Abstract
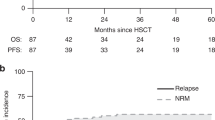
We report outcomes after unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for 91 patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) transplanted in the US in 1989–2005. Fifty-one percent were <1 year at HCT and 29% had Lansky performance scores <90%. Most (80%) were conditioned with BU, CY, and etoposide (VP16) with or without anti-thymocyte globulin. Bone marrow was the predominant graft source. Neutrophil recovery was 91% at day-42. The probabilities of grades 2–4 acute GVHD at day-100 and chronic GVHD at 5 years were 41 and 23%, respectively. The overall mortality rate was higher in patients who did not receive BU/CY/VP16-conditioning regimen (RR 1.95, P=0.035). The 5-year probability of overall survival was 53% in patients who received BU/CY/VP16 compared to 24% in those who received other regimens. In the subset of patients with known disease-specific characteristics, only one of five patients with active disease at HCT is alive. For those in clinical remission at HCT (n=46), the 5-year probability of overall survival was 49%. Early mortality rates after HCT were high, 35% at day-100. These data demonstrate that a BU/CY/VP16-conditioning regimen provides cure in approximately 50% of patients and future studies should explore strategies to lower early mortality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2007; 48: 124–131.
Ueda I, Ishii E, Morimoto A, Ohga S, Sako M, Imashuku S . Correlation between phenotypic heterogeneity and gene mutational characteristics in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL). Pediatr Blood Cancer 2006; 46: 482–488.
Stepp SE, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Le Deist F, Bhawan S, Certain S, Mathew PA et al. Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science 1999; 286: 1957–1959.
Feldmann J, Callebaut I, Raposo G, Certain S, Bacq D, Dumont C et al. Munc13-4 is essential for cytolytic granules fusion and is mutated in a form of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL3). Cell 2003; 115: 461–473.
Rudd E, Goransdotter Ericson K, Zheng C, Uysal Z, Ozkan A, Gurgey A et al. Spectrum and clinical implications of syntaxin 11 gene mutations in familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: association with disease-free remissions and haematopoietic malignancies. J Med Genet 2006; 43: e14.
Arico M, Janka G, Fischer A, Henter JI, Blanche S, Elinder G et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Report of 122 children from the International Registry. FHL Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Leukemia 1996; 10: 197–203.
Henter JI, Samuelsson-Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Elinder G, Filipovich AH et al. Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 immunochemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2002; 100: 2367–2373.
Farag SS, Bacigalupo A, Eapen M, Hurley C, Dupont B, Caligiuri MA et al. The effect of KIR ligand incompatibility on the outcome of unrelated donor transplantation: a report from the center for international blood and marrow transplant research, the European blood and marrow transplant registry, and the Dutch registry. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 876–884.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Klein J, Moeschberger M . Survival Analysis: Techniques of Censored and Truncated Data, 2nd edn. Springer Verlag: New York, NY, 2003.
Cox DR . Regression models and life-tables. J Royal Stat Soc 1972; 34: 187–202.
Henter JI, Arico M, Egeler RM, Elinder G, Favara BE, Filipovich AH et al. HLH-94: a treatment protocol for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. HLH study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol 1997; 28: 342–347.
Baker KS, DeLaat CA, Steinbuch M, Gross TG, Shapiro RS, Loechelt B et al. Successful correction of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with related or unrelated bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1997; 89: 3857–3863.
Ouachee-Chardin M, Elie C, de Saint Basile G, Le Deist F, Mahlaoui N, Picard C et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-center report of 48 patients. Pediatrics 2006; 117: e743–e750.
Blanche S, Caniglia M, Girault D, Landman J, Griscelli C, Fischer A . Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation: a single-center study of 22 cases. Blood 1991; 78: 51–54.
Adachi S, Kubota M, Akiyama Y, Kato T, Kitoh T, Furusho K . Successful bone marrow transplantation from an HLA-identical unrelated donor in a patient with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 183–185.
Chan KW, Mullen CA, Korbling M . Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for active hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 301–302.
Jacobsohn DA . Acute graft-versus-host disease in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 215–221.
Zecca M, Prete A, Rondelli R, Lanino E, Balduzzi A, Messina C et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease in children: incidence, risk factors, and impact on outcome. Blood 2002; 100: 1192–1200.
Cooper N, Rao K, Gilmour K, Hadad L, Adams S, Cale C et al. Stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2006; 107: 1233–1236.
Favara BE . Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a hemophagocytic syndrome. Semin Diagn Pathol 1992; 9: 63–74.
Lee SJ, Klein J, Haagenson M, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer DL, Eapen M et al. High-resolution donor-recipient HLA matching contributes to the success of unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 4576–4583.
Acknowledgements
The CIBMTR is supported by Public Health Service Grant U24-CA76518 from the National Cancer Institute, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute; Office of Naval Research; Health Resources and Services Administration (DHHS); and grants from AABB; Aetna; American International Group Inc.; American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation; Amgen Inc.; Anonymous donation to the Medical College of Wisconsin; Astellas Pharma US Inc.; Baxter International Inc.; Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals; BioOne Corporation; BloodCenter of Wisconsin; Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association; Bone Marrow Foundation; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Cangene Corporation; Celgene Corporation; CellGenix, GmbH; Cerus Corporation; Cubist Pharmaceuticals; Cylex Inc.; CytoTherm; DOR BioPharma Inc.; Dynal Biotech, an Invitrogen Company; EKR Therapeutics; Enzon Pharmaceuticals Inc.; Gambro BCT Inc.; Gamida Cell, Ltd.; Genzyme Corporation; Gift of Life Bone Marrow Foundation; GlaxoSmithKline Inc.; Histogenetics Inc.; HKS Medical Information Systems; Hospira Inc.; Infectious Diseases Society of America; Kiadis Pharma; Kirin Brewery Co., Ltd.; Merck & Company; The Medical College of Wisconsin; MGI Pharma Inc.; Millennium Pharmaceuticals Inc.; Miller Pharmacal Group; Milliman USA Inc.; Miltenyi Biotec Inc.; MultiPlan Inc.; National Marrow Donor Program; Nature Publishing Group; Oncology Nursing Society; Osiris Therapeutics Inc.; Pall Life Sciences; PDL BioPharma Inc; Pfizer Inc; Pharmion Corporation; Roche Laboratories; Schering Plough Corporation; Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America; StemCyte, Inc.; StemSoft Software, Inc.; SuperGen, Inc.; Sysmex; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries; The Marrow Foundation; THERAKOS Inc.; University of Colorado Cord Blood Bank; ViaCell Inc.; Vidacare Corporation; ViraCor Laboratories; ViroPharma Inc.; and Wellpoint Inc. The views expressed in this article do not reflect the official policy or position of the National Institute of Health, the Department of the Navy, the Department of Defense, or any other agency of the US Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, K., Filipovich, A., Gross, T. et al. Unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 42, 175–180 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.133
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.133
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sequential haplo-identical conditioning transplant regimen for pediatric patients with relapsed or refractory hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Treosulfan-Based Conditioning in Matched Family, Unrelated and Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Genetic Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Experience and Outcomes over 10 Years from India
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2022)
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult HLH: a retrospective study by the chronic malignancies and inborn errors working parties of EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Improved transplant outcomes with myeloablative conditioning for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in HLA-matched and mismatched donors: a national multicenter retrospective study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Impact of graft-versus-host disease on the clinical outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for non-malignant diseases
International Journal of Hematology (2020)