Abstract
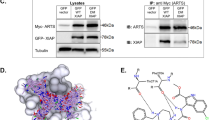
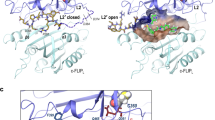
The inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins (IAPs)1 regulate programmed cell death by inhibiting members of the caspase family of enzymes2,3,4,5. Recently, a mammalian protein called Smac6 (also named DIABLO7) was identified that binds to the IAPs and promotes caspase activation. Although undefined in the X-ray structure, the amino-terminal residues of Smac are critical for its function8,9. To understand the structural basis for molecular recognition between Smac and the IAPs, we determined the solution structure of the BIR3 domain of X-linked IAP (XIAP) complexed with a functionally active nine-residue peptide derived from the N terminus of Smac. The peptide binds across the third β-strand of the BIR3 domain in an extended conformation with only the first four residues contacting the protein. The complex is stabilized by four intermolecular hydrogen bonds, an electrostatic interaction involving the N terminus of the peptide, and several hydrophobic interactions. This structural information, along with the binding data from BIR3 and Smac peptide mutants reported here, should aid in the design of small molecules that may be used for the treatment of cancers that overexpress IAPs10,11,12.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crook, N. E., Clem, R. J. & Miller, L. K. An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J. Virol. 67, 2168–2174 (1993).
Hawkins, C. J., Uren, A. G., Häcker, G., Medcalf, R. L. & Vaux, D. L. Inhibition of interleukin 1β-converting enzyme-mediated apoptosis of mammalian cells by baculovirus IAP. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 13786–13790 (1996).
Deveraux, Q. L., Takahashi, R., Salvesen, G. S. & Reed, J. C. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature 388, 300–304 (1997).
Roy, N., Deveraux, Q. L., Takahashi, R., Salvesen, G. S. & Reed, J. C. The c-IAP-1 and c-IAP-2 proteins are direct inhibitors of specific caspases. EMBO J. 16, 6914–6925 (1997).
Deveraux, Q. L. et al. Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J. 18, 5242–5251 (1999).
Du, C., Fang, M., Li, Y., Li, L. & Wang, X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102, 33–42 (2000).
Verhagen, A. M. et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102, 43–53 (2000).
Srinivasula, S. M. et al. Molecular determinants of the caspase-promoting activity of Smac/DIABLO and its role in the death receptor pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36152–36157 (2000).
Chai, J. et al. Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 406, 855–862 (2000).
Tamm, I. et al. Expression and prognostic significance of IAP-family genes in human cancers and myeloid leukemias. Clin. Cancer Res. 6, 1796–1803 (2000).
Ambrosini, G., Adida, C. & Altieri, D. C. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nature Med. 3, 917–217 (1997).
LaCasse, E. C., Baird, S., Korneluk, R. G. & MacKenzie, A. E. The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 17, 3247–3259 (1998).
Sun, C. et al. NMR structure and mutagenesis of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein XIAP. Nature 401, 818–822 (1999).
Sun, C. et al. NMR structure and mutagenesis of the third BIR domain of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 33777–33781 (1998).
Verdecia, M. A. et al. Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement. Nature Struct. Biol. 7, 602–608 (2000).
Muchmore, S. W. et al. Crystal structure and mutagenic analysis of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein survivin. Mol. Cell 6, 173–182 (2000).
Chantalat, L. et al. Crystal structure of human survivin reveals a bow-tie-shaped dimer with two unusual α-helical extensions. Mol. Cell 6, 183–189 (2000).
Kleywegt, G. J. & Jones, T. A. in From First Map to Final Model (eds Bailey, S., Hubbard, R. & Waller, D.) 59–66 (Daresbury Laboratory, Daresbury, UK, 1994).
Vucic, D., Kaiser, W. J. & Miller, L. K. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins physically interact with and block apoptosis induced by Drosophila proteins Hid and Grim. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 3300–3309 (1998).
Cutforth, T. & Gaul, U. A methionine aminopeptidase and putative regulator of translation initiation is required for cell growth and patterning in Drosophila. Mech. Dev. 82, 23–28 (1999).
Clore, G. M. & Gronenborn, A. M. Multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 239, 349–363 (1994).
Cornilescu, G., Delaglio, F. & Bax, A. Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J. Biomol. NMR 13, 289–302 (1999).
Stein E. G., Rice, L. M. & Brünger, A. T. Torsion-angle molecular dynamics as a new efficient tool for NMR structure calculation. J. Magn. Reson. B 124, 154–164 (1997).
Nilges, M., Gronenborn, A. M., Brünger, A. T. & Clore, G. M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins by simulated annealing with interproton distance restraints. Application to crambin, potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor and barley serine proteinase inhibitor 2. Protein Eng. 2, 27–38 (1988).
Nilges, M., Macias, M. J., O'Donoghue, S. I. & Oschkinat, H. Automated NOESY interpretation with ambiguous distance restraints: The refined NMR solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from β-spectrin. J. Mol. Biol. 269, 408–422 (1997).
Laskowski, R. A., Rullmann, J. A., MacArthur, M. W., Kaptein, R. & Thornton, J. M. AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: Programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J. Biomol. NMR 8, 477–486 (1996).
Carson, M. J. Ribbon models of macromolecules. J. Mol. Graphics 5, 103–106 (1987).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Barrett and P. Richardson for help in the synthesis of some of the peptides, L. Miesbauer for the mass spectrometry data, and J. Noel and co-workers for the coordinates of human survivin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Sun, C., Olejniczak, E. et al. Structural basis for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain. Nature 408, 1004–1008 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35050006
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35050006
This article is cited by
-
A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
BAX and SMAC regulate bistable properties of the apoptotic caspase system
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)
-
Anti-apoptotic proteins in the autophagic world: an update on functions of XIAP, Survivin, and BRUCE
Journal of Biomedical Science (2020)
-
The design and development of covalent protein-protein interaction inhibitors for cancer treatment
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.