Abstract
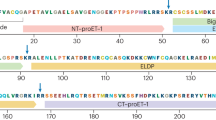
OCCLUSION of the diseased coronary artery in humans causes acute myocardial infarction, survivors of which have a high risk for the development of chronic heart failure1. Cardiac myocytes and vascular endothelial cells produce endothelin-1 (refs 2–4), which increases the contractility of cardiac muscle and of vascular smooth muscle cells2,3,5. Endothelin-1 also exerts long-term effects such as myocardial hypertrophy, and causes cellular injury in cardiac myocytes3,5–7. Production of endothelin-1 is markedly increased in the myocardium of rats with heart failure, and acute application of an endothelin-receptor antagonist decreases myocardial contractility in such rats, indicating that myocardial endothelin-1 may help to support contractility of the failing heart8. But we report here that the upregulated myocardial endothelin system may contribute to the progression of chronic heart failure, because long-term treatment with an endothelin-receptor antagonist greatly improved the survival of rats with chronic heart failure. This beneficial effect was accompanied by significant amelioration of left ventricular dysfunction and prevention of ventricular remodelling, in which there is usually an increase in the ventricular mass and cavity enlargement of the ventricle.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pfeffer, M. A. Annu. Rev. Med. 46, 455–466 (1995).
Yanagisawa, M. et al. Nature 332, 411–415 (1988).
Rubanyi, G. M. & Polokoff, M. A. Pharmacol. Rev. 45, 325–415 (1994).
Suzuki, T. et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 193, 823–830 (1993).
Goto, K. & Warner, T. D. Nature 375, 539–540 (1995).
Miyauchi, T. et al. Circ. Res. 73, 887–897 (1993).
Prasad, M. R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 174, 952–957 (1991).
Sakai, S. et al. Circulation 93, 1214–1222 (1996).
Pfeffer, M. A. et al. Circ. Res. 44, 503–512 (1979).
Pfeffer, J. M. et al. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 57, 805–826 (1995).
Ihara, M. et al. Life Sci. 50, 247–255 (1992).
Melillo, G. et al. Circulation 93, 1447–1458 (1996).
Molenaar, P. et al. Circ. Res. 72, 526–538 (1993).
Packer, M. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 325, 1468–1475 (1991).
Katz, A. M. Circulation 73, III-184–III-188 (1986).
Yorikane, R. & Koike, H. Jpn J. Pharmacol. 53, 259–263 (1990).
Yorikane, R. et al. FEBS Lett. 332, 31–34 (1993).
Kiowski, W. et al. Lancet 346, 732–736 (1995).
Ishikawa, S., Miyauchi, T. et al. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 110, 271–273 (1995).
Stewart, D. J. et al. Circulation 85, 510–517 (1992).
Kobayashi, M. et al. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 28, 129–136 (1995).
Miyauchi, T. et al. Lancet ii, 53–54 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, S., Miyauchi, T., Kobayashi, M. et al. Inhibition of myocardial endothelin pathway improves long-term survival in heart failure. Nature 384, 353–355 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384353a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384353a0
This article is cited by
-
CYP2J2 Modulates Diverse Transcriptional Programs in Adult Human Cardiomyocytes
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Endothelins in cardiovascular biology and therapeutics
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2019)
-
Heart failure as a substrate and trigger for ventricular tachycardia
Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology (2019)
-
Biomechanical stress in myocardial infarctions: can endothelin-1 and growth differentiation factor 15 serve as immunohistochemical markers?
International Journal of Legal Medicine (2018)
-
Endothelin-1 prolongs intracellular calcium transient decay in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes
Heart and Vessels (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.