Abstract
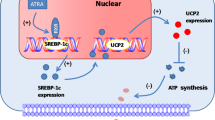
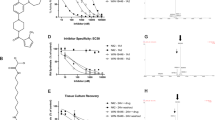
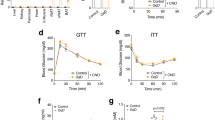
Retinoic acid receptors (RAR), thyroid hormone receptors (TR), peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs) and the orphan receptor, LXR, bind preferentially to DNA as heterodimers with a common partner, retinoid X receptor (RXR), to regulate transcription1–6. We investigated whether RXR-selective agonists replicate the activity of ligands for several of these receptors? We demonstrate here that RXR-selective ligands (referred to as rexinoids) function as RXR heterodimer-selective agonists, activating RXR: PPARγ and RXR:LXR dimers but not RXR:RAR or RXR:TR heterodimers. Because PPARγ is a target for antidiabetic agents, we investigated whether RXR ligands could alter insulin and glucose signalling. In mouse models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and obesity, RXR agonists function as insulin sensitizers and can decrease hyperglycaemia, hypertriglyceridaemia and hyperinsulinaemia. This antidiabetic activity can be further enhanced by combination treatment with PPARγ agonists, such as thiazolidinediones. These data suggest that the RXR:PPARγ heterodimer is a single-function complex serving as a molecular target for treatment of insulin resistance. Activation of the RXR:PPARγ dimer with rexinoids may provide a new and effective treatment for NIDDM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, V. C. et al. RXRβ: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell 67, 1251–1266 (1991).
Zhang, X. K., Hoffman, B., Tran, P. B., Graupner, G. & Pfahl, M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature 355, 441–446 (1992).
Leid, M. et al. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell 68, 377–395 (1992).
Kliewer, S. A., Umesono, K., Mangelsdorf, D. J. & Evans, R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature 355, 446–449 (1992).
Kliewer, S. A., Umesono, K., Noonan, D. J., Heyman, R. A. & Evans, R. M. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature 358, 771–774 (1992).
Willy, P. J. et al. LXR, a nuclear receptor that defines a distinct retinoid response pathway. Genes Dev. 9, 1033–1045 (1995).
Boehm, M. F. et al. Design and synthesis of potent retinoid X receptor selective ligands that induce apoptosis in leukemia cells. J. Med. Chem. 38, 3146–3155 (1995).
Boehm, M. F. et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel retinoid X receptor selective retinoids. J. Med. Chem. 37, 2930–2941 (1994).
Lala, D. et al. Activation of specific RXR heterodimers by an antagonist of RXR homodimers. Nature 383, 450–453 (1996).
Lehman, J. M. et al. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12953–12956 (1995).
Kliewer, S. A. et al. A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Cell 83, 813–819 (1995).
Forman, B. M. et al. 15-Deoxy-delta 12,14-postaglandin J2 is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPAR gamma. Cell 83, 803–812 (1995).
Janowski, B. A., Willy, P. J., Devi, T. R., Falck, J. R. & Mangelsdorf, D. J. An oxysterol signalling pathway mediated by the uclear receptor LXRα. Nature 383, 728–731 (1996).
Mangelsdorf, D. J., Ong, E. S., Dyck, J. A. & Evans, R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature 345, 224–229 (1990).
Kurokawa, R. et al. Regulation of retinoid signalling by receptor polarity and allosteric control of ligand binding. Nature 371, 528–531 (1994).
Forman, B. M., Umesono, K., Chen, J. & Evans, R. M. Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors. Cell 81, 541–550 (1995).
Willson, T. M. et al. The structure-activity relationship between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonism and the antihyperglycemic activity of thiazolidinediones. J. Med. Chem. 39, 665–668 (1996).
Coleman, D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia 14, 141–148 (1978).
Ingalls, A. M., Dickie, M. M. & Snell, G. D. Obese, a new mutation in the mouse. J. Hered. 41, 41, 317 (1950).
Zhang, Y. et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372, 425–432 (1994).
Chen, H. et al. Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell 84, 491–495 (1996).
Fujiwara, T., Yoshioka, S., Yoshioka, T., Ushiyama, I. & Horikoshi, H. Characterizaiton of new oral antidiabetic agent CS-045. Diabetes 37, 1549–1558 (1988).
Sportn, M. B., Dunlop, N. M., Newton, D. L. & Smith, J. M. Prevention of chemical carcinogenesis by vitamin A and its synthetic analogs (retinoids). Fed. Proc. 35, 1332–1338 (1976).
Suter, S. L., Nolan, J. J., Wallace, P., Gumbiner, B. & Olefsky, J. M. Metabolic effects of new oral hypoglycemic agent CS-045 in NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care 15, 193–203 (1992).
Mukherjee, R., Jow, L, Croson, G. E. & Paterniti, J. R. Identification, characterization, tissue distribution of human PPARγ2 versus PPARγ1 and activation with RXR agonists and antagonists. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 8071–8076 (1997).
Umesono, K., Giguere, V., Glass, C. K., Rosenfeld, M. G. & Evans, R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature 336, 262–265 (1988).
Berger, T. S., Parandoosh, Z., Perry, B. W. & Stein, R. B. Interaction of glucocorticoid analogues with the human glucocorticoid receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41, 733–738 (1992).
Trinder, D. Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 6, 24–25 (1969).
Mondon, C. E., Dolkas, C. B. & Oyama, J. Enhanced skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in year-old rats adapted to hypergravity. Amer. J. Physiol 240, E482–488 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, R., Davies, P., Crombie, D. et al. Sensitization of diabetic and obese mice to insulin by retinoid X receptor agonists. Nature 386, 407–410 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/386407a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/386407a0
This article is cited by
-
Human nutritional relevance and suggested nutritional guidelines for vitamin A5/X and provitamin A5/X
Nutrition & Metabolism (2023)
-
Latexin deficiency attenuates adipocyte differentiation and protects mice against obesity and metabolic disorders induced by high-fat diet
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
A validated analysis pipeline for mass spectrometry-based vitreous proteomics: new insights into proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Clinical Proteomics (2021)
-
Omega-3 fatty acid-rich fish oil supplementation prevents rosiglitazone-induced osteopenia in aging C57BL/6 mice and in vitro studies
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Silencing of tissue factor by antisense deoxyoligonucleotide mitigates thioacetamide-induced liver injury
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.