Kelly, T. J. Molec. cell. Biol. 5, 1238–1246 (1985).
Stillman, B. W. & Gluzman, Y. Molec. cell. Biol. 5, 2051–2060 (1985).
Wobbe, C. R., Dean, F., Weissbach, L. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 5710–5714 (1985).
Stillman, B. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 5, 197–245 (1989).
Challberg, M. D. & Kelly, T. J. A. Rev. Biochem. 58, 671–717 (1989).
Borowiec, J. A., Dean, F. B., Bullock, P. A. & Hurwitz, J. Cell 60, 181–184 (1990).
Prelich, G., Kostura, M., Marshak, D. R., Mathews, M. B. & Stillman, B. Nature 326, 471–475 (1987).
Prelich, G. et al. Nature 326, 517–520 (1987).
Wold, M. S., Weinberg, D. H., Virshup, D. M., Li, J. J. & Kelly, T. J. J. biol. Chem. 264, 2801–2809 (1989).
Prelich, G. & Stillman, B. Cell 53, 117–126 (1988).
Tsurimoto, T. & Stillman, B. EMBO J. 8, 3883–3889 (1989).
Weinberg, D. H. & Kelly, T. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 9742–9746 (1989).
Lee, S-H., Eki, T. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 7361–7365 (1989).
Dean, F. B. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 16–20 (1987).
Wold, M. S., Li, J. J. & Kelly, T. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 3643–3647 (1987).
Borowiec, J. A. & Hurwitz, J. EMBO J. 7, 3149–3158 (1988).
Tsurimoto, T., Fairman, M. P. & Stillman, B. Molec. cell. Biol. 9, 3839–3849 (1989).
Roberts, J. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 3939–3943 (1989).
Deb, S. P. & Tegtmeyer, P. J. Virol. 61, 3649–3654 (1987).
Dean, F. B., Dodson, M., Echols, H. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 8981–8985 (1987).
Mastrangelo, I. A. et al. Nature 338, 658–662 (1989).
Fry, L. A. & Loeb, L. A. Animal Cell DNA Polymerases (CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 1986).
Tsurimoto, T. & Stillman, B. Molec. cell. Biol. 9, 609–619 (1989).
Kenny, M. K., Lee, S-H. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 9757–9761 (1989).
Bauer, G. A., Heller, H. M. & Burgers, P. M. J. J. biol. Chem. 263, 917–924 (1988).
Boulet, A., Simon, M., Faye, G., Bauer, G. A. & Burgers, P. M. J. EMBO J. 8, 1849–1854 (1989).
Sitney, K. C., Budd, M. E. & Campbell, J. L. Cell 56, 599–605 (1989).
Tsurimoto, T. & Stillman, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 1023–1027 (1990).
Blow, J. J. Trends Genet. 5, 134–136 (1989).
Wobbe, C. R. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 1834–1838 (1987).
Ishimi, Y., Claude A., Bullock, P. & Hurwitz, J. J. biol. Chem. 263, 19723–19733 (1988).
Murakami, Y., Wobbe, C. R., Weissbach, L., Dean, F. B. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 2869–2873 (1986).
Smale, S. T. & Tjian, R. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 4077–4087 (1986).
Gannon, J. V. & Lane, D. P. Nature 329, 456–458 (1987).
Brill, S. J. & Stillman, B. Nature 342, 92–95 (1989).
Hay, R. T. & DePamphilis, M. L. Cell 28, 767–779 (1982).
Wiekowski, M., Droge, P. & Stahl, H. J. Virol. 61, 411–418 (1987).
Dodson, M., Dean, F. B., Bullock, P., Echols, H. & Hurwitz, J. Science 238, 964–967 (1987).
Din, S., Brill, S. J., Fairman, M. P. & Stillman, B. Genes Dev. 4, 968–977 (1990).
Cha, T.-A. & Alberts, B. M. in Eukaryotic DNA Replication. Cancer Cells 6, 1–10 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1988).
Herendeen, D. R., Kassavetis, G. A., Barry, J., Alberts, B. M. & Geiduschek, E. P. Science 245, 952–958 (1989).
Wang, T. S-F., Wong, S. W. & Korn, D. FASEB J. 3, 14–21 (1989).
McHenry, C. S. A. Rev. Biochem. 57, 519–550 (1988).
Fairman, M. P. & Stillman, B. EMBO J. 7, 1211–1218 (1988).
Lee, M. Y. W. T., Tan, C-K., Downey, K. M. & So, A. G. Biochemistry 23, 1906–1913 (1984).
Maniatas, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsurimoto, T., Melendy, T. & Stillman, B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature 346, 534–539 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/346534a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/346534a0
This article is cited by
-
Molekulare Klassifikation beim Endometriumkarzinom
Die Gynäkologie (2023)
-
Resonance assignments of the ORC2-WH domain of the human ORC protein
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2022)
-
Host-Immune Interactions in JC Virus Reactivation and Development of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2019)
-
When proteins play tag: the dynamic nature of the replisome
Biophysical Reviews (2019)
-
In search of the holy replicator
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2004)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.