Abstract
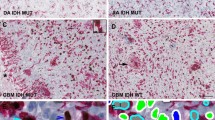
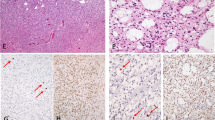
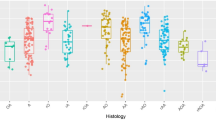
The expression of p53 protein, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and Ki-67 nuclear antigen was examined by immunohistochemistry in biopsies of 16 types of human brain tumours, including 43 astrocytomas. P53 protein, almost certainly its mutant form, was expressed in seven of the 16, and EGFR in 11 of the 16 types of tumours. In astrocytomas both the proportion of tumours which expressed p53 or EGFR increased with grade of malignancy as did the mean Ki-67 labelling index (LI): p53-0% in grade 1, 17% in grade 2, 38% in grade 3, 65% in grade 4; EGFR-0% in grade 1, 33% in grade 2, 85% in grade 3, 95% in grade 4; mean Ki-67 L1-1.1% in grades 1 and 2, 8.3% in grade 3, and 13.4% in grade 4. Astrocytomas which expressed p53 or EGFR had a significantly higher Ki-67 LI at P less than 0.05 (11.8% and 10.7%, resp.) than those that did not (6.2% or 4.1%, resp.). Patients with astrocytomas expressing p53 or EGFR had a significantly reduced survival (P = 0.035 and P = 0.007, resp.): only 11% of the p53 + ve and 13% of the EGFR + ve patients were alive at 100 weeks following diagnosis compared to 36% of p53-ve or 60% of EGFR-ve patients. Patients with Ki-67 LI greater than 5% had a reduced survival (P less than 0.0001)--none survived beyond 86 weeks following diagnosis, whilst 63% of patients with less than 5% positive cells were still alive at 100 weeks. The univariate analysis showed that in astrocytomas expression of p53 mutants, EGFR protein, and Ki-67 greater than 5% are associated with malignant progression and poor prognosis. The multivariate analysis revealed that only tumour grade and Ki-67LI were independent prognostic factors for survival.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaros, E., Perry, R., Adam, L. et al. Prognostic implications of p53 protein, epidermal growth factor receptor, and Ki-67 labelling in brain tumours. Br J Cancer 66, 373–385 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1992.273
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1992.273
This article is cited by
-
Monocentric evaluation of Ki-67 labeling index in combination with a modified RPA score as a prognostic factor for survival in IDH-wildtype glioblastoma patients treated with radiochemotherapy
Strahlentherapie und Onkologie (2022)
-
Treatments of gliosarcoma of the brain: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2021)
-
Lycorine inhibits glioblastoma multiforme growth through EGFR suppression
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
-
Prognostic value of Ki-67 index in adult medulloblastoma after accounting for molecular subgroup: a retrospective clinical and molecular analysis
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2018)
-
Insights into the prognostic value of DJ-1 and MIB-1 in astrocytic tumors
Diagnostic Pathology (2013)