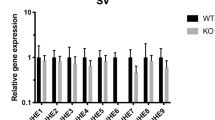
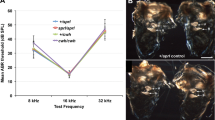
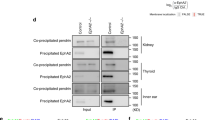
Abstract
Deafness can result from a variety of gene defects1. Some genes involved in the physiology of hearing encode membrane transporters that regulate the ionic composition of the fluid bathing the inner ear. The endolymph is an extracellular fluid with an atypical composition that resembles the intracellular milieu, high in K+ and low in Na+. Recent studies have emphasized the prominent role of K+ channels in endolymph secretion2,3,4 and mechanical transduction5. Coupled electroneutral transport of Na+, K+ and Cl- is mediated by two isoforms of the Na-K-2Cl co-transporter: the absorptive isoform BSC1 (also called NKCC2, encoded by Slc12a1 in mouse) that is exclusively expressed in kidney; and BSC2/NKCC1 (encoded by Slc12a2 in mouse), the secretory isoform which has a wider pattern of expression including epithelia, muscle cells, neurons and red blood cells6,7. These co-transporters share 57% homology at the amino acid level8,9,10,11 and are pharmacologically inhibited by loop diuretics. There is functional12,13,14 and histochemical15,16,17 evidence for the presence of the secretory isoform of the Na-K-2Cl co-transporter in gerbil, rat and rabbit inner ear. We disrupted mouse Slc12a2 and report here that Slc12a2-/- mice are deaf and exhibit classic shaker/waltzer behaviour, indicative of inner-ear defects. We localized the co-transporter to key secreting epithelia of the mouse inner ear and show that absence of functional co-transporter leads to structural damages in the inner ear consistent with a decrease in endolymph secretion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petit, C. Genes responsible for human hereditary deafness: symphony of a thousand. Nature Genet. 14, 385–391 (1996).
Schulze-Bahr, E. et al. KCNE1 mutations causes Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome. Nature Genet. 17, 267–268 (1997).
Neyroud, N. et al. A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nature Genet. 15, 186–189 (1997).
Vetter, D.E. et al. Inner ear defects induced by null mutation of the isk gene. Neuron 17, 1251–1264 (1996).
Kubisch, C. et al. KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness. Cell 96, 437–446 (1999).
Mount, D.B. et al. The electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. J. Exp. Biol. 201, 2091–2102 (1998).
Haas, M. & Forbush, B. III The Na-K-Cl cotransporters. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 30, 161–172 (1998).
Gamba, G. et al. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and characterization of two members of the mammalian electroneutral sodium-(potassium)-chloride cotransporter family expressed in kidney. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 17713–17722 (1994).
Simon, D.B. et al. Bartter's syndrome, hypokalaemic alkalosis with hypercalciuria, is caused by mutations in the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter NKCC2. Nature Genet. 13, 183–188 (1996).
Delpire, E., Rauchman, M.I., Beier, D.R., Hebert, S.C. & Gullans, S.R. Molecular cloning and chromosome localization of a putative basolateral Na-K-2Cl cotransporter from mouse inner medullary collecting duct (mIMCD-3) cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 25677–25683 (1994).
Payne, J.A. et al. Primary structure, functional expression, and chromosome localization of the bumetanide sensitive Na-K-Cl cotransporter in human colon. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 17977–17985 (1995).
Marcus, N.Y. & Marcus, D.C. Potassium secretion by nonsensory region of gerbil utricle in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 253, F613–F621 (1987).
Marcus, D.C., Marcus, N.Y. & Greger, R. Sidedness of action of loop diuretics and ouabain on nonsensory cells of utricle: a micro-Ussing chamber for inner ear tissues. Hearing Res. 30, 55–64 (1987).
Shiga, N. & Wangemann, P. Ion selectivity of volume regulatory mechanisms present during a hypoosmotic challenge in vestibular dark cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1240, 48–54 (1995).
Crouch, J.J., Sakaguchi, N., Lytle, C. & Schulte, B.A. Immunohistochemical localization of the Na-K-Cl co-transporter (NKCC1) in the gerbil inner ear. J. Histochem. 45, 773–778 (1997).
Goto, S., Oshima, T., Ikeda, K., Ueda, N. & Takasaka, T. Expression and localization of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter in the rat cochlea. Brain Res. 765, 324–326 (1997).
Mizuta, K., Adachi, M. & Isawa, K.H. Ultrastructural localization of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter in the lateral wall of the rabbit cochlear duct. Hearing Res. 106, 154–162 (1997).
Deol, M.S. Inherited diseases of the inner ear in man in light of studies on the mouse. J. Mol. Genet. 5, 137–158 (1968).
Belal, A. & Ylikoski, J. Pathologic significance of Meniere's symptom complex: a histopathologic and electron microscopic study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1, 275–284 (1980).
Plotkin, M.D. et al. Expression of the Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter BSC2 in the nervous system. Am. J. Physiol. 272, C173–C183 (1997).
Alvarez-Leefmans, F.J., Nani, A. & Marquez, S. in Presynaptic Inhibition and Neural Control (eds Rudomin, P., Romo, R. & Mendell, L.M.) 50–79 (Oxford University Press, New York, 1998).
Wangemann, P., Liu, J. & Marcus, D.C. Ion transport mechanisms responsible for K+ secretion and the transepithelial voltage across marginal cells of stria vascularis in vitro. Hearing Res. 84, 19–29 (1995).
Rybak, L.P. Ototoxicity of loop diuretics. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 26, 829–844 (1993).
Ikeda, K., Oshima, T., Hidaka, H. & Takasaka, T. Molecular and clinical implications of loop diuretic ototoxicity. Hearing Res. 107, 1–8 (1997).
Cooperman, L.G. & Rubin, I.L. Toxicity of ethacrynic acid and furosemide. Am. Heart J. 85, 831–834 (1973).
Rose, B.D. Diuretics. Kidney Int. 39, 336–252 (1991).
Kalatziz, V. & Petit, C. The fundamental and medical impacts of recent progress in research on hereditary hearing loss. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7, 1589–1597 (1998).
Lynch, E.D. et al. Nonsyndromic deafness DFNA1 associated with mutations of a human homolog of the Drosophila gene diaphanous. Science 278, 1315–1318 (1997).
Randall, J., Thorne, T. & Delpire, E. Partial cloning and characterization of Slc12a2: the gene encoding the secretory Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter. Am. J. Physiol. 273, C1267–C1277 (1997).
Mountford, P. et al. Dicistronic targeting constructs: reporters and modifiers of mammalian gene expression. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 4303–4307 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank The Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center Transgenic/ES Cell Shared Resource Core for expertise and help, and D.B. Mount for helpful discussions. This work was supported by NHLBI and a Vanderbilt University Medical Center intramural grant. E.D. is an Established Investigator from the American Heart Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delpire, E., Lu, J., England, R. et al. Deafness and imbalance associated with inactivation of the secretory Na-K-2Cl co-transporter. Nat Genet 22, 192–195 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/9713
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/9713
This article is cited by
-
Age-appropriate potassium clearance from perinatal cerebrospinal fluid depends on choroid plexus NKCC1
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2023)
-
Serine 937 phosphorylation enhances KCC2 activity and strengthens synaptic inhibition
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Development of cochlear spiral ligament fibrocytes of the common marmoset, a nonhuman model animal
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Development of the stria vascularis in the common marmoset, a primate model
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Clinical characterization and further confirmation of the autosomal recessive SLC12A2 disease
Journal of Human Genetics (2021)