Abstract
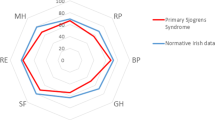
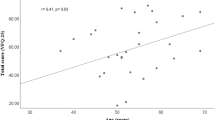
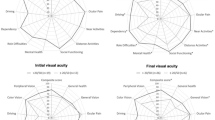
Ocular GvHD affects about 40–60% of patients receiving bone marrow transplantation. Ocular complaints worsen quality of life (QoL), which, besides survival time, is a primary end point in a patient's follow-up. The aim of our study was to assess the ocular surface status and vision-related QoL (VRQoL) and explore the potential determinants in VRQoL in patients with chronic GvHD with ocular involvement. In this cross-sectional study, we investigated 40 patients with ocular GvHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation assessing ocular symptoms and signs, VRQoL and ophthalmologic parameters. The median age was 52.1 years; 32.5% were females. Most of them presented a multiple organ involvement. Ophthalmological parameter examinations were on average abnormal. Corneal staining was severe/very severe in 25%; conjunctival staining in 10% of subjects. The worse QoL scores were on ‘general vision’, ‘ocular pain’, ‘vision-specific mental health’ and ‘vision-specific role difficulties’. Both symptoms and sign scores indicate poor VRQoL. A lower VRQoL was related to schooling level, job position, underlying disease and extracorporeal photopheresis. Corneal staining, Schirmer and tear film breakup time were negatively associated to visual function-related subscales. An accurate ophthalmological and VRQoL assessment should be mandatory for a long time to promptly recognize early signs of ocular suffering, and to prevent irreversible ocular complications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grulke N, Albani C, Bailer H . Quality of life in patients before and after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation measured with the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life Core Questionnaire QLQ-C30. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 473–482.
Dignan FL, Scarisbrick JJ, Cornish J, Clark A, Amrolia P, Jackson G et al. Organ-specific management and supportive care in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol 2012; 158: 62–78.
Riemens A, te Boome L, Imhof S, Kuball J, Rothova A . Current insights into ocular graft-versus-host disease. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2010; 21: 485–494.
Shikari H, Antin JH, Dana R . Ocular graft-versus-host disease: a review. Surv Ophthalmol 2013; 58: 233–251.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Kim SK . Update on ocular graft versus host disease. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2006; 17: 344–348.
Pallua S, Giesinger J, Oberguggenberger A, Kemmler G, Nachbaur D, Clausen J et al. Impact of GvHD on QoL in long-term survivors of haematopoietic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 1534–1539.
Westeneng AC, Hettinga Y, Lokhorst H, Verdonck L, van Dorp S, Rothova A . Ocular graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Cornea 2010; 29: 758–763.
Bron AJ, Evans VE, Smith JA . Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea 2003; 22: 640–650.
Rossi GC, Milano G, Tinelli C . The Italian version of the 25-item National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire: translation, validity, and reliability. J Glaucoma 2003; 12: 213–220.
Rossi GC, Pasinetti GM, Scudeller L, Milano G, Mazzone A, Raimondi M et al. The Italian version of the Glaucoma Symptom Scale Questionnaire: translation, validation, and reliability. J Glaucoma 2013; 22: 44–51.
Riemens A, Te Boome LC, Kalinina Ayuso V, Kuiper JJ, Imhof SM, Lokhorst HM et al. Impact of ocular graft-versus-host disease on visual QoL in patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: questionnaire study. Acta Ophthalmol 2014; 92: 82–87.
Nassiri N, Eslani M, Panahi N, Mehravaran S, Ziaei A, Djalilian AR . Ocular graft versus host disease following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a review of current knowledge and recommendations. J Ophthalmic Vis Res 2013; 8: 351–358.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pezzotta, S., Rossi, G., Scudeller, L. et al. A cross-sectional study on vision-related quality of life in patients with ocular GvHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 1224–1226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.24
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.24
This article is cited by
-
Vision-specific and cancer-specific quality of life in ocular graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2023)
-
Long-term safety and efficacy of autologous platelet lysate drops for treatment of ocular GvHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
Okuläre Graft-versus-Host-Disease
Der Ophthalmologe (2017)